
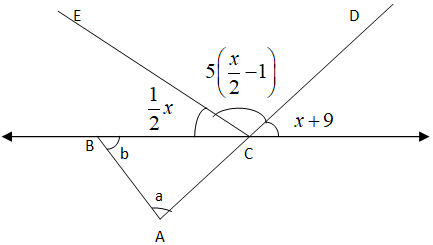
In the given figure, find $a + b$

Answer
617.4k+ views
Hint: In order to solve the problem use the concept of linear pair that sum of the angles at a point on the line is equal to ${180^0}$ in order to find the unknown variable at the point of intersection of the lines and finally use exterior angle property of the triangle to find the final solution.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First we will try to find the value of unknown variable x.
As we know that the sum of angles at line is equal to ${180^0}$
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}x} \right) + 5\left( {\dfrac{x}{2} - 1} \right) + \left( {x + 9} \right) = {180^0}\]
Simplifying the above equation in order to find the variable x.
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{2} + \dfrac{{5x}}{2} - 5 + x + 9 = {180^0} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{6x}}{2} + x + 9 - 5 = {180^0} \\
\Rightarrow 4x + 4 = {180^0} \\
\Rightarrow 4x = {180^0} - {4^0} \\
\Rightarrow 4x = {176^0} \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{{{176}^0}}}{4} \\
\Rightarrow x = {44^0} \\
\]
Now, in order to find out our end result, we will apply exterior angle property on triangle ABC .
As we know that the exterior angle of the triangle is the sum of the opposite interior angles. So for triangle ABC
\[
\Rightarrow \angle BCD = \angle CBA + \angle CAB \\
\Rightarrow \angle BCE + \angle ECD = \angle CBA + \angle CAB\left[ {\because \angle BCD = \angle BCE + \angle ECD} \right] \\
\]
Substituting all the values in the given equation we have
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}x + 5\left( {\dfrac{x}{2} - 1} \right) = b + a\]
Substituting the value of x in the given equation we have
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} \times {44^0} + 5\left( {\dfrac{{{{44}^0}}}{2} - 1} \right) = b + a \\
\Rightarrow a + b = {22^0} + 5\left( {{{22}^0} - {1^0}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow a + b = {22^0} + 5 \times {21^0} \\
\Rightarrow a + b = {22^0} + {105^0} \\
\Rightarrow a + b = {127^0} \\
\]
Hence, the value of $a + b = {127^0}$
Note: In order to solve the problem, never try to find the individual values of “a” and “b” and then the sum, as the problem will take a lot of time and also some other consideration. Rather the method of exterior angle to find directly the sum is easier. The exterior angle theorem is Proposition 1.16 in Euclid's elements, which states that the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is greater than either of the measures of the remote interior angles.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First we will try to find the value of unknown variable x.
As we know that the sum of angles at line is equal to ${180^0}$
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}x} \right) + 5\left( {\dfrac{x}{2} - 1} \right) + \left( {x + 9} \right) = {180^0}\]
Simplifying the above equation in order to find the variable x.
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{2} + \dfrac{{5x}}{2} - 5 + x + 9 = {180^0} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{6x}}{2} + x + 9 - 5 = {180^0} \\
\Rightarrow 4x + 4 = {180^0} \\
\Rightarrow 4x = {180^0} - {4^0} \\
\Rightarrow 4x = {176^0} \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{{{176}^0}}}{4} \\
\Rightarrow x = {44^0} \\
\]
Now, in order to find out our end result, we will apply exterior angle property on triangle ABC .
As we know that the exterior angle of the triangle is the sum of the opposite interior angles. So for triangle ABC
\[
\Rightarrow \angle BCD = \angle CBA + \angle CAB \\
\Rightarrow \angle BCE + \angle ECD = \angle CBA + \angle CAB\left[ {\because \angle BCD = \angle BCE + \angle ECD} \right] \\
\]
Substituting all the values in the given equation we have
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}x + 5\left( {\dfrac{x}{2} - 1} \right) = b + a\]
Substituting the value of x in the given equation we have
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} \times {44^0} + 5\left( {\dfrac{{{{44}^0}}}{2} - 1} \right) = b + a \\
\Rightarrow a + b = {22^0} + 5\left( {{{22}^0} - {1^0}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow a + b = {22^0} + 5 \times {21^0} \\
\Rightarrow a + b = {22^0} + {105^0} \\
\Rightarrow a + b = {127^0} \\
\]
Hence, the value of $a + b = {127^0}$
Note: In order to solve the problem, never try to find the individual values of “a” and “b” and then the sum, as the problem will take a lot of time and also some other consideration. Rather the method of exterior angle to find directly the sum is easier. The exterior angle theorem is Proposition 1.16 in Euclid's elements, which states that the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is greater than either of the measures of the remote interior angles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




