
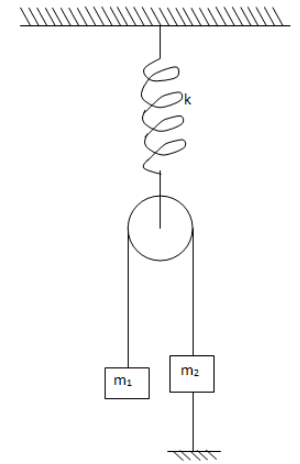
In the figure shows, pulley and spring are ideal. Find the potential energy stored in the spring (\[{m_1} > {m_2}\])

Answer
556.8k+ views
Hint:We are asked to find the potential energy stored in the spring. First, recall the formula to find potential energy stored in a spring. Draw a free body diagram of the problem. Using this diagram, find the value of displacement and use this value to find potential energy of the spring.
Complete step by step answer:
Given a figure where pulley and spring are ideal.The formula to find potential energy stored in a spring is,
\[P.E = \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}\] (i)
where \[k\] is the spring constant and \[x\] is the displacement from the mean position.
Let us draw the free body diagram for the problem.
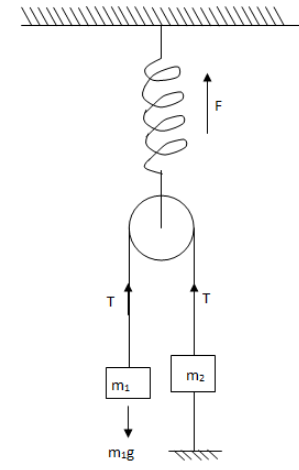
In the figure, \[F\] is the restoring force of the spring, \[T\] is the tension on the string and \[g\] is acceleration due to gravity.
Restoring force is given by the formula,
\[F = kx\] (ii)
where \[k\] is the spring constant and \[x\] is the displacement from the mean position.
From the figure we observe,
\[T + T = F\]
Putting the value of \[F\] we get,
\[T + T = kx\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2T = kx\]
\[ \Rightarrow T = \dfrac{1}{2}kx\] (iii)
From the figure we get,
\[T = {m_1}g\]
Putting the value of \[T\] we get,
\[\dfrac{1}{2}kx = {m_1}g\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{2{m_1}g}}{k}\]
Now, putting this value of \[x\] in equation (i) we get the potential energy as,
\[P.E = \dfrac{1}{2}k{\left( {\dfrac{{2{m_1}g}}{k}} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow P.E = \dfrac{1}{2}k\left( {\dfrac{{4{m_1}^2{g^2}}}{{{k^2}}}} \right)\]
\[ \therefore P.E = \dfrac{{2{m_1}^2{g^2}}}{k}\]
Therefore the potential energy stored in the spring is \[\dfrac{{2{m_1}^2{g^2}}}{k}\].
Note:For such types of problems, before proceeding for calculations, draw a free body diagram. A free body diagram is a diagram showing the forces and their directions acting on a given system. Here we have used the term restoring force, restoring force is the force which brings back an object to its mean position or equilibrium.
Complete step by step answer:
Given a figure where pulley and spring are ideal.The formula to find potential energy stored in a spring is,
\[P.E = \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}\] (i)
where \[k\] is the spring constant and \[x\] is the displacement from the mean position.
Let us draw the free body diagram for the problem.

In the figure, \[F\] is the restoring force of the spring, \[T\] is the tension on the string and \[g\] is acceleration due to gravity.
Restoring force is given by the formula,
\[F = kx\] (ii)
where \[k\] is the spring constant and \[x\] is the displacement from the mean position.
From the figure we observe,
\[T + T = F\]
Putting the value of \[F\] we get,
\[T + T = kx\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2T = kx\]
\[ \Rightarrow T = \dfrac{1}{2}kx\] (iii)
From the figure we get,
\[T = {m_1}g\]
Putting the value of \[T\] we get,
\[\dfrac{1}{2}kx = {m_1}g\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{2{m_1}g}}{k}\]
Now, putting this value of \[x\] in equation (i) we get the potential energy as,
\[P.E = \dfrac{1}{2}k{\left( {\dfrac{{2{m_1}g}}{k}} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow P.E = \dfrac{1}{2}k\left( {\dfrac{{4{m_1}^2{g^2}}}{{{k^2}}}} \right)\]
\[ \therefore P.E = \dfrac{{2{m_1}^2{g^2}}}{k}\]
Therefore the potential energy stored in the spring is \[\dfrac{{2{m_1}^2{g^2}}}{k}\].
Note:For such types of problems, before proceeding for calculations, draw a free body diagram. A free body diagram is a diagram showing the forces and their directions acting on a given system. Here we have used the term restoring force, restoring force is the force which brings back an object to its mean position or equilibrium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




