
In the following acid-base reaction, how would you identify the acid, base and their conjugate acids and bases:
\[NH_4^ + \, + \,HCO_3^ - \, \to \,N{H_3}\, + \,{H_2}C{O_3}\]
Answer
548.4k+ views
Hint: When an acid and base get reacted it forms a salt. The parent acid and the parent base can be determined by splitting the salt into the cationic part and anionic part. The pH of salt will be neutral, that’s the reason when acid and base react the neutralization takes place. Since, the acid pH lies between \[pH\,\,1 - 6\] and base \[pH\] lies between \[pH\,\,8 - 14\] .
Complete step-by-step answer:An acid is a substance which can donate its proton. The base is a substance which can donate its hydroxy ions. Base and acid react to form salt and water. The hydroxy comes from base and proton from the acid to form water.
Salt can be defined as the neutralization of a product from acid and base.
Let’s discuss the Lewis acid and Lewis base;
Lewis acid: the ion which can accept the pair of electrons also known as Bronsted-lowry base.
Lewis base: the ion which can donate the pair of electrons also known as Bronsted-lowry acid.
The change from\[NH_4^ + \] to \[N{H_3}\] shows that a proton was donated from \[NH_4^ + \], so simply put, \[NH_4^ + \]is the acid, and we know that\[N{H_3}\] is the base.
Since \[N{H_3}\] is the neutral state, \[NH_4^ + \]is the conjugate acid.
The change from \[HCO_3^ - \] to \[{H_2}C{O_3}\] shows that a proton was accepted by \[HCO_3^ - \], so simply put, \[HCO_3^ - \]is the base, and \[{H_2}C{O_3}\] is the acid.
Since \[{H_2}C{O_3}\] is the neutral state, \[HCO_3^ - \]is the conjugate base.
Overall, we have:
\[NH_4^ + \]:
Proton donor (Bronsted -Lowry acid)
Electron acceptor (Lewis acid)
\[N{H_3}\]:
Proton acceptor (Bronsted -Lowry base)
Electron donor (Lewis base)
\[HCO_3^ - \]:
Proton acceptor (Bronsted -Lowry base)
Electron donor (Lewis base)
\[{H_2}C{O_3}\]:
Proton donor (Bronsted -Lowry acid)
Electron acceptor (Lewis acid)
Let’s observe the diagram of how it shows;
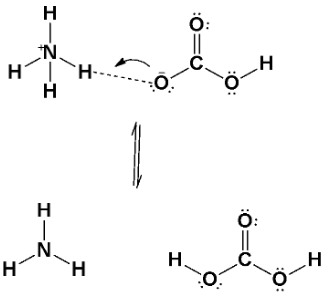
Note: A Lewis acid is a substance, such as the \[{H^ + }\] ion, that can accept a pair of nonbonding electrons. In simple words, a Lewis acid is an electron-pair acceptor. A Lewis base is any substance, such as the \[O{H^ - }\] ion, that can donate a pair of nonbonding electrons. A Lewis base is, therefore, an electron-pair donor.
Complete step-by-step answer:An acid is a substance which can donate its proton. The base is a substance which can donate its hydroxy ions. Base and acid react to form salt and water. The hydroxy comes from base and proton from the acid to form water.
Salt can be defined as the neutralization of a product from acid and base.
Let’s discuss the Lewis acid and Lewis base;
Lewis acid: the ion which can accept the pair of electrons also known as Bronsted-lowry base.
Lewis base: the ion which can donate the pair of electrons also known as Bronsted-lowry acid.
The change from\[NH_4^ + \] to \[N{H_3}\] shows that a proton was donated from \[NH_4^ + \], so simply put, \[NH_4^ + \]is the acid, and we know that\[N{H_3}\] is the base.
Since \[N{H_3}\] is the neutral state, \[NH_4^ + \]is the conjugate acid.
The change from \[HCO_3^ - \] to \[{H_2}C{O_3}\] shows that a proton was accepted by \[HCO_3^ - \], so simply put, \[HCO_3^ - \]is the base, and \[{H_2}C{O_3}\] is the acid.
Since \[{H_2}C{O_3}\] is the neutral state, \[HCO_3^ - \]is the conjugate base.
Overall, we have:
\[NH_4^ + \]:
Proton donor (Bronsted -Lowry acid)
Electron acceptor (Lewis acid)
\[N{H_3}\]:
Proton acceptor (Bronsted -Lowry base)
Electron donor (Lewis base)
\[HCO_3^ - \]:
Proton acceptor (Bronsted -Lowry base)
Electron donor (Lewis base)
\[{H_2}C{O_3}\]:
Proton donor (Bronsted -Lowry acid)
Electron acceptor (Lewis acid)
Let’s observe the diagram of how it shows;

Note: A Lewis acid is a substance, such as the \[{H^ + }\] ion, that can accept a pair of nonbonding electrons. In simple words, a Lewis acid is an electron-pair acceptor. A Lewis base is any substance, such as the \[O{H^ - }\] ion, that can donate a pair of nonbonding electrons. A Lewis base is, therefore, an electron-pair donor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




