
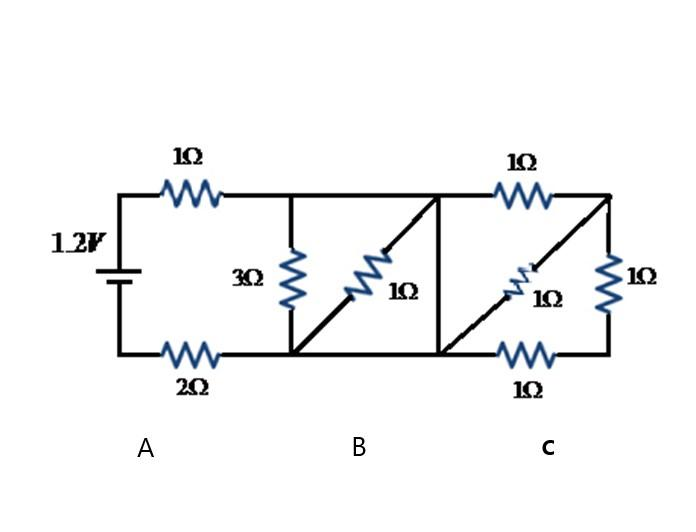
In the given circuit, the current through $2\Omega $ resistor is
$A. 0.2A$
$B. 0.4A$
$C. 0.3A$
$D. 0.1A$

Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: Resistances are said to be in parallel combination if the potential across each resistance is same and equal to the applied potential Current through each resistance is different and is inversely proportional to resistance of resistor whereas a combination is called to be in series when different resistances are joined with each other such that there is only one path for the flow of electric current .
Complete answer:
For solving the given complex circuit, we segregate the circuit into three sections A, B and C in order to simplify the solving procedure.
As per the given question, the voltage value of the source is $1.2V$
The resistance value of resistors in section A are as follows:
The resistance of the resistor 1: $1\Omega $
The resistance of the resistor 2:$3\Omega $
The resistance of the resistor 3:$2\Omega $
The resistance value of resistor in section B is as follows:
The resistance of the resistor 4: $1\Omega $
The resistance value of resistors in section C is as follows:
The resistance of the resistor 5: $1\Omega $
The resistance of the resistor 6: $1\Omega $
The resistance of the resistor 7: $1\Omega $
The resistance of the resistor 8: $1\Omega $
In section C,
The resistor 7 and resistor 8 are in series to one another.
So, their equivalent resistance will be:
$R={{R}_{7}}+{{R}_{8}}$
$R=1+1$
$R=2\Omega $
The resistor 5, resistor 6 and net resistance ‘R’ are joined in parallel connection to one another.
Therefore, their resultant resistance will be:
$R'=\frac{{{R}_{5}}\times {{R}_{6}}\times R}{{{R}_{5}}+{{R}_{6}}+R}$
$R'=\frac{1\times 1\times 2}{1+1+2}$
$R'=\frac{2}{4}=\frac{1}{2}\Omega $
Now this $R'$is in series with resistor 4 in section B.
Therefore,
The resultant resistance of \[R\]and resistor 4 is:
$R''=R'+{{R}_{4}}$
$R''=1+\frac{1}{2}$
$R''=\frac{3}{2}\Omega $
Now in section A:
$R''$and resistor 2 are in parallel connection to one another.
$\therefore $
$R'''=\frac{R''\times {{R}_{2}}}{R''+{{R}_{2}}}$
$R'''=\frac{\frac{3}{2}\times 3}{\frac{3}{2}+3}$
$R'''=\frac{9}{9}=1\Omega $
Now Resistor 1, resistor 3 and $R'''$ are in series with each other.
So, their resultant resistance will be:
${{R}_{eq}}=R'''+{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{3}}$
${{R}_{eq}}=1+1+2$
${{R}_{eq}}=4\Omega $
This is the equivalent resistance of the given electrical circuit
Now the current i through the resistor 3 having a resistance of $2\Omega $ will be:
$i=\frac{V}{{{R}_{eq}}}$
$i=\frac{1.2V}{4\Omega }$
$i=0.3A$
This is because resistor 1, resistor 3 and $R'''$are in series, so the same amount current will flow across them.
Hence the correct option will be option (C) 0.3A
Note:
One is advised to carefully observe and remember that current flowing through each of the resistors is different from the other and is inversely proportional to resistance of resistor. The total current flowing through the system is also conserved until and unless it dissipates out in the form of heat or sound energy.
Complete answer:
For solving the given complex circuit, we segregate the circuit into three sections A, B and C in order to simplify the solving procedure.
As per the given question, the voltage value of the source is $1.2V$
The resistance value of resistors in section A are as follows:
The resistance of the resistor 1: $1\Omega $
The resistance of the resistor 2:$3\Omega $
The resistance of the resistor 3:$2\Omega $
The resistance value of resistor in section B is as follows:
The resistance of the resistor 4: $1\Omega $
The resistance value of resistors in section C is as follows:
The resistance of the resistor 5: $1\Omega $
The resistance of the resistor 6: $1\Omega $
The resistance of the resistor 7: $1\Omega $
The resistance of the resistor 8: $1\Omega $
In section C,
The resistor 7 and resistor 8 are in series to one another.
So, their equivalent resistance will be:
$R={{R}_{7}}+{{R}_{8}}$
$R=1+1$
$R=2\Omega $
The resistor 5, resistor 6 and net resistance ‘R’ are joined in parallel connection to one another.
Therefore, their resultant resistance will be:
$R'=\frac{{{R}_{5}}\times {{R}_{6}}\times R}{{{R}_{5}}+{{R}_{6}}+R}$
$R'=\frac{1\times 1\times 2}{1+1+2}$
$R'=\frac{2}{4}=\frac{1}{2}\Omega $
Now this $R'$is in series with resistor 4 in section B.
Therefore,
The resultant resistance of \[R\]and resistor 4 is:
$R''=R'+{{R}_{4}}$
$R''=1+\frac{1}{2}$
$R''=\frac{3}{2}\Omega $
Now in section A:
$R''$and resistor 2 are in parallel connection to one another.
$\therefore $
$R'''=\frac{R''\times {{R}_{2}}}{R''+{{R}_{2}}}$
$R'''=\frac{\frac{3}{2}\times 3}{\frac{3}{2}+3}$
$R'''=\frac{9}{9}=1\Omega $
Now Resistor 1, resistor 3 and $R'''$ are in series with each other.
So, their resultant resistance will be:
${{R}_{eq}}=R'''+{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{3}}$
${{R}_{eq}}=1+1+2$
${{R}_{eq}}=4\Omega $
This is the equivalent resistance of the given electrical circuit
Now the current i through the resistor 3 having a resistance of $2\Omega $ will be:
$i=\frac{V}{{{R}_{eq}}}$
$i=\frac{1.2V}{4\Omega }$
$i=0.3A$
This is because resistor 1, resistor 3 and $R'''$are in series, so the same amount current will flow across them.
Hence the correct option will be option (C) 0.3A
Note:
One is advised to carefully observe and remember that current flowing through each of the resistors is different from the other and is inversely proportional to resistance of resistor. The total current flowing through the system is also conserved until and unless it dissipates out in the form of heat or sound energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




