
In the following circuit, the resistance of wire AB is 10Ω, and its length is 1m. Rests of the quantities are given in the diagram. The potential gradient on the wire will be
A. \[0.08\dfrac{V}{m}\]
B. \[0.008\dfrac{V}{m}\]
C. \[0.8\dfrac{V}{m}\]
D. None

Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint: In this question voltage and its internal resistance is given which is supplying a current to the wire whose length is 1m; first we will calculate the net resistance of the source and the wire then we will calculate the current from the source to wire AB, and by using this current we will find the voltage in the wire through which potential gradient will be calculated.
Complete step by step answer:
The resistance of the wire AB \[R = 10\Omega \]
Length of the wire AB \[l = 1m\]
Now since the 15Ω resistance is in series with the 10Ω resistance, then its net resistance will be \[{R_{net}} = 10 + 15 = 25\Omega \]
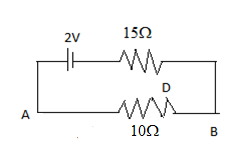
Now since the net resistance of the wire is 25Ω, so now we calculate the current flowing through the wire AB by using Ohm’s law
\[V = IR - - (i)\]
Hence by substituting the values, we get
\[
I = \dfrac{V}{R} \\
= \dfrac{2}{{25}} \\
= 0.08A \\
\]
Now we have the current and the resistance through the wire AB, so now we calculate the potential difference in the wire AB by using equation (i)
\[
V = IR \\
= 0.08 \times 10 \\
= 0.8V \\
\]
Now we have to calculate the potential gradient per unit length of the wire AB whose length is 1m which is given as
\[P.G = \dfrac{V}{L} - - (ii)\]
Hence by substituting the values in equation (ii), we get
\[
P.G = \dfrac{V}{L} \\
= \dfrac{{0.8}}{1} \\
= 0.8\dfrac{V}{m} \\
\]
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
Students must note that when a constant current flows through a wire of uniform cross section, then the potential drop will be directly proportional to the length of the wire. The potential gradient is the measure of the potential drop measured when the length of the wire is changed.
Complete step by step answer:
The resistance of the wire AB \[R = 10\Omega \]
Length of the wire AB \[l = 1m\]
Now since the 15Ω resistance is in series with the 10Ω resistance, then its net resistance will be \[{R_{net}} = 10 + 15 = 25\Omega \]

Now since the net resistance of the wire is 25Ω, so now we calculate the current flowing through the wire AB by using Ohm’s law
\[V = IR - - (i)\]
Hence by substituting the values, we get
\[
I = \dfrac{V}{R} \\
= \dfrac{2}{{25}} \\
= 0.08A \\
\]
Now we have the current and the resistance through the wire AB, so now we calculate the potential difference in the wire AB by using equation (i)
\[
V = IR \\
= 0.08 \times 10 \\
= 0.8V \\
\]
Now we have to calculate the potential gradient per unit length of the wire AB whose length is 1m which is given as
\[P.G = \dfrac{V}{L} - - (ii)\]
Hence by substituting the values in equation (ii), we get
\[
P.G = \dfrac{V}{L} \\
= \dfrac{{0.8}}{1} \\
= 0.8\dfrac{V}{m} \\
\]
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
Students must note that when a constant current flows through a wire of uniform cross section, then the potential drop will be directly proportional to the length of the wire. The potential gradient is the measure of the potential drop measured when the length of the wire is changed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




