
In the given circuit, the current \[I\] equals to:
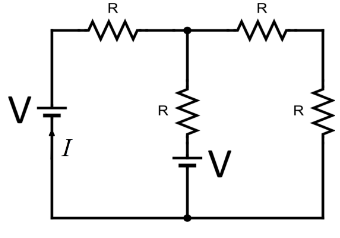
A. \[\dfrac{V}{{5R}}\]
B. \[\dfrac{V}{{4R}}\]
C. \[\dfrac{{2V}}{{5R}}\]
D. \[0\]

Answer
537k+ views
Hint: To solve this problem, use Kirchhoff’s voltage law for both the loops and find the current through the circuit solving the equations. Kirchhoff’s voltage law states that in any closed loop network, the total voltage around the loop is equal to the sum of all the voltage drops within the same loop. Mathematical expression of the Kirchhoff’s voltage law can be given as, \[\sum {{V_j}} = \sum {{I_i}{R_i}} \] where \[\sum {{V_j}} \] is the algebraic sum of all the voltage sources and \[\sum {{I_i}{R_i}} \] is the algebraic sum of all the voltage drops across elements.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given circuit let’s take the first loop as loop-I and another as loop –II . Let’s assume the current through the loop-I is \[I\]and current through loop –II is \[{I_1}\].
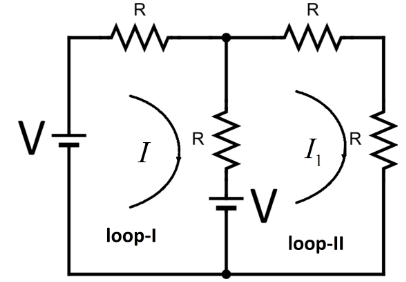
So, applying KVL in the first loop we can get,( loop-I)
\[IR + (I - {I_1})R = V - V\]
\[\Rightarrow IR + (I - {I_1})R = 0\]
Further simplifying we get,
\[2IR = {I_1}R\]
\[\Rightarrow {I_1} = 2I\]..........................[Since, resistance \[R\] is not zero]
Now, applying KVL in the second loop we can get,( loop –II)
\[({I_1} - I)R + {I_1}R + {I_1}R = V\]
\[\Rightarrow ({I_1} - I)R + 2{I_1}R = V\]
Putting the value of \[{I_1}\] from previous equation we get,
\[(2I - I)R + 2 \cdot 2I \cdot R = V\]
\[\Rightarrow IR + 4IR = V\]
\[\Rightarrow 5IR = V\]
\[\therefore I = \dfrac{V}{{5R}}\]
Hence, the current through the first loop will be equal to \[\dfrac{V}{{5R}}\]. Now, we can see that this is the same current as the circuit current. So, the current \[I\] is equal to \[\dfrac{V}{{5R}}\].
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note: The sign convention for the voltage source is: when a voltage source is traversed from positive terminal to negative terminal then voltage of the source is taken as negative and when a voltage source is traversed from negative terminal to positive terminal then voltage of the source is taken as positive. Voltage drop across an element for a loop current is negative when the current is flowing in the opposite direction of the loop traversed and it is taken positive when the current is flowing in the same direction of the loop traversed.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given circuit let’s take the first loop as loop-I and another as loop –II . Let’s assume the current through the loop-I is \[I\]and current through loop –II is \[{I_1}\].

So, applying KVL in the first loop we can get,( loop-I)
\[IR + (I - {I_1})R = V - V\]
\[\Rightarrow IR + (I - {I_1})R = 0\]
Further simplifying we get,
\[2IR = {I_1}R\]
\[\Rightarrow {I_1} = 2I\]..........................[Since, resistance \[R\] is not zero]
Now, applying KVL in the second loop we can get,( loop –II)
\[({I_1} - I)R + {I_1}R + {I_1}R = V\]
\[\Rightarrow ({I_1} - I)R + 2{I_1}R = V\]
Putting the value of \[{I_1}\] from previous equation we get,
\[(2I - I)R + 2 \cdot 2I \cdot R = V\]
\[\Rightarrow IR + 4IR = V\]
\[\Rightarrow 5IR = V\]
\[\therefore I = \dfrac{V}{{5R}}\]
Hence, the current through the first loop will be equal to \[\dfrac{V}{{5R}}\]. Now, we can see that this is the same current as the circuit current. So, the current \[I\] is equal to \[\dfrac{V}{{5R}}\].
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note: The sign convention for the voltage source is: when a voltage source is traversed from positive terminal to negative terminal then voltage of the source is taken as negative and when a voltage source is traversed from negative terminal to positive terminal then voltage of the source is taken as positive. Voltage drop across an element for a loop current is negative when the current is flowing in the opposite direction of the loop traversed and it is taken positive when the current is flowing in the same direction of the loop traversed.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE




