
In the following reactions:
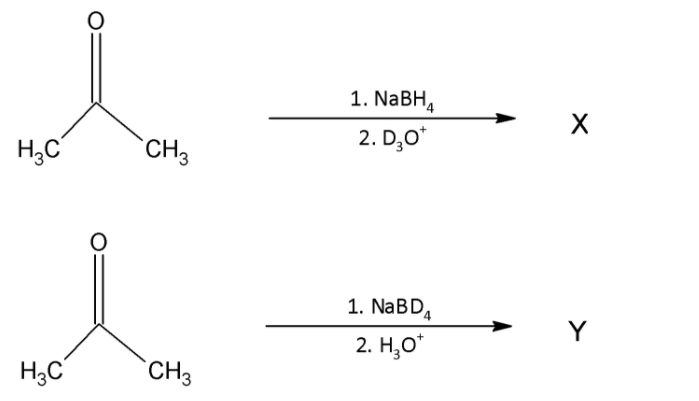
X and Y are:

Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you must recall the mechanism of the reduction reaction of ketones with sodium borohydride followed by hydrolysis to yield alcohols. The use of deuterium in place of hydrogen does not affect the reaction occurring.
Complete answer:
Sodium borohydride is used for taking aldehydes and ketones, one rung down the oxidation ladder, i.e. from carbonyl group to alcoholic group. Let us discuss the mechanism of this reduction reaction:
The reaction takes place in two steps. In the first step, the borohydride on, releases a hydride ion which because of the negative charge is a nucleophile. The carbonyl carbon, i.e. the carbon atom bonded to oxygen is electrophilic in nature due to the higher electronegativity of oxygen atom. Thus, it is susceptible to nucleophilic attack and is attacked by the hydride ion. Thus, the carbon hydrogen bond is formed and the carbon oxygen double bon becomes a single bond with oxygen carrying a negative charge.
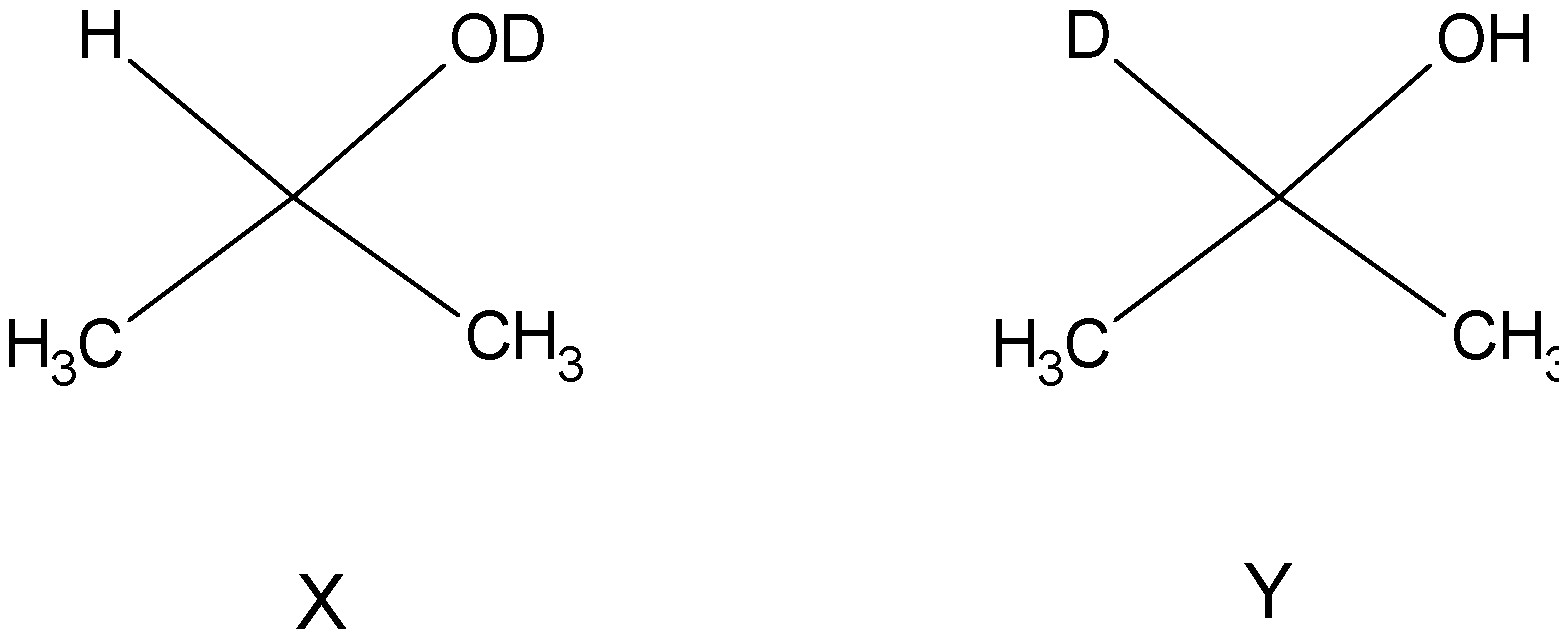
In the second step, i.e. introduction of acid, protonation occurs and the alkoxide is protonated to an alcohol. So, we can see that the hydrogen bonded to carbon comes from sodium borohydride and the hydrogen in hydroxyl group comes from the acid. So X and Y are:
Note:
Sodium borohydride is a good reducing agent and is a source of hydride ion. Although it is not as powerful a reducing agent as lithium aluminium hydride, it is a very effective reagent for carrying out the reduction of carbonyl compounds aldehydes and ketones to alcohols. It does not reduce esters or carboxylic acids or amides.
Complete answer:
Sodium borohydride is used for taking aldehydes and ketones, one rung down the oxidation ladder, i.e. from carbonyl group to alcoholic group. Let us discuss the mechanism of this reduction reaction:
The reaction takes place in two steps. In the first step, the borohydride on, releases a hydride ion which because of the negative charge is a nucleophile. The carbonyl carbon, i.e. the carbon atom bonded to oxygen is electrophilic in nature due to the higher electronegativity of oxygen atom. Thus, it is susceptible to nucleophilic attack and is attacked by the hydride ion. Thus, the carbon hydrogen bond is formed and the carbon oxygen double bon becomes a single bond with oxygen carrying a negative charge.
In the second step, i.e. introduction of acid, protonation occurs and the alkoxide is protonated to an alcohol. So, we can see that the hydrogen bonded to carbon comes from sodium borohydride and the hydrogen in hydroxyl group comes from the acid. So X and Y are:

Note:
Sodium borohydride is a good reducing agent and is a source of hydride ion. Although it is not as powerful a reducing agent as lithium aluminium hydride, it is a very effective reagent for carrying out the reduction of carbonyl compounds aldehydes and ketones to alcohols. It does not reduce esters or carboxylic acids or amides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




