
In the figure, the disc D does not slip on the surface S. The pulley P has mass, and the string does not slip on it. The string is wound around the disc. Then, which of the following statement(s) is/are true?
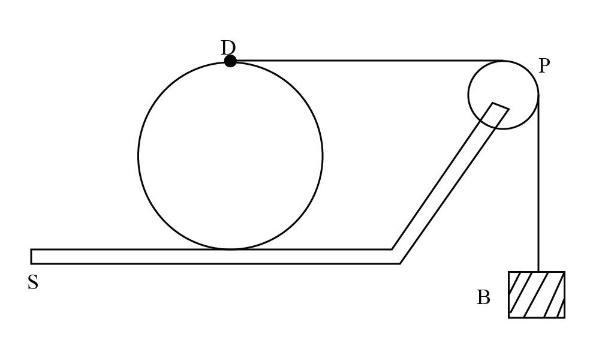
(A) The acceleration of the block B is double the acceleration of the center of D.
(B) The force of friction exerted by D on S acts to the left.
(C) The horizontal and the vertical sections of the string have the same tension.
(D) The sum of the kinetic energies of D and B is less than the loss in the potential energy of B as it moves down.

Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: You should firstly draw a free-body diagram which will help to solve the question more efficiently. Use the concept of angular acceleration to find the acceleration of the disc with respect to the block. Also, you need to apply the work-energy theorem in the question.
Complete step by step answer:
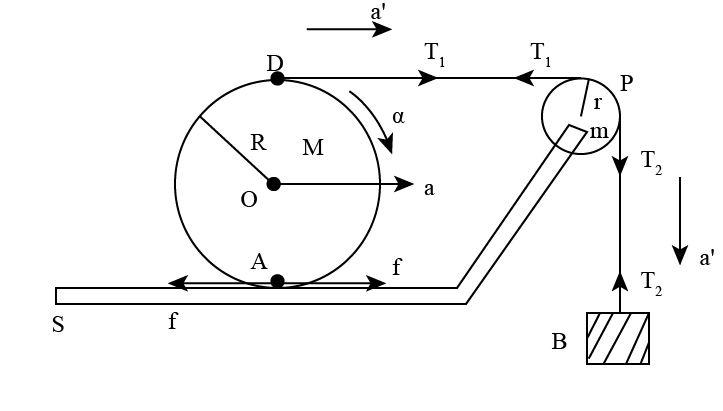
Let us consider that the disc D is having mass M and is moving right with the acceleration, say a. Let, the angular acceleration of the disc be $\alpha $.
As the disc does not slip on the surface and the string, that is on position A and D. We can say that ${a_A} = 0$ and ${a_D} = a'$.
So,
$a = R\alpha $
Further we can write that,
$\begin{array}
a + a &= a'\\
a' &= 2a
\end{array}$
Thus, the acceleration of the block B is double the acceleration of the center of D.
As the point A will tend to move in the left direction. So, the direction friction force exerted by the disc D on the surface S will act in the opposite direction that is towards the left.
We know that, whenever the height of the object decreases, the potential energy also decreases. So, in this case, when the block B moves in the downward direction, the potential energy decreases and the kinetic energy increases. Also, the kinetic energy of the disc increases. We can write the expression for the work-energy theorem as,
${\left( {KE} \right)_D} + {\left( {KE} \right)_B} + {\left( {KE} \right)_{pulley}} = mgh$
As the pulleys have some mass and will rotate as the block moves. It will gain some kinetic energy. So we can write as,
${\left( {KE} \right)_D} + {\left( {KE} \right)_B} < loss\;in\;{\left( {PE} \right)_B}$
Therefore, the correct options are (A), (B), and (D).
Note:You may make a mistake if you try to solve the question without a free-body diagram. Also, make sure that you take the direction of friction force opposite to the motion. Also, apply the work-energy theorem properly.
Complete step by step answer:

Let us consider that the disc D is having mass M and is moving right with the acceleration, say a. Let, the angular acceleration of the disc be $\alpha $.
As the disc does not slip on the surface and the string, that is on position A and D. We can say that ${a_A} = 0$ and ${a_D} = a'$.
So,
$a = R\alpha $
Further we can write that,
$\begin{array}
a + a &= a'\\
a' &= 2a
\end{array}$
Thus, the acceleration of the block B is double the acceleration of the center of D.
As the point A will tend to move in the left direction. So, the direction friction force exerted by the disc D on the surface S will act in the opposite direction that is towards the left.
We know that, whenever the height of the object decreases, the potential energy also decreases. So, in this case, when the block B moves in the downward direction, the potential energy decreases and the kinetic energy increases. Also, the kinetic energy of the disc increases. We can write the expression for the work-energy theorem as,
${\left( {KE} \right)_D} + {\left( {KE} \right)_B} + {\left( {KE} \right)_{pulley}} = mgh$
As the pulleys have some mass and will rotate as the block moves. It will gain some kinetic energy. So we can write as,
${\left( {KE} \right)_D} + {\left( {KE} \right)_B} < loss\;in\;{\left( {PE} \right)_B}$
Therefore, the correct options are (A), (B), and (D).
Note:You may make a mistake if you try to solve the question without a free-body diagram. Also, make sure that you take the direction of friction force opposite to the motion. Also, apply the work-energy theorem properly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




