
In the figure, the block A, B and C of mass $m$ each, have acceleration ${a_1}$, ${a_2}$ and ${a_3}$ respectively. ${F_1}$ and ${F_2}$ are external forces of magnitude $2\;mg$ and $mg$ respectively. Then
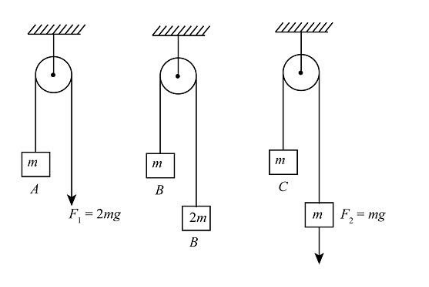
(a) ${a_1} = {a_2} = {a_3}$
(b) ${a_1}\rangle {a_3}\rangle {a_2}$
(c) ${a_1} = {a_2}$, ${a_2}\rangle {a_3}$
(d) \[{a_1}\rangle {a_2}\], ${a_2} = {a_3}$

Answer
582k+ views
Hint: We will use Newton's law for the determination of the acceleration of the various blocks. In Newton's law, use the magnitude of the net force for the calculation of the acceleration. We will apply Newton's law on each block separately so that we can get information about the sequence of the accelerations.
Complete step by step answer:
It is given in the question that magnitudes of the forces ${F_1}$ and ${F_2}$ is $2\;mg$ and $mg$, and acceleration of the blocks A, B and C are ${a_1}$, ${a_2}$ and ${a_3}$. We will use this information in the calculation of acceleration of blocks.
First, we will apply Newton's law on block A.
Therefore, we get
$
\Rightarrow {F_{net}} = m{a_1}\\
\Rightarrow {F_1} - mg = m{a_1}
$
It is given in the question that the magnitude of the force ${F_1}$ is $2mg$, so substitute value of ${F_1}$ in the above equation.
$
\Rightarrow 2mg - mg = m{a_1}\\
\Rightarrow mg = m{a_1}\\
\Rightarrow {a_1} = g
$
Now we will apply Newton's law on block B.
Therefore, we get
$
\Rightarrow {F_{net}} = m{a_2}\\
\Rightarrow 2mg - mg = (2m + m){a_2}\\
\Rightarrow mg = 3m{a_2}\\
\Rightarrow {a_2} = \dfrac{g}{3}
$
Again, we will apply Newton's law on block C.
Therefore, we get
$\Rightarrow {F_2} + mg - mg = (m + m){a_3}\\
\Rightarrow {F_2} = 2m{a_3}
$
It is given in the question that the magnitude of the force ${F_2}$ is $mg$, so substitute the value of ${F_2}$ in the above equation.
$
\Rightarrow mg = 2m{a_3}\\
\Rightarrow {a_3} = \dfrac{g}{2}
$
Therefore, the accelerations of block A, B and C are $g$, $g/3$ and $g/2$, so the sequence of the accelerations of the blocks are ${a_1}\rangle {a_3}\rangle {a_2}$ and option (b) is correct.
Note: In this solution, the determination of the net force is the main thing. Here, additional load or force is applied on the other side of the block. So, for the determination of the magnitude of the net force on the block, we will resolve the forces. After getting the net force, we can easily put the given values for the calculation of acceleration.
Complete step by step answer:
It is given in the question that magnitudes of the forces ${F_1}$ and ${F_2}$ is $2\;mg$ and $mg$, and acceleration of the blocks A, B and C are ${a_1}$, ${a_2}$ and ${a_3}$. We will use this information in the calculation of acceleration of blocks.
First, we will apply Newton's law on block A.
Therefore, we get
$
\Rightarrow {F_{net}} = m{a_1}\\
\Rightarrow {F_1} - mg = m{a_1}
$
It is given in the question that the magnitude of the force ${F_1}$ is $2mg$, so substitute value of ${F_1}$ in the above equation.
$
\Rightarrow 2mg - mg = m{a_1}\\
\Rightarrow mg = m{a_1}\\
\Rightarrow {a_1} = g
$
Now we will apply Newton's law on block B.
Therefore, we get
$
\Rightarrow {F_{net}} = m{a_2}\\
\Rightarrow 2mg - mg = (2m + m){a_2}\\
\Rightarrow mg = 3m{a_2}\\
\Rightarrow {a_2} = \dfrac{g}{3}
$
Again, we will apply Newton's law on block C.
Therefore, we get
$\Rightarrow {F_2} + mg - mg = (m + m){a_3}\\
\Rightarrow {F_2} = 2m{a_3}
$
It is given in the question that the magnitude of the force ${F_2}$ is $mg$, so substitute the value of ${F_2}$ in the above equation.
$
\Rightarrow mg = 2m{a_3}\\
\Rightarrow {a_3} = \dfrac{g}{2}
$
Therefore, the accelerations of block A, B and C are $g$, $g/3$ and $g/2$, so the sequence of the accelerations of the blocks are ${a_1}\rangle {a_3}\rangle {a_2}$ and option (b) is correct.
Note: In this solution, the determination of the net force is the main thing. Here, additional load or force is applied on the other side of the block. So, for the determination of the magnitude of the net force on the block, we will resolve the forces. After getting the net force, we can easily put the given values for the calculation of acceleration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




