
In the following structure, the double bonds are marked as I, II, III and IV. Geometrical isomerism is not possible at site (S):
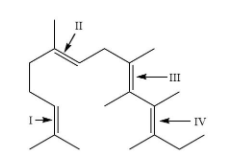
A. III and IV
B. I and III
C. III
D. I

Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: We know that isomers are described as the molecules which have the same molecular formula but different arrangement of atoms bonded to each other, they also have different chemical properties. The geometrical isomers are the isomers which have a double bond and the functional group attached to the both carbons bonded to each other via double bond have different functional groups.
Complete answer
Isomers are divided in the two branches: constitutional isomer and stereoisomer.
1. Stereoisomers are of two types: geometrical isomer and optical isomer.
2. Optical isomers are non-super impossible mirror images of the same molecule.
Functional groups should be attached to the one carbon out of the two carbon which are double bonded with each other and cannot be rotated as shown in the figure below. The carbon numbers two and three have the same functional group but the group attached to the carbon two are different, one is hydrogen and other is methyl. The methyl group should not be present on the same carbon or hydrogen should not be attached to the same carbon otherwise it will not remain the geometrical isomer.
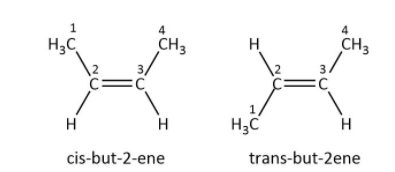
These are geometrical isomers of but-2-ene: cis-but-2-ene same groups are present on the same side of the double bonded carbon and trans- but-2-ene functional group attached to the double bonded carbon are present in different planes i.e. above and below the plane diagonally.
The site (I) contains two identical \[C{H_3}\] groups attached to a double bond. This site will not show geometrical isomerism as they are present on the same carbon.
Hence, the answer is option (D) that is I.
Note:
Read the question carefully what it is asked. The question is which is “not” the geometrical isomer, so that the elimination of the options becomes easy.
Complete answer
Isomers are divided in the two branches: constitutional isomer and stereoisomer.
1. Stereoisomers are of two types: geometrical isomer and optical isomer.
2. Optical isomers are non-super impossible mirror images of the same molecule.
Functional groups should be attached to the one carbon out of the two carbon which are double bonded with each other and cannot be rotated as shown in the figure below. The carbon numbers two and three have the same functional group but the group attached to the carbon two are different, one is hydrogen and other is methyl. The methyl group should not be present on the same carbon or hydrogen should not be attached to the same carbon otherwise it will not remain the geometrical isomer.

These are geometrical isomers of but-2-ene: cis-but-2-ene same groups are present on the same side of the double bonded carbon and trans- but-2-ene functional group attached to the double bonded carbon are present in different planes i.e. above and below the plane diagonally.
The site (I) contains two identical \[C{H_3}\] groups attached to a double bond. This site will not show geometrical isomerism as they are present on the same carbon.
Hence, the answer is option (D) that is I.
Note:
Read the question carefully what it is asked. The question is which is “not” the geometrical isomer, so that the elimination of the options becomes easy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




