
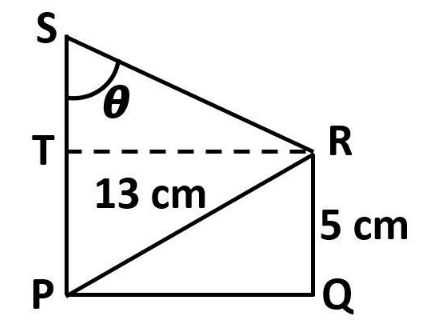
In the given figure, if $ PS = 14cm $ , then the value of $ \tan \theta $ is equal to:
(A) $ \dfrac{4}{3} $
(B) $ \dfrac{{14}}{3} $
(C) $ \dfrac{5}{3} $
(D) $ \dfrac{{13}}{3} $

Answer
567k+ views
Hint: $ \tan \theta $ is the ratio of perpendicular to the base. Observe the figure carefully to find the values of the perpendicular or the opposite side. And the base or the adjacent side. Then find their ratio to solve the question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Observe the diagram
It is given in the question that,
$ PS = 14cm $
From the diagram, we can observe that,
$ PT = QR = 5cm $
And $ PS = PT + TS $
$ \Rightarrow 14 = 5 + TS $
Rearranging it we can write
$ TS = 9cm $
Now, in $ \Delta SRT $
We know that the trigonometric ratio of tan is the ratio of perpendicular to the base.
$ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{{TR}}{{ST}} $ . . . (1)
In $ \Delta PQR $ , from the diagram, and by Pythagoras theorem, we can observe that,
$ P{R^2} = R{Q^2} + P{Q^2} $
By substituting the given values, we get
$ \Rightarrow {13^2} = {5^2} + P{Q^2} $
Rearranging it we can write
$ P{Q^2} = 169 - 25 = 144 $
$ \Rightarrow P{Q^2} = {12^2} $
$ PQ = 12cm $
Now, from the diagram, we can observe that,
$ PQ = TR = 12cm $
By substituting these values in equation (1), we can write
\[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{12}}{9}\]
$ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{4}{3} $
Therefore, from the above explanation, the correct answer is, option (A) $ \dfrac{4}{3} $
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: In this question, the most important part was observing the diagram carefully and understanding which side is equal, where will Pythagoras theorem be required etc. The solution was easy, difficult and an important part was how to reach the solution.
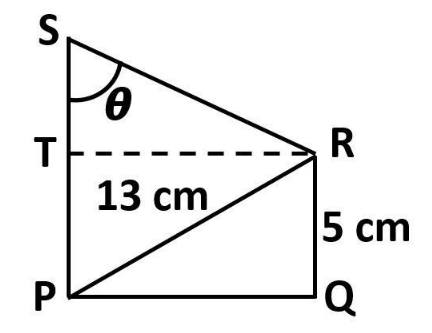
Complete step-by-step answer:
Observe the diagram

It is given in the question that,
$ PS = 14cm $
From the diagram, we can observe that,
$ PT = QR = 5cm $
And $ PS = PT + TS $
$ \Rightarrow 14 = 5 + TS $
Rearranging it we can write
$ TS = 9cm $
Now, in $ \Delta SRT $
We know that the trigonometric ratio of tan is the ratio of perpendicular to the base.
$ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{{TR}}{{ST}} $ . . . (1)
In $ \Delta PQR $ , from the diagram, and by Pythagoras theorem, we can observe that,
$ P{R^2} = R{Q^2} + P{Q^2} $
By substituting the given values, we get
$ \Rightarrow {13^2} = {5^2} + P{Q^2} $
Rearranging it we can write
$ P{Q^2} = 169 - 25 = 144 $
$ \Rightarrow P{Q^2} = {12^2} $
$ PQ = 12cm $
Now, from the diagram, we can observe that,
$ PQ = TR = 12cm $
By substituting these values in equation (1), we can write
\[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{12}}{9}\]
$ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{4}{3} $
Therefore, from the above explanation, the correct answer is, option (A) $ \dfrac{4}{3} $
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: In this question, the most important part was observing the diagram carefully and understanding which side is equal, where will Pythagoras theorem be required etc. The solution was easy, difficult and an important part was how to reach the solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




