
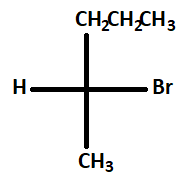
In the following monobromination reaction, the number of possible chiral products is:

Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint:A chiral molecule or ion exists in two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other, called enantiomers. Any reaction or process in which bromine is introduced into a molecule is called bromination. Since an alkane group is present, alkane halogenation reaction will take place.
Complete answer:
A molecule or ion is called chiral if it cannot be superposed on its mirror image by any combination of rotations and translations. When the mirror image of the object is placed over the original object and they do not overlap, they are called non-superimposable. Chiral carbon centers are carbon atoms that are attached to four different substituents, that are placed at the corners of a tetrahedron.
These reactions include free radical halogenations of alkanes.
${R_3}C - H + {X_2} \to {R_3}C - X + H - X$
Initiation and propagation takes place in a bromination reaction in which the different products $H - Br$ and $C{H_3}C{H_2}Br$ are formed. Light energy breaks the Br-Br bond giving two separate bromine atoms (Br). Each Br formed has the ability to remove an H from ethane. When Br removes an H along with one of the electrons in the C-H bond. H-Br forms and leaves behind a reactive molecular fragment (CH3-CH2) called as an ethyl radical.
The different chiral products which can be formed from the reaction are :
1.

2.
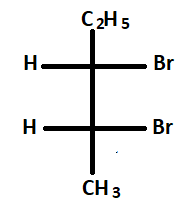
3.
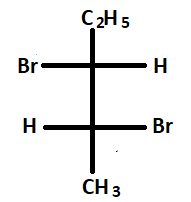
4.

5.
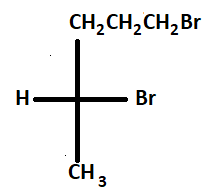
Thus there are five chiral products along with two achiral products.
Hence the total no. of chiral products are 5.
Note:
The carbon connected to the bromine turned into a chiral center during the reaction and it is the only chiral center of the molecule. the diastereomers in the halogenation of chiral substrates may not be formed in equal amounts.
Complete answer:
A molecule or ion is called chiral if it cannot be superposed on its mirror image by any combination of rotations and translations. When the mirror image of the object is placed over the original object and they do not overlap, they are called non-superimposable. Chiral carbon centers are carbon atoms that are attached to four different substituents, that are placed at the corners of a tetrahedron.
These reactions include free radical halogenations of alkanes.
${R_3}C - H + {X_2} \to {R_3}C - X + H - X$
Initiation and propagation takes place in a bromination reaction in which the different products $H - Br$ and $C{H_3}C{H_2}Br$ are formed. Light energy breaks the Br-Br bond giving two separate bromine atoms (Br). Each Br formed has the ability to remove an H from ethane. When Br removes an H along with one of the electrons in the C-H bond. H-Br forms and leaves behind a reactive molecular fragment (CH3-CH2) called as an ethyl radical.
The different chiral products which can be formed from the reaction are :
1.

2.

3.

4.

5.

Thus there are five chiral products along with two achiral products.
Hence the total no. of chiral products are 5.
Note:
The carbon connected to the bromine turned into a chiral center during the reaction and it is the only chiral center of the molecule. the diastereomers in the halogenation of chiral substrates may not be formed in equal amounts.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




