
In the given figure $ \angle DAB={{90}^{\circ }} $ , then find the area of the field.
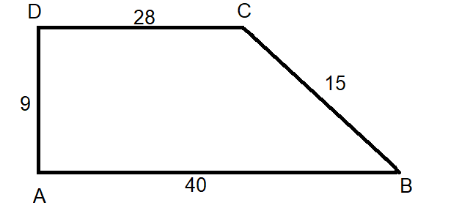
A. $ 208\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{2}} $
B. $ 402\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{2}} $
C. $ 300\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{2}} $
D. $ 306\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{2}} $
E. none of these

Answer
543.3k+ views
Hint: We first divide the whole area into different parts, one being a rectangle and the other one being a right-angle triangle. We find their individual areas. Then we add them to find the total area of the full part.
Complete step by step solution:
We first draw a perpendicular from point C on the line AB which intersects AB at point E.
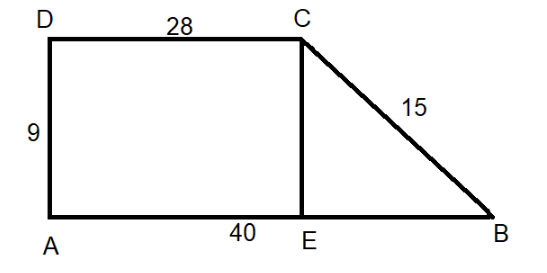
As $ \angle DAB=\angle CEA={{90}^{\circ }} $ , the quadrilateral AECD becomes the rectangle. Therefore, the opposite sides are equal. We get $ DC=AE;AD=EC=9 $ .
The $ \Delta BCE $ is a right-angle triangle whose $ \angle CEB={{90}^{\circ }} $ .
We now find the area of the two figures separately.
The rectangle has two consecutive sides with lengths of 28 and 9.
The area of the rectangle is $ 28\times 9=252 $ square meter.
The length of EB will be $ EB=AB-AE=40-28=12 $ meter.
Now for the right-angle triangle the area will be $ \dfrac{1}{2}\times 12\times 9=54 $ square meter.
The total area will be $ 252+54=306 $ square meter.
The correct option is D.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: We used the theorem of $ \dfrac{1}{2}\times base\times height $ for the area of the right-angle triangle. For the rectangle we used the concept of $ length\times breadth $ . We also could have used the diagonal concept to find the full area.
Complete step by step solution:
We first draw a perpendicular from point C on the line AB which intersects AB at point E.

As $ \angle DAB=\angle CEA={{90}^{\circ }} $ , the quadrilateral AECD becomes the rectangle. Therefore, the opposite sides are equal. We get $ DC=AE;AD=EC=9 $ .
The $ \Delta BCE $ is a right-angle triangle whose $ \angle CEB={{90}^{\circ }} $ .
We now find the area of the two figures separately.
The rectangle has two consecutive sides with lengths of 28 and 9.
The area of the rectangle is $ 28\times 9=252 $ square meter.
The length of EB will be $ EB=AB-AE=40-28=12 $ meter.
Now for the right-angle triangle the area will be $ \dfrac{1}{2}\times 12\times 9=54 $ square meter.
The total area will be $ 252+54=306 $ square meter.
The correct option is D.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: We used the theorem of $ \dfrac{1}{2}\times base\times height $ for the area of the right-angle triangle. For the rectangle we used the concept of $ length\times breadth $ . We also could have used the diagonal concept to find the full area.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





