
In the given figure $ AB||DE $ . Show that $ \angle x + \angle y - \angle z = {180^ \circ } $ .
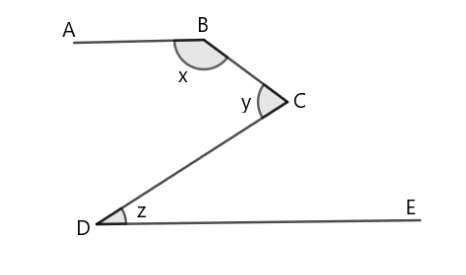

Answer
515.4k+ views
Hint: In the above question we have been given that $ AB||DE $ . To solve this question we will first draw a line starting from C and ending on line E by making a triangle. Then we will apply the properties of parallel lines and their transversal to solve the question. We should note that the sum of co interior angles is always equal to $ {180^ \circ } $ .
Complete step by step solution:
Let us first draw the diagram in which we join the line starting from C to E at point F.
And also we will draw a line parallel to AB and DE from C such that $ MN||AB||DE $ .
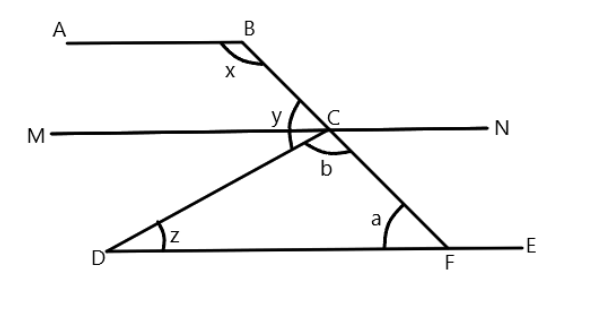
We have assumed the point on line E starting from C to be F , so we have a triangle CDF. Now we assume $ \angle DCF = b $ and $ \angle CED = a $ .
We know that $ a,x $ are the co- interior angles, so we can write:
$ a + x = {180^ \circ } $ . (Because $ MN||AB||DE $ ).
By transferring $ x $ to the R.H.S , It can also be written as:
$ a = 180 - x $ .
Similarly we have $ BCF $ is a straight line and we know that $ b,y $ are linear pairs and the sum of linear pairs is $ {180^ \circ } $ .
So we can write it as
$ b + y = 180 $ .
Here we can isolate the term $ b $ , so we can write the above equation as
$ b = 180 - y $ .
We should know that the linear pairs are two adjacent angles that create a line and they must add up to $ {180^ \circ } $ .
Now we have $ \Delta CDF $ , so by interior angle property we can write that
$ a + z = y $ .
Again by transferring $ a $ to the right hand side, it can also be written as:
$ z = y - a $ .
We know that sum of angles of a triangle is $ {180^ \circ } $ ,
So by applying the above property in $ \Delta CDF $ , we can write that
$ \angle CDF + \angle DFC + \angle FCD = 180 $ .
Here we have $ \angle CDF = z,\angle DFC = a,\angle FCD = b $ .
So we can substitute the values, We can write this as:
$ z + a + b = {180^ \circ } $ .
Now we can put the values we get in the above solution and we can write: $ y - a + {180^ \circ } - y + {180^ \circ } - x = {180^ \circ } $ .
On adding and solving we can write:
$ 360 - x - a = 180 $ .
Further solving, by transferring the constant term to the R.H.S,
It gives: $ - x - a = 180 - 360 $ .
We can cancel the negative sign if we have it in both the sides of the equation without actually changing the meaning if the equation i.e.
$ - (x + a) = - 180 $ .
The new equation will be $ x + a = 180 $ .
Now in the above we have $ a + z = y $ by interior angle property, we can write it also as:
$ a = y - z $ .
So by putting this value in the place of $ a $ we can write:
$ x + y - z = 180 $ .
Hence it is proved that $ \angle x + \angle y - \angle z = {180^ \circ } $ .
Note: Before solving this kind of question we should have the clear concept of parallel lines and their properties along with the interior angle property of the triangle. We know that the interior angle property says that- If a side of a triangle is produced, then the exterior angle formed is equal to the sum of the two interior opposite angles.
In the above question $ MN||AB||DE $ and BE is a transversal. The co interior angles property says that they are interior angles that are on the same side of a transversal and they sum up to $ {180^ \circ } $ . So since $ MN||AB||DE $ , we can write:
$ a + x = 180 $ .
Complete step by step solution:
Let us first draw the diagram in which we join the line starting from C to E at point F.
And also we will draw a line parallel to AB and DE from C such that $ MN||AB||DE $ .

We have assumed the point on line E starting from C to be F , so we have a triangle CDF. Now we assume $ \angle DCF = b $ and $ \angle CED = a $ .
We know that $ a,x $ are the co- interior angles, so we can write:
$ a + x = {180^ \circ } $ . (Because $ MN||AB||DE $ ).
By transferring $ x $ to the R.H.S , It can also be written as:
$ a = 180 - x $ .
Similarly we have $ BCF $ is a straight line and we know that $ b,y $ are linear pairs and the sum of linear pairs is $ {180^ \circ } $ .
So we can write it as
$ b + y = 180 $ .
Here we can isolate the term $ b $ , so we can write the above equation as
$ b = 180 - y $ .
We should know that the linear pairs are two adjacent angles that create a line and they must add up to $ {180^ \circ } $ .
Now we have $ \Delta CDF $ , so by interior angle property we can write that
$ a + z = y $ .
Again by transferring $ a $ to the right hand side, it can also be written as:
$ z = y - a $ .
We know that sum of angles of a triangle is $ {180^ \circ } $ ,
So by applying the above property in $ \Delta CDF $ , we can write that
$ \angle CDF + \angle DFC + \angle FCD = 180 $ .
Here we have $ \angle CDF = z,\angle DFC = a,\angle FCD = b $ .
So we can substitute the values, We can write this as:
$ z + a + b = {180^ \circ } $ .
Now we can put the values we get in the above solution and we can write: $ y - a + {180^ \circ } - y + {180^ \circ } - x = {180^ \circ } $ .
On adding and solving we can write:
$ 360 - x - a = 180 $ .
Further solving, by transferring the constant term to the R.H.S,
It gives: $ - x - a = 180 - 360 $ .
We can cancel the negative sign if we have it in both the sides of the equation without actually changing the meaning if the equation i.e.
$ - (x + a) = - 180 $ .
The new equation will be $ x + a = 180 $ .
Now in the above we have $ a + z = y $ by interior angle property, we can write it also as:
$ a = y - z $ .
So by putting this value in the place of $ a $ we can write:
$ x + y - z = 180 $ .
Hence it is proved that $ \angle x + \angle y - \angle z = {180^ \circ } $ .
Note: Before solving this kind of question we should have the clear concept of parallel lines and their properties along with the interior angle property of the triangle. We know that the interior angle property says that- If a side of a triangle is produced, then the exterior angle formed is equal to the sum of the two interior opposite angles.
In the above question $ MN||AB||DE $ and BE is a transversal. The co interior angles property says that they are interior angles that are on the same side of a transversal and they sum up to $ {180^ \circ } $ . So since $ MN||AB||DE $ , we can write:
$ a + x = 180 $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




