
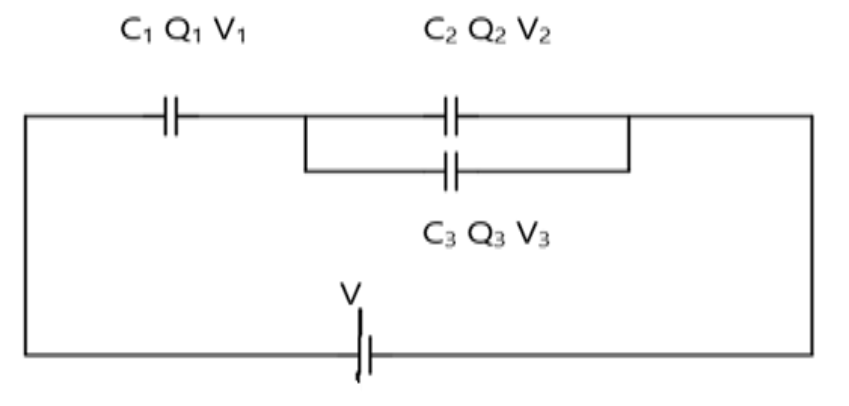
In the figure, the capacitance ${C_1}$, ${C_2}$ and ${C_3}$are joined to a battery with symbols having their usual meaning, the correct condition will be:
A) \[{Q_1} = {Q_2} = {Q_3}{\text{ }}and{\text{ }}{V_1} = {V_2} = {V_3} + V\]
B) ${Q_1} = {Q_2} + {Q_3}{\text{ }}and{\text{ }}V = {V_1} + {V_2} + {V_3}$
C) ${Q_1} = {Q_2} + {Q_3}{\text{ }}and{\text{ }}V = {V_1} + {V_2}$
D) ${Q_{_2}} = {Q_3}{\text{ }}and{\text{ }}{V_2} = {V_3}$

Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: This circuit consists of capacitors; the capacitor is a device used to store electrostatic energy. A capacitor is the combination of two conductors which contain equal and opposite charges such that the potential difference between the conductors is not affected by the presence of other conductors.
Complete step-by-step solution:
In this case, the total amount of charges entering the circuit from the positive terminal of the battery and enters in the first capacitor ${C_1}$, and then the charges splits equally into two wires ${C_2}$ and ${C_3}$. The voltage in the first circuit is ${V_1}$ and the voltage stored in the second capacitor is ${V_2}$and the voltage in the third capacitor is ${V_3}$.
At the first junction, the charge ${Q_{}}$ will be equally divided into ${Q_2}$and ${Q_3}$
Hence, ${Q_1} = {Q_2} + {Q_3}$
As the capacitor $C_2$ and $C_3$ are connected in parallel combination, therefore the potential on them will be equal in magnitude. That is ${V_2} = {V_3}$
The total potential difference in the circuit is V which is divided into ${V_1}$, ${V_2}$, ${V_3}$
Therefore, we can write that
$V = {V_1} + {V_2}$
$ \Rightarrow {V_1} + {V_3}$
Hence,Answer: The correct option is (C).
Note: Potential difference: Mathematically potential difference is equal to voltage and it is the product of current and resistance of the circuit. The potential difference of a circuit is measured in Volts. It is the work done or the energy released in the transfer of a unit quantity of electricity from one point to the other.
This circuit combination obeys Kirchhoff’s 2nd law which states that the conservation of energy in a closed circuit. For a closed path the algebraic sum of all the voltage around any closed loop in a circuit is equal to zero.
Complete step-by-step solution:
In this case, the total amount of charges entering the circuit from the positive terminal of the battery and enters in the first capacitor ${C_1}$, and then the charges splits equally into two wires ${C_2}$ and ${C_3}$. The voltage in the first circuit is ${V_1}$ and the voltage stored in the second capacitor is ${V_2}$and the voltage in the third capacitor is ${V_3}$.
At the first junction, the charge ${Q_{}}$ will be equally divided into ${Q_2}$and ${Q_3}$
Hence, ${Q_1} = {Q_2} + {Q_3}$
As the capacitor $C_2$ and $C_3$ are connected in parallel combination, therefore the potential on them will be equal in magnitude. That is ${V_2} = {V_3}$
The total potential difference in the circuit is V which is divided into ${V_1}$, ${V_2}$, ${V_3}$
Therefore, we can write that
$V = {V_1} + {V_2}$
$ \Rightarrow {V_1} + {V_3}$
Hence,Answer: The correct option is (C).
Note: Potential difference: Mathematically potential difference is equal to voltage and it is the product of current and resistance of the circuit. The potential difference of a circuit is measured in Volts. It is the work done or the energy released in the transfer of a unit quantity of electricity from one point to the other.
This circuit combination obeys Kirchhoff’s 2nd law which states that the conservation of energy in a closed circuit. For a closed path the algebraic sum of all the voltage around any closed loop in a circuit is equal to zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




