
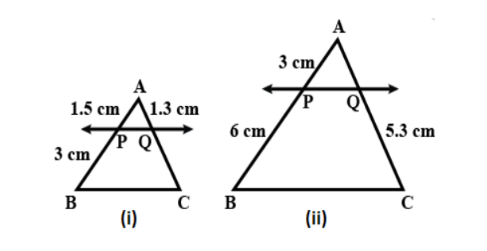
In the given figure, \[(i)\] and \[(ii)\] , \[PQ\parallel BC\] . Find \[QC\] in \[(i)\] and \[AQ\] in \[(ii)\] .

Answer
528.3k+ views
Hint: In order to the Basic determine the triangle of the unknown side by the Proportionality theorem is also called Thales Theorem. According to him, for any two equiangular triangles, the ratio of any two corresponding sides is always the same, \[\dfrac{{AP}}{{PB}} = \dfrac{{AQ}}{{QC}}\] . Based on this concept, we have a basic proportionality theorem. We find out the required answer.
Complete step by step solution:
In the given problem,
We are given diagrammatic representation of the triangle \[ABC\] ,
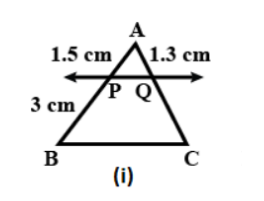
In the diagram \[(i)\] \[\Delta {\rm A}{\rm B}C\] , \[PQ\parallel BC\]
The given values are \[AP = 1.5cm,PB = 3cm,AQ = 1.3cm\]
We have to find the value of \[QC\] . Here, we apply basic proportionality theorem
In a triangle whose two sides are equal, \[PBAP = QCAQ\]
If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, then the other two sides are divided in the same ratio.
\[\dfrac{{AP}}{{PB}} = \dfrac{{AQ}}{{QC}}\]
Now, substitute the measurement values, we can get
\[\
\dfrac{{1.5}}{3} = \dfrac{{1.3}}{{QC}} \\
QC = \dfrac{{1.3 \times 3}}{{1.5}} = 2.6 \\
\ \]
Therefore, we have find out the value of \[QC = 2.6cm\]
So, the correct answer is “ \[QC = 2.6cm\] ”.
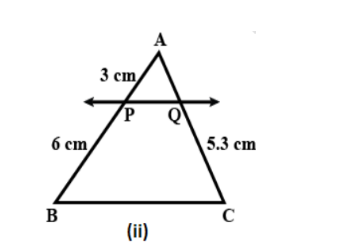
In the diagram \[(i)\] \[\Delta {\rm A}{\rm B}C\] , it is given that \[PQ\parallel BC\]
The given values are \[AP = 3cm,PB = 6cm,AQ = 5.3cm\]
We have to find the value of \[AQ\] . Here, we apply basic proportionality theorem
In a triangle whose two sides are equal, \[PBAP = QCAQ\]
If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, then the other two sides are divided in the same ratio.
\[\dfrac{{AP}}{{PB}} = \dfrac{{AQ}}{{QC}}\]
Now, substitute the measurement values into the above ratio, we can get
\[\
\dfrac{3}{6} = \dfrac{{AQ}}{{5.3}} \\
AQ = \dfrac{{3 \times 5.3}}{6} = 2.6 \\
\ \]
Therefore, we have find out the value of \[AQ = 2.6cm\]
So, the correct answer is “ \[AQ = 2.6cm\] ”.
Note: This basic proportionality theorem concept has been introduced in similar triangles.
If two triangles are similar to each other then,
Corresponding angles of both the triangles are equal
Corresponding sides of both the triangles are in proportion to each other
Let us now try to prove the basic proportionality theorem statement.
Complete step by step solution:
In the given problem,
We are given diagrammatic representation of the triangle \[ABC\] ,

In the diagram \[(i)\] \[\Delta {\rm A}{\rm B}C\] , \[PQ\parallel BC\]
The given values are \[AP = 1.5cm,PB = 3cm,AQ = 1.3cm\]
We have to find the value of \[QC\] . Here, we apply basic proportionality theorem
In a triangle whose two sides are equal, \[PBAP = QCAQ\]
If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, then the other two sides are divided in the same ratio.
\[\dfrac{{AP}}{{PB}} = \dfrac{{AQ}}{{QC}}\]
Now, substitute the measurement values, we can get
\[\
\dfrac{{1.5}}{3} = \dfrac{{1.3}}{{QC}} \\
QC = \dfrac{{1.3 \times 3}}{{1.5}} = 2.6 \\
\ \]
Therefore, we have find out the value of \[QC = 2.6cm\]
So, the correct answer is “ \[QC = 2.6cm\] ”.

In the diagram \[(i)\] \[\Delta {\rm A}{\rm B}C\] , it is given that \[PQ\parallel BC\]
The given values are \[AP = 3cm,PB = 6cm,AQ = 5.3cm\]
We have to find the value of \[AQ\] . Here, we apply basic proportionality theorem
In a triangle whose two sides are equal, \[PBAP = QCAQ\]
If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, then the other two sides are divided in the same ratio.
\[\dfrac{{AP}}{{PB}} = \dfrac{{AQ}}{{QC}}\]
Now, substitute the measurement values into the above ratio, we can get
\[\
\dfrac{3}{6} = \dfrac{{AQ}}{{5.3}} \\
AQ = \dfrac{{3 \times 5.3}}{6} = 2.6 \\
\ \]
Therefore, we have find out the value of \[AQ = 2.6cm\]
So, the correct answer is “ \[AQ = 2.6cm\] ”.
Note: This basic proportionality theorem concept has been introduced in similar triangles.
If two triangles are similar to each other then,
Corresponding angles of both the triangles are equal
Corresponding sides of both the triangles are in proportion to each other
Let us now try to prove the basic proportionality theorem statement.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




