
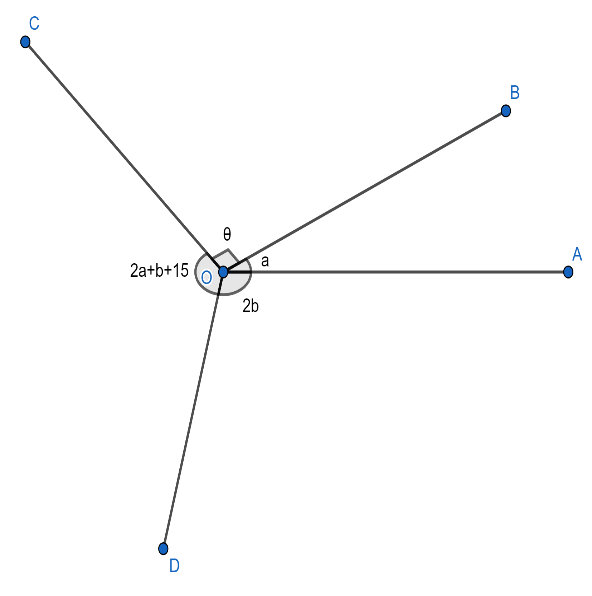
In the given figure, $2b-a={{65}^{\circ }}$ and $\angle BOC={{90}^{\circ }}$ , find the measure of $\angle AOB,\angle AOD$ and $\angle COD$ .
(a) $\angle AOB={{35}^{\circ }}$
(b) $\angle AOD={{100}^{\circ }}$
(c) $\angle COD={{135}^{\circ }}$
(d) $\text{All of the above}$

Answer
609.3k+ views
Hint: For solving this question we will simply apply the simple concept of geometry that if an angle is measured about a circle with its centre at the common endpoint of the segments then their sum will be equal to ${{360}^{\circ }}$ so, $\angle BOC+\angle AOB+\angle AOD+\angle COD={{360}^{\circ }}$ . After that, we will put the value of $\angle AOB={{a}^{\circ }}$ , $\angle AOD=2{{b}^{\circ }}$ and $\angle COD=2a+b+15$ . Then, we will solve for the value of $a$ and $b$ to find the values of $\angle AOB,\angle AOD$ and $\angle COD$ easily.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given:
It is given that $2b-a={{65}^{\circ }}$ and $\angle BOC={{90}^{\circ }}$ , and we have to find the measure of $\angle AOB,\angle AOD$ and $\angle COD$ .
Now, we have the following figure:
In the above figure we have the following equations:
$\begin{align}
& 2b-a={{65}^{\circ }}..............\left( 1 \right) \\
& \angle BOC={{90}^{\circ }}............\left( 2 \right) \\
& \angle AOB={{a}^{\circ }}..............\left( 3 \right) \\
& \angle AOD=2{{b}^{\circ }}............\left( 4 \right) \\
& \angle COD=2a+b+15...........\left( 5 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, as the lines are concurrent and intersect at point O. So, sum of the angles $\angle BOC$ , $\angle AOB$ , $\angle AOD$ and $\angle COD$ will be ${{360}^{\circ }}$ . Then,
$\angle BOC+\angle AOB+\angle AOD+\angle COD={{360}^{\circ }}$
Now, substitute value of $\angle BOC={{90}^{\circ }}$ from equation (2), the value of $\angle AOB={{a}^{\circ }}$ from equation (3), the value of $\angle AOD=2{{b}^{\circ }}$ from equation (4) and value of $\angle COD=2a+b+15$ from equation (5). Then,
$\begin{align}
& 90+a+2b+2a+b+15=360 \\
& \Rightarrow 3a+3b=255 \\
& \Rightarrow a+b=85...............\left( 6 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, adding equation (1) and equation (6). Then,
$\begin{align}
& 2b-a+a+b=65+85 \\
& \Rightarrow 3b=150 \\
& \Rightarrow b={{50}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
Now, substitute the value of $b={{50}^{\circ }}$ from the above equation into equation (1). Then,
$\begin{align}
& 2b-a={{65}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow 2\times {{50}^{\circ }}-a={{65}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow a={{100}^{\circ }}-{{65}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow a={{35}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
Now, substitute the value of $a={{35}^{\circ }}$ into equation (3). Then,
$\begin{align}
& \angle AOB=a \\
& \Rightarrow \angle AOB={{35}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
Now, substitute the value of $b={{50}^{\circ }}$ into equation (4). Then,
$\begin{align}
& \angle AOD=2b \\
& \Rightarrow \angle AOD={{100}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
Now, substitute the value of $a={{35}^{\circ }}$ and the value of $b={{50}^{\circ }}$ into equation (5). Then,
$\begin{align}
& \angle COD=2a+b+15 \\
& \Rightarrow \angle COD=70+50+15 \\
& \Rightarrow \angle COD={{135}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
Now, from the above calculation results, we conclude that value of $\angle AOB={{35}^{\circ }}$ , value of $\angle AOD={{100}^{\circ }}$ and $\angle COD={{135}^{\circ }}$ .
Now, we have to select the most suitable option and after going through all the four options we conclude that option (d) is the most suitable option.
Hence, option (d) will be the correct option.
Note: Here, the student should first understand what is asked in the question and then proceed in the right direction to get the correct answer quickly. Moreover, though the question is very easy, but we should use the figure and try to apply the suitable concept of geometry that if an angle is measured about a circle with its centre at the common endpoint of the segments then their sum will be equal to ${{360}^{\circ }}$ in a correct way. Then, avoid calculation mistakes while solving to get the correct values of $\angle AOB,\angle AOD$ and $\angle COD$ . After that, we should select the most suitable option.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given:
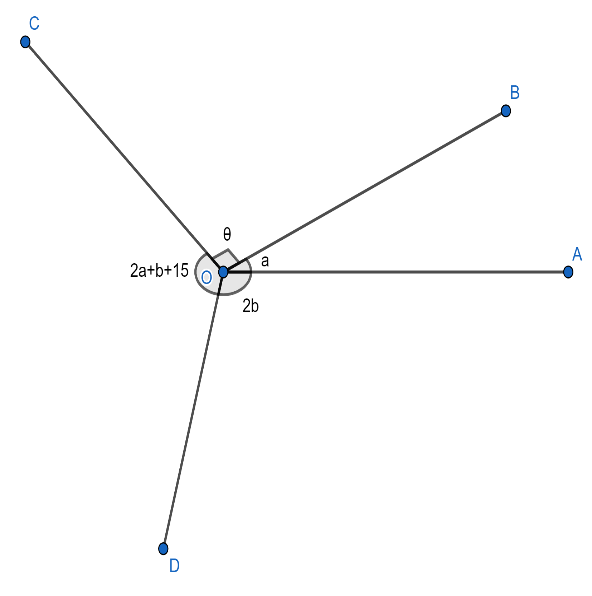
It is given that $2b-a={{65}^{\circ }}$ and $\angle BOC={{90}^{\circ }}$ , and we have to find the measure of $\angle AOB,\angle AOD$ and $\angle COD$ .
Now, we have the following figure:

In the above figure we have the following equations:
$\begin{align}
& 2b-a={{65}^{\circ }}..............\left( 1 \right) \\
& \angle BOC={{90}^{\circ }}............\left( 2 \right) \\
& \angle AOB={{a}^{\circ }}..............\left( 3 \right) \\
& \angle AOD=2{{b}^{\circ }}............\left( 4 \right) \\
& \angle COD=2a+b+15...........\left( 5 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, as the lines are concurrent and intersect at point O. So, sum of the angles $\angle BOC$ , $\angle AOB$ , $\angle AOD$ and $\angle COD$ will be ${{360}^{\circ }}$ . Then,
$\angle BOC+\angle AOB+\angle AOD+\angle COD={{360}^{\circ }}$
Now, substitute value of $\angle BOC={{90}^{\circ }}$ from equation (2), the value of $\angle AOB={{a}^{\circ }}$ from equation (3), the value of $\angle AOD=2{{b}^{\circ }}$ from equation (4) and value of $\angle COD=2a+b+15$ from equation (5). Then,
$\begin{align}
& 90+a+2b+2a+b+15=360 \\
& \Rightarrow 3a+3b=255 \\
& \Rightarrow a+b=85...............\left( 6 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, adding equation (1) and equation (6). Then,
$\begin{align}
& 2b-a+a+b=65+85 \\
& \Rightarrow 3b=150 \\
& \Rightarrow b={{50}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
Now, substitute the value of $b={{50}^{\circ }}$ from the above equation into equation (1). Then,
$\begin{align}
& 2b-a={{65}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow 2\times {{50}^{\circ }}-a={{65}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow a={{100}^{\circ }}-{{65}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow a={{35}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
Now, substitute the value of $a={{35}^{\circ }}$ into equation (3). Then,
$\begin{align}
& \angle AOB=a \\
& \Rightarrow \angle AOB={{35}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
Now, substitute the value of $b={{50}^{\circ }}$ into equation (4). Then,
$\begin{align}
& \angle AOD=2b \\
& \Rightarrow \angle AOD={{100}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
Now, substitute the value of $a={{35}^{\circ }}$ and the value of $b={{50}^{\circ }}$ into equation (5). Then,
$\begin{align}
& \angle COD=2a+b+15 \\
& \Rightarrow \angle COD=70+50+15 \\
& \Rightarrow \angle COD={{135}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
Now, from the above calculation results, we conclude that value of $\angle AOB={{35}^{\circ }}$ , value of $\angle AOD={{100}^{\circ }}$ and $\angle COD={{135}^{\circ }}$ .
Now, we have to select the most suitable option and after going through all the four options we conclude that option (d) is the most suitable option.
Hence, option (d) will be the correct option.
Note: Here, the student should first understand what is asked in the question and then proceed in the right direction to get the correct answer quickly. Moreover, though the question is very easy, but we should use the figure and try to apply the suitable concept of geometry that if an angle is measured about a circle with its centre at the common endpoint of the segments then their sum will be equal to ${{360}^{\circ }}$ in a correct way. Then, avoid calculation mistakes while solving to get the correct values of $\angle AOB,\angle AOD$ and $\angle COD$ . After that, we should select the most suitable option.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




