
In the following reaction:
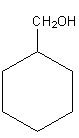 is changed into
is changed into
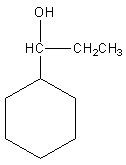 by
by
A. (i) ${\text{Cu}}\,\,{\text{30}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{C}}$ (ii) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{MgBr,H}}_3^ + {\text{O}}$
B. (i) ${\text{Cr}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ (ii) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{MgBr,H}}_3^ + {\text{O}}$
C. (i) ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ (ii) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{MgBr,H}}_3^ + {\text{O}}$
D. (i) ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_7} + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ (ii) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{MgBr,H}}_3^ + {\text{O}}$


Answer
563.4k+ views
Hint:To answer this question we should know the functioning of all the given reagents. The reagents given here in (i), do oxidation of alcohol. The copper is mild whereas the remaining all are strong. The reagent given in (II) is known as Grignard reagent. It is used for alkylation.
Complete solution:
We will check one by one every reagent to obtain the desired product.
A. (i) ${\text{Cu}}\,\,{\text{30}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{C}}$:
Copper is a mild oxidizing agent. It oxidises the primary alcohol to primary aldehyde and secondary alcohol to ketone.
The reaction of benzyl alcohol with ${\text{Cu}}\,\,{\text{30}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{C}}$ is as follows:
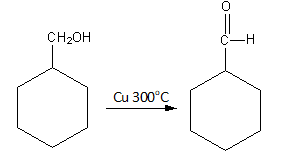
So, benzyl alcohol converts into benzaldehyde by the oxidation caused by copper.
(ii) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{MgBr,H}}_3^ + {\text{O}}$:
Ethyl magnesium bromide is known as Grignard reagent. This reagent is used for the preparation of alkyl nucleophiles. Ethyl magnesium bromide will give ethyl nucleophile. We know that carbonyl carbon is very electrophilic, so ethyl nucleophiles will attack at carbonyl carbon. The attacks is shown as follows:
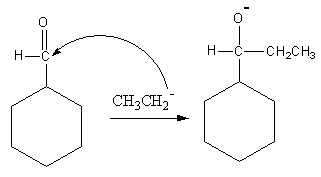
Now the hydronium ion gives protons to the negatively charged oxygen.
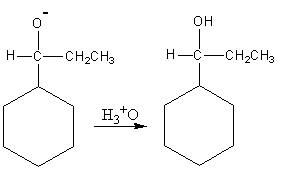
So, the reaction of benzaldehyde with ethyl magnesium bromide gives cyclohexyl propanol which is the desired product. So, option (A) is correct.
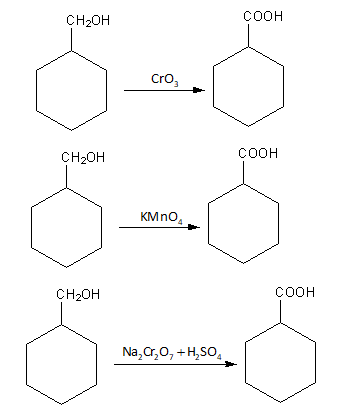
Chromium oxide ${\text{Cr}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$, potassium permanganate ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ and sodium dichromate with sulphuric acid ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_7} + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$, all are strong oxidising agent.
So, the reaction of benzyl alcohol with chromium oxide${\text{Cr}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$, potassium permanganate ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ and sodium dichromate with sulphuric acid gives benzoic acid.
The reactions are shown as follows:
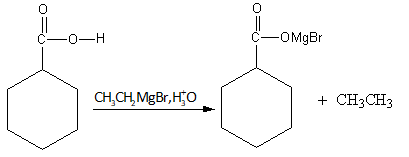
As the ethyl magnesium bromide gives ethyl nucleophile which abstracts the acidic proton from the benzoic acid and gives the benzoate ion and ethane.
So, the reaction of benzyl alcohol with chromium oxide${\text{Cr}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$, potassium permanganate ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ and sodium dichromate with sulphuric acid does not give the desired product.
Hence, option (D) is the correct answer for the given question.
Note:The conversion of alcohol to carbonyl or carboxylic acid is known as oxidation. The reagent cause the oxidation is known as oxidizing agent. Oxidizing agents convert the primary alcohol to carboxylic acid. Mild oxidizing agents convert into carbonyl only. Strong oxidizing agent converts into carboxylic acid. The electron-deficient species is known as electrophile. The electron-rich species is known as nucleophile.
Complete solution:
We will check one by one every reagent to obtain the desired product.
A. (i) ${\text{Cu}}\,\,{\text{30}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{C}}$:
Copper is a mild oxidizing agent. It oxidises the primary alcohol to primary aldehyde and secondary alcohol to ketone.
The reaction of benzyl alcohol with ${\text{Cu}}\,\,{\text{30}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{C}}$ is as follows:

So, benzyl alcohol converts into benzaldehyde by the oxidation caused by copper.
(ii) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{MgBr,H}}_3^ + {\text{O}}$:
Ethyl magnesium bromide is known as Grignard reagent. This reagent is used for the preparation of alkyl nucleophiles. Ethyl magnesium bromide will give ethyl nucleophile. We know that carbonyl carbon is very electrophilic, so ethyl nucleophiles will attack at carbonyl carbon. The attacks is shown as follows:

Now the hydronium ion gives protons to the negatively charged oxygen.

So, the reaction of benzaldehyde with ethyl magnesium bromide gives cyclohexyl propanol which is the desired product. So, option (A) is correct.
Chromium oxide ${\text{Cr}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$, potassium permanganate ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ and sodium dichromate with sulphuric acid ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_7} + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$, all are strong oxidising agent.
So, the reaction of benzyl alcohol with chromium oxide${\text{Cr}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$, potassium permanganate ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ and sodium dichromate with sulphuric acid gives benzoic acid.
The reactions are shown as follows:

As the ethyl magnesium bromide gives ethyl nucleophile which abstracts the acidic proton from the benzoic acid and gives the benzoate ion and ethane.

So, the reaction of benzyl alcohol with chromium oxide${\text{Cr}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$, potassium permanganate ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ and sodium dichromate with sulphuric acid does not give the desired product.
Hence, option (D) is the correct answer for the given question.
Note:The conversion of alcohol to carbonyl or carboxylic acid is known as oxidation. The reagent cause the oxidation is known as oxidizing agent. Oxidizing agents convert the primary alcohol to carboxylic acid. Mild oxidizing agents convert into carbonyl only. Strong oxidizing agent converts into carboxylic acid. The electron-deficient species is known as electrophile. The electron-rich species is known as nucleophile.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




