
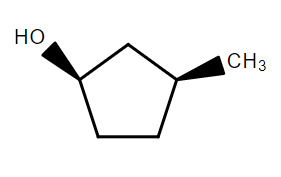
In the following reaction sequence the correct structure of $X$ is:
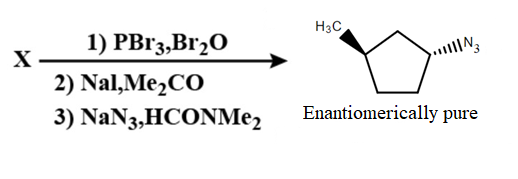
A.
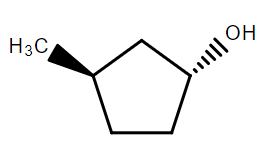
B.
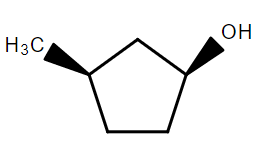
C.
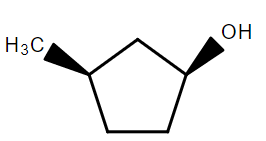
D.





Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you should recall the concept of nucleophilic substitution reactions. The substitution reactions are the type of reactions where a functional group of one chemical compound is substituted by another group or it is a reaction which involves the replacement of one atom or a molecule of a compound with another atom or molecule.
Complete Step by step solution:
The given reaction is an example of $S{N^2}$ reaction:
$S{N^2}$ reactions are bimolecular reactions in which there are simultaneous bond-making and bond-breaking steps.
$S{N^2}$ reactions do not proceed via an intermediate.
$S{N^2}$ reactions result in inverted stereochemistry at the reaction centre.
Steric effects are particularly important in $S{N^2}$reactions.
Unhindered back of the substrate makes the formation of carbon-nucleophile bonds easy. Therefore, methyl and primary substrates undergo nucleophilic substitution easily.
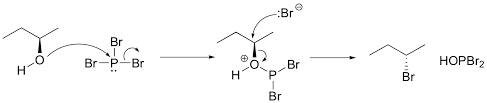
In the first reaction the reaction with \[PB{r_3}{\text{ and }}E{t_2}O\] the reaction with an alcohol can be shown as:
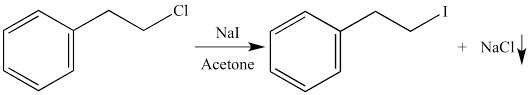
In the second reaction the reaction with $NaI$in presence of acetone:
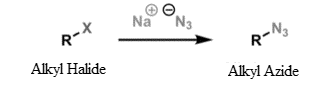
In the third reaction of $Na{N_3}$with DMF:
We can write the overall mechanism of the reaction as:
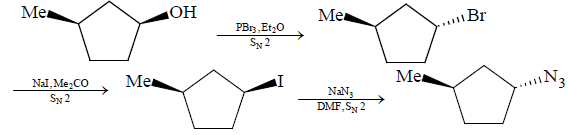
Hence, option B is correct.
Note: Make sure you remember the difference between $S{N^1}$ and $S{N^2}$ reaction mechanism. $S{N^1}$ involves the formation of a carbocation intermediate which is generally in case of tertiary or secondary alkyl halides as their intermediates are stabilised by hyperconjugation with secondary or tertiary alcohols under strongly acidic or strongly basic conditions. The $S{N^1}$ mechanism also is known as a dissociative mechanism. In the $S{N^2}$ reaction mechanism, the nucleophile approaches the given substrate at an angle of\[{180^o}\] to the carbon-leaving group bond. Now, the leaving group is pushed out of the transition state on the opposite side of the carbon-nucleophile bond, forming the required product. It is important to note that the product is formed with an inversion of the tetrahedral geometry at the atom in the centre.
Complete Step by step solution:
The given reaction is an example of $S{N^2}$ reaction:
$S{N^2}$ reactions are bimolecular reactions in which there are simultaneous bond-making and bond-breaking steps.
$S{N^2}$ reactions do not proceed via an intermediate.
$S{N^2}$ reactions result in inverted stereochemistry at the reaction centre.
Steric effects are particularly important in $S{N^2}$reactions.
Unhindered back of the substrate makes the formation of carbon-nucleophile bonds easy. Therefore, methyl and primary substrates undergo nucleophilic substitution easily.
In the first reaction the reaction with \[PB{r_3}{\text{ and }}E{t_2}O\] the reaction with an alcohol can be shown as:

In the second reaction the reaction with $NaI$in presence of acetone:

In the third reaction of $Na{N_3}$with DMF:

We can write the overall mechanism of the reaction as:

Hence, option B is correct.
Note: Make sure you remember the difference between $S{N^1}$ and $S{N^2}$ reaction mechanism. $S{N^1}$ involves the formation of a carbocation intermediate which is generally in case of tertiary or secondary alkyl halides as their intermediates are stabilised by hyperconjugation with secondary or tertiary alcohols under strongly acidic or strongly basic conditions. The $S{N^1}$ mechanism also is known as a dissociative mechanism. In the $S{N^2}$ reaction mechanism, the nucleophile approaches the given substrate at an angle of\[{180^o}\] to the carbon-leaving group bond. Now, the leaving group is pushed out of the transition state on the opposite side of the carbon-nucleophile bond, forming the required product. It is important to note that the product is formed with an inversion of the tetrahedral geometry at the atom in the centre.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




