
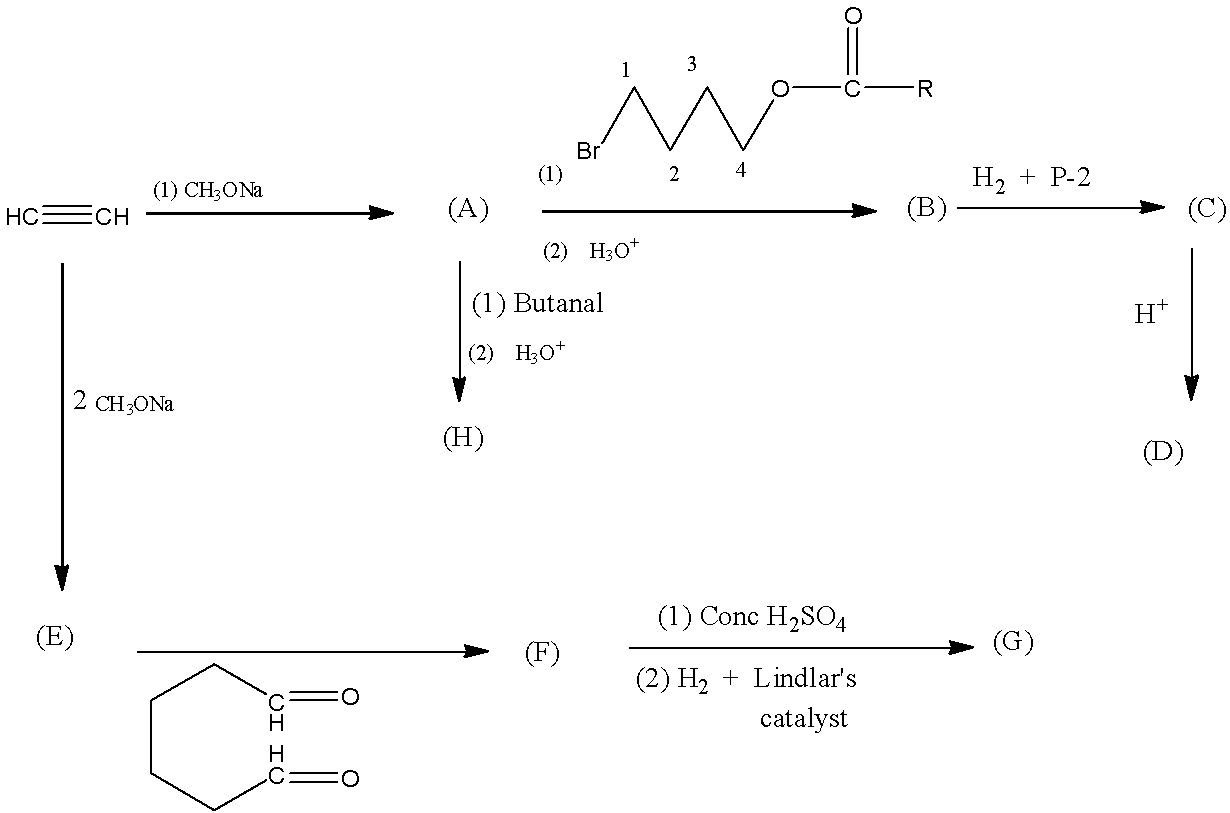
In the following sequence of reactions, products (A) to (H) are formed. Then the compound (C) is:

Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: Reaction of ethyne with sodium methoxide then one of the hydrogen atoms of the ethyne molecule will be replaced with a sodium atom. Hydrogen gas and P-2 are added to an unsaturated molecule then there will be syn-addition of hydrogen atoms to the double or triple bond.
Complete answer:
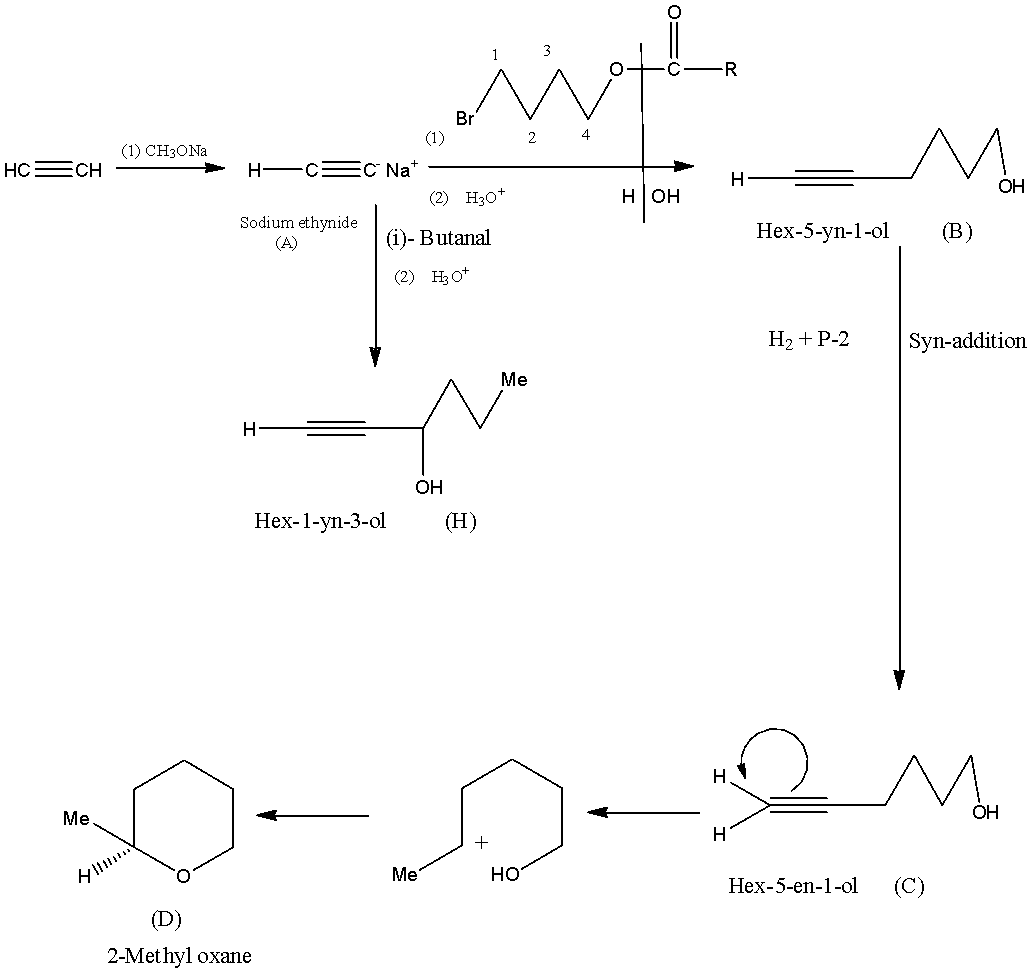
The reactant molecule in the above reaction is ethyne, to form A it is reacted with sodium methoxide, then there will be the formation of sodium ethoxide because one hydrogen atom is replaced with a sodium atom.
Now, A is being converted into B by a catalyst which first converts into alcohol with the help of acidified water molecules (second catalyst). This molecule will attach with the replacement of the sodium atom in sodium ethynide. So, the compound (B) will be Hex-5-yn-1-ol.
Now, when the compound (B) Hex-5-yn-1-ol is treated with hydrogen gas and P-2 there will be syn-addition of a hydrogen atom to the triple bond, forming the compound (C) Hex-5-en-1-ol.
Now, this compound (C) Hex-5-en-1-ol, is acidified to form a cyclic structure known as 2-Methyl oxane compound (D).
Now, A is being converted into H by a catalyst which first converts into alcohol with the help of acidified water molecules (second catalyst). This molecule will attach with the replacement of the sodium atom in sodium ethynide. The compound H will be Hex-1-yne-3-ol.
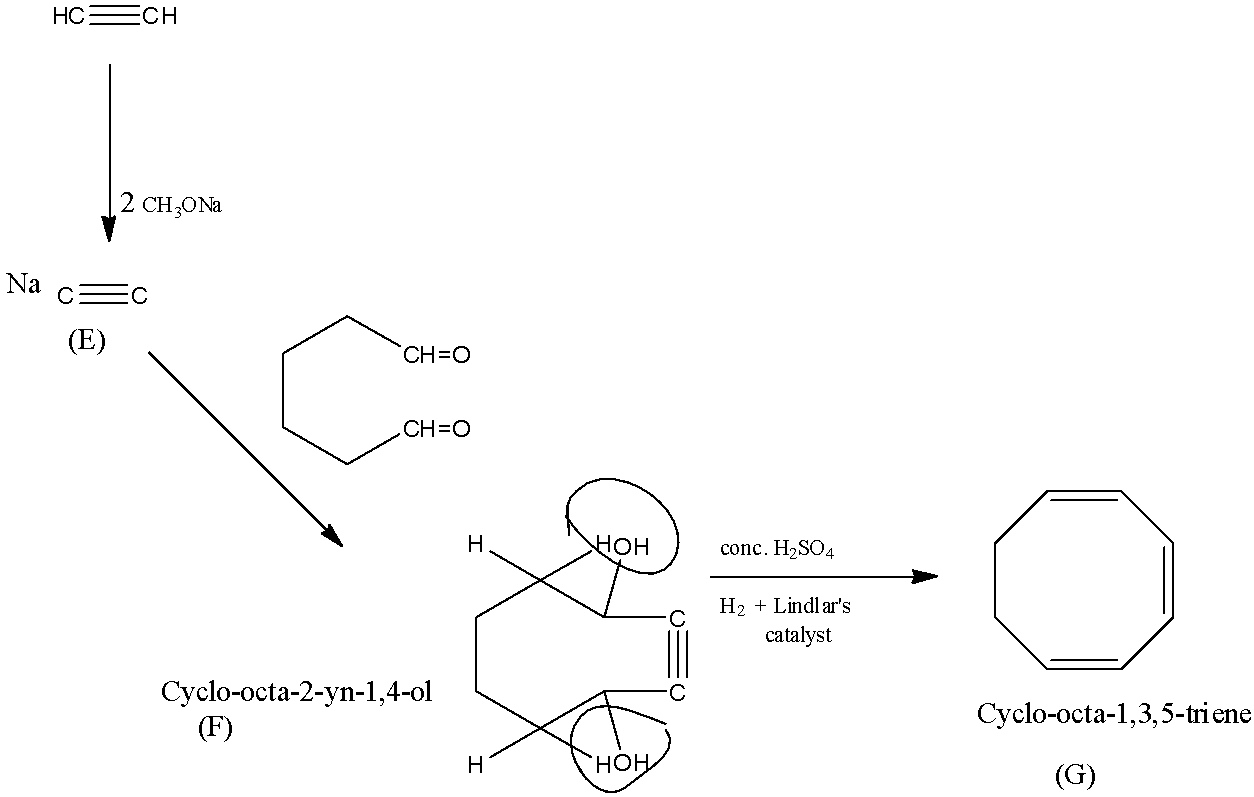
Now coming to the formation of E from ethyne, two molecules of sodium methoxide are treated with ethyne, then, both the hydrogen atoms will be replaced with sodium atoms.
The compound (F) is cyclo-octa-2-yne-1,4-diol which is formed from compound E.
Now, the concentrated sulfuric acid will remove the water reduced while with the Lindlar’s catalyst, the triple bond in the compound will be reduced to the double bond-forming the compound G.
The reactions are given below:
So, compound C is Hex-5-en-1-ol.
Note:
We know that there can be the formation of two alkenes, i.e., cis-alkene or trans-alkene. So, for cis-alkene, the catalyst used is Lindlar’s catalyst while to form trans-alkene, sodium in liquid ammonia is used also known as Birch reduction.
Complete answer:
The reactant molecule in the above reaction is ethyne, to form A it is reacted with sodium methoxide, then there will be the formation of sodium ethoxide because one hydrogen atom is replaced with a sodium atom.
Now, A is being converted into B by a catalyst which first converts into alcohol with the help of acidified water molecules (second catalyst). This molecule will attach with the replacement of the sodium atom in sodium ethynide. So, the compound (B) will be Hex-5-yn-1-ol.
Now, when the compound (B) Hex-5-yn-1-ol is treated with hydrogen gas and P-2 there will be syn-addition of a hydrogen atom to the triple bond, forming the compound (C) Hex-5-en-1-ol.
Now, this compound (C) Hex-5-en-1-ol, is acidified to form a cyclic structure known as 2-Methyl oxane compound (D).
Now, A is being converted into H by a catalyst which first converts into alcohol with the help of acidified water molecules (second catalyst). This molecule will attach with the replacement of the sodium atom in sodium ethynide. The compound H will be Hex-1-yne-3-ol.
Now coming to the formation of E from ethyne, two molecules of sodium methoxide are treated with ethyne, then, both the hydrogen atoms will be replaced with sodium atoms.
The compound (F) is cyclo-octa-2-yne-1,4-diol which is formed from compound E.
Now, the concentrated sulfuric acid will remove the water reduced while with the Lindlar’s catalyst, the triple bond in the compound will be reduced to the double bond-forming the compound G.
The reactions are given below:


So, compound C is Hex-5-en-1-ol.
Note:
We know that there can be the formation of two alkenes, i.e., cis-alkene or trans-alkene. So, for cis-alkene, the catalyst used is Lindlar’s catalyst while to form trans-alkene, sodium in liquid ammonia is used also known as Birch reduction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




