
In the following diagrams, a particle with small charge −q is free to move up or down, but not sideways near a larger fixed charge Q. The small charge is in equilibrium because in the positions shown, the electrical upward force is equal to the weight of the particle. Which statement is true?
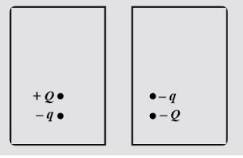
A. In Fig (a), -q is in stable equilibrium.
B. In Fig (a), -q is in neutral equilibrium.
C. In Fig (b), -q is in stable equilibrium.
D. Neither in fig.(a) nor in fig (b), -q is in stable equilibrium

Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: The stable equilibrium is defined as the state that a particle or molecule or any kind of body will attain its original position when it is tried to move. So in this question, we have to replace the charge according to the force upward.
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
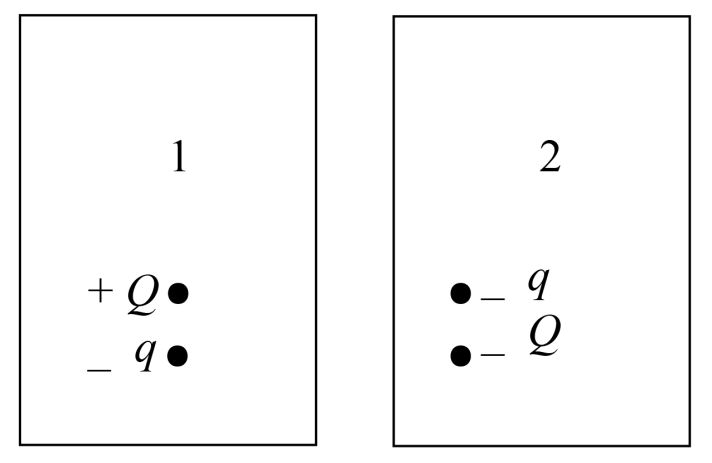
The small charge that is free to move up and down is \[ - q\].
The large charge that is fixed is \[ - Q\].
It is also given that, \[ - q\] is able to move only two directions, they are upward and downward directions and no other movement is not possible.
Let us assume the electrical upward will be \[{f_u}\] and
The weight of the particle will be \[w = mg\].
And given a statement that, the electrical upward force is equal to the weight of the particle, it means
\[{f_u} = mg\]
Now, in the first diagram, if we try to move the \[ - q\] upward, then the charge will accelerate or come downward because the electrostatic force is less the weight of the particle so the charge is in unstable equilibrium.
Coming to the first diagram, if we try to move the \[ - q\] downward position the charge will move to the upward, if we move the charge upward then the charge will again move downwards, it just means the charge is already in stable equilibrium.
Therefore, in the fig (b) the negative charge is in stable equilibrium.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
While the charge is moved upward, the gravitational force should be more than it otherwise the charge will again come to the original position, so according to this we have to remember that the charge is not stable.
Complete step by step answer:
Given:

The small charge that is free to move up and down is \[ - q\].
The large charge that is fixed is \[ - Q\].
It is also given that, \[ - q\] is able to move only two directions, they are upward and downward directions and no other movement is not possible.
Let us assume the electrical upward will be \[{f_u}\] and
The weight of the particle will be \[w = mg\].
And given a statement that, the electrical upward force is equal to the weight of the particle, it means
\[{f_u} = mg\]
Now, in the first diagram, if we try to move the \[ - q\] upward, then the charge will accelerate or come downward because the electrostatic force is less the weight of the particle so the charge is in unstable equilibrium.
Coming to the first diagram, if we try to move the \[ - q\] downward position the charge will move to the upward, if we move the charge upward then the charge will again move downwards, it just means the charge is already in stable equilibrium.
Therefore, in the fig (b) the negative charge is in stable equilibrium.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
While the charge is moved upward, the gravitational force should be more than it otherwise the charge will again come to the original position, so according to this we have to remember that the charge is not stable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




