
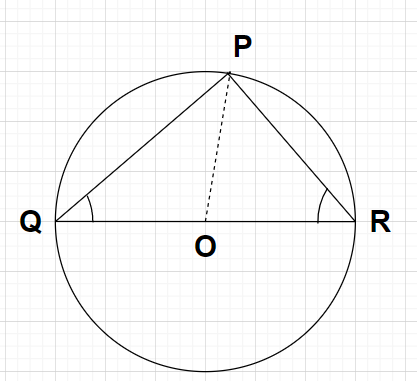
In the figure, what is the value of $\angle {\text{PQR}} + \angle {\text{PRQ}}$.
$
{\text{A}}{\text{. 7}}{{\text{0}}^\circ} \\
{\text{B}}{\text{. 8}}{{\text{0}}^\circ} \\
{\text{C}}{\text{. 9}}{{\text{0}}^\circ} \\
{\text{D}}{\text{. 10}}{{\text{0}}^\circ} \\
$

Answer
618k+ views
Hint: Here, we will proceed by using the property that the angle formed by drawing lines from the ends of the diameter of a circle to its circumference forms a right angle (${\text{9}}{{\text{0}}^\circ}$) and then, using the property of the triangle i.e., the sum of all the interior angles of any triangle is always equal to ${\text{18}}{{\text{0}}^\circ}$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the figure, point O is the centre of the circle so the line segment QR is the diameter of the circle because the diameter of any circle passes through the centre of that circle.
As we know that the angle formed by drawing lines from the ends of the diameter of a circle to its circumference forms a right angle (${\text{9}}{{\text{0}}^\circ}$)
Using the above concept, we can say that $\angle {\text{QPR}} = {90^\circ}$
Also we know that according to the property of the triangle, the sum of all the interior angles of any triangle is always equal to ${\text{18}}{{\text{0}}^\circ}$
Using the above property of the triangle, we can write
In $\vartriangle $PQR, $\angle {\text{QPR}} + \angle {\text{PQR}} + \angle {\text{PRQ}} = {180^\circ}{\text{ }} \to {\text{(1)}}$
By putting the value of $\angle {\text{QPR}} = {90^\circ}$ in equation (1), we get
\[
\Rightarrow {90^\circ} + \angle {\text{PQR}} + \angle {\text{PRQ}} = {180^\circ} \\
\Rightarrow \angle {\text{PQR}} + \angle {\text{PRQ}} = {180^\circ} - {90^\circ} \\
\Rightarrow \angle {\text{PQR}} + \angle {\text{PRQ}} = {90^\circ} \\
\]
Therefore, the value of $\angle {\text{PQR}} + \angle {\text{PRQ}}$ is equal to ${\text{9}}{{\text{0}}^\circ}$
Hence, option C is correct.
Note: In this particular problem, we had to find the value for $\angle {\text{PQR}} + \angle {\text{PRQ}}$ which can be done by forming an equation which will consist of both of these angles (i.e., $\angle {\text{PQR}}$ and $\angle {\text{PRQ}}$). Also, the length OP in the figure will be equal to the radius of the given circle because point O is the centre of the circle and point P is any point on the circumference of the given circle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the figure, point O is the centre of the circle so the line segment QR is the diameter of the circle because the diameter of any circle passes through the centre of that circle.
As we know that the angle formed by drawing lines from the ends of the diameter of a circle to its circumference forms a right angle (${\text{9}}{{\text{0}}^\circ}$)
Using the above concept, we can say that $\angle {\text{QPR}} = {90^\circ}$
Also we know that according to the property of the triangle, the sum of all the interior angles of any triangle is always equal to ${\text{18}}{{\text{0}}^\circ}$
Using the above property of the triangle, we can write
In $\vartriangle $PQR, $\angle {\text{QPR}} + \angle {\text{PQR}} + \angle {\text{PRQ}} = {180^\circ}{\text{ }} \to {\text{(1)}}$
By putting the value of $\angle {\text{QPR}} = {90^\circ}$ in equation (1), we get
\[
\Rightarrow {90^\circ} + \angle {\text{PQR}} + \angle {\text{PRQ}} = {180^\circ} \\
\Rightarrow \angle {\text{PQR}} + \angle {\text{PRQ}} = {180^\circ} - {90^\circ} \\
\Rightarrow \angle {\text{PQR}} + \angle {\text{PRQ}} = {90^\circ} \\
\]
Therefore, the value of $\angle {\text{PQR}} + \angle {\text{PRQ}}$ is equal to ${\text{9}}{{\text{0}}^\circ}$
Hence, option C is correct.
Note: In this particular problem, we had to find the value for $\angle {\text{PQR}} + \angle {\text{PRQ}}$ which can be done by forming an equation which will consist of both of these angles (i.e., $\angle {\text{PQR}}$ and $\angle {\text{PRQ}}$). Also, the length OP in the figure will be equal to the radius of the given circle because point O is the centre of the circle and point P is any point on the circumference of the given circle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




