
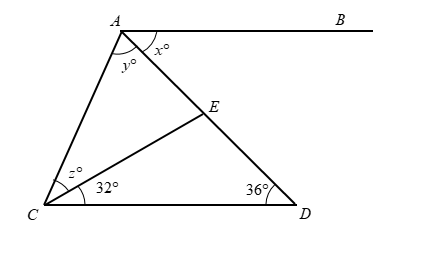
In the given figure, \[AB{\rm{| |}}CD\] and \[CA = CE\]. Find the values of \[x\], \[y\], and \[z\].

Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: Here, we need to find the values of \[x\], \[y\], and \[z\]. We will use the alternate interior angles property, the isosceles triangle property, the exterior angle property, and the angle sum property to find the required values. The alternate interior angles on the opposite sides of a transversal, intersecting two parallel lines, are equal. In an isosceles triangle, the angles that are opposite to equal sides are equal. The exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of two opposite interior angles. The angle sum property states that the sum of the three interior angles of a triangle is always \[180^\circ \].
Complete step-by-step answer:
We can observe that \[AB\] is parallel to \[CD\], and \[AD\] is the transversal.
Therefore, we get the alternate interior angles
\[\angle BAD = \angle ADC\]
Substituting \[\angle BAD = x^\circ \] and \[\angle ADC = 36^\circ \], we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow x^\circ = 36^\circ \\ \Rightarrow x = 36\end{array}\]
Thus, we get the value of \[x\] as 36.
Next, it is given that \[CA = CE\].
Therefore, \[ACE\] is an isosceles triangle.
We know that in an isosceles triangle, the angles that are opposite to equal sides are equal.
Therefore, since \[CA = CE\] in triangle \[ACE\], we get
\[\angle CAE = \angle CEA\]
Substituting \[\angle CAE = y^\circ \], we get
\[ \Rightarrow y^\circ = \angle CEA\]
Now, we will use the exterior angle property of a triangle.
In triangle \[ECD\], we get
\[\angle CEA = \angle ECD + \angle EDC\]
Substituting \[\angle CEA = y^\circ \], \[\angle ECD = 32^\circ \], and \[\angle EDC = 36^\circ \] in the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow y^\circ = 32^\circ + 36^\circ \]
Adding the terms in the expression, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow y^\circ = 68^\circ \\ \Rightarrow y = 68\end{array}\]
Thus, we get the value of \[y\] as 68.
Therefore, we get \[\angle CAE = \angle CEA = 68^\circ \].
Finally, we will use the angle sum property of a triangle to get the value of \[z\].
Using the angle sum property in triangle \[CAE\], we get
\[\angle CAE + \angle CEA + \angle ACE = 180^\circ \]
Substituting \[\angle ACE = z^\circ \] and \[\angle CAE = \angle CEA = 68^\circ \] in the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 68^\circ + 68^\circ + z^\circ = 180^\circ \]
Adding the terms of the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 136^\circ + z^\circ = 180^\circ \]
Subtracting \[136^\circ \] from both sides of the equation, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow 136^\circ + z^\circ - 136^\circ = 180^\circ - 136^\circ \\ \Rightarrow z^\circ = 44^\circ \end{array}\]
Thus, we get the value of \[z\] as 44.
Therefore, the values of \[x\], \[y\], and \[z\] are 36, 68, and 44 respectively.
Note: We can also calculate the value of \[z\] using the property of co-interior angles.
The co-interior angles on the same side of a transversal, intersecting two parallel lines, are supplementary.
We can observe that \[AB\] is parallel to \[CD\], and \[AD\] is the transversal.
Therefore, we get
\[\angle CAB + \angle ACD = 180^\circ \]
Rewriting \[\angle CAB = x^\circ + y^\circ \] and \[\angle ACD = z^\circ + 32^\circ \], we get
\[ \Rightarrow x^\circ + y^\circ + z^\circ + 32^\circ = 180^\circ \]
Substituting \[x^\circ = 36^\circ \] and \[y^\circ = 68^\circ \], we get
\[ \Rightarrow 36^\circ + 68^\circ + z^\circ + 32^\circ = 180^\circ \]
Adding the terms of the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 136^\circ + z^\circ = 180^\circ \]
Subtracting \[136^\circ \] from both sides of the equation, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow 136^\circ + z^\circ - 136^\circ = 180^\circ - 136^\circ \\ \Rightarrow z^\circ = 44^\circ \end{array}\]
Thus, we get the value of \[z\]as 44.
\[\therefore\] The values of \[x\], \[y\], and \[z\] are 36, 68, and 44 respectively.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We can observe that \[AB\] is parallel to \[CD\], and \[AD\] is the transversal.
Therefore, we get the alternate interior angles
\[\angle BAD = \angle ADC\]
Substituting \[\angle BAD = x^\circ \] and \[\angle ADC = 36^\circ \], we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow x^\circ = 36^\circ \\ \Rightarrow x = 36\end{array}\]
Thus, we get the value of \[x\] as 36.
Next, it is given that \[CA = CE\].
Therefore, \[ACE\] is an isosceles triangle.
We know that in an isosceles triangle, the angles that are opposite to equal sides are equal.
Therefore, since \[CA = CE\] in triangle \[ACE\], we get
\[\angle CAE = \angle CEA\]
Substituting \[\angle CAE = y^\circ \], we get
\[ \Rightarrow y^\circ = \angle CEA\]
Now, we will use the exterior angle property of a triangle.
In triangle \[ECD\], we get
\[\angle CEA = \angle ECD + \angle EDC\]
Substituting \[\angle CEA = y^\circ \], \[\angle ECD = 32^\circ \], and \[\angle EDC = 36^\circ \] in the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow y^\circ = 32^\circ + 36^\circ \]
Adding the terms in the expression, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow y^\circ = 68^\circ \\ \Rightarrow y = 68\end{array}\]
Thus, we get the value of \[y\] as 68.
Therefore, we get \[\angle CAE = \angle CEA = 68^\circ \].
Finally, we will use the angle sum property of a triangle to get the value of \[z\].
Using the angle sum property in triangle \[CAE\], we get
\[\angle CAE + \angle CEA + \angle ACE = 180^\circ \]
Substituting \[\angle ACE = z^\circ \] and \[\angle CAE = \angle CEA = 68^\circ \] in the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 68^\circ + 68^\circ + z^\circ = 180^\circ \]
Adding the terms of the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 136^\circ + z^\circ = 180^\circ \]
Subtracting \[136^\circ \] from both sides of the equation, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow 136^\circ + z^\circ - 136^\circ = 180^\circ - 136^\circ \\ \Rightarrow z^\circ = 44^\circ \end{array}\]
Thus, we get the value of \[z\] as 44.
Therefore, the values of \[x\], \[y\], and \[z\] are 36, 68, and 44 respectively.
Note: We can also calculate the value of \[z\] using the property of co-interior angles.
The co-interior angles on the same side of a transversal, intersecting two parallel lines, are supplementary.
We can observe that \[AB\] is parallel to \[CD\], and \[AD\] is the transversal.
Therefore, we get
\[\angle CAB + \angle ACD = 180^\circ \]
Rewriting \[\angle CAB = x^\circ + y^\circ \] and \[\angle ACD = z^\circ + 32^\circ \], we get
\[ \Rightarrow x^\circ + y^\circ + z^\circ + 32^\circ = 180^\circ \]
Substituting \[x^\circ = 36^\circ \] and \[y^\circ = 68^\circ \], we get
\[ \Rightarrow 36^\circ + 68^\circ + z^\circ + 32^\circ = 180^\circ \]
Adding the terms of the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 136^\circ + z^\circ = 180^\circ \]
Subtracting \[136^\circ \] from both sides of the equation, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow 136^\circ + z^\circ - 136^\circ = 180^\circ - 136^\circ \\ \Rightarrow z^\circ = 44^\circ \end{array}\]
Thus, we get the value of \[z\]as 44.
\[\therefore\] The values of \[x\], \[y\], and \[z\] are 36, 68, and 44 respectively.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are gulf countries and why they are called Gulf class 8 social science CBSE

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Advantages and disadvantages of science

The pH of the gastric juices released during digestion class 8 biology CBSE

What are the methods of reducing friction. Explain




