
In the figure shown, find the net velocity at point P? The diameter of the wheel is 35 cm and the center of mass velocity is 35 cm/s and the wheel is performing pure rolling.
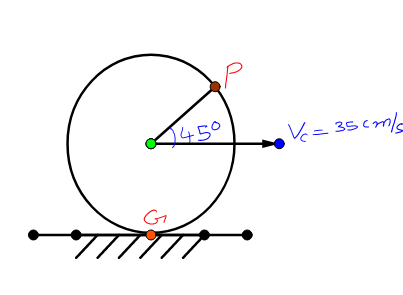
50 cm/s
75 cm/s
65 cm/s
10 cm/s

Answer
610.8k+ views
- Hint: In this problem, it is given that the wheel is performing a pure rolling, which means that the resultant velocity at the contact point between the wheel and the surface is zero.
Complete step-by-step solution -
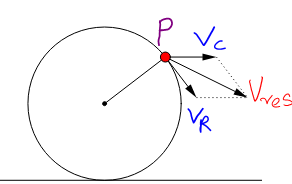
In the figure given above, we have denoted the different velocities at point ‘P’, they are ${{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}$ is the velocity of center of mass, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{R}}}$is the rotational velocity, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{res}}}$ is the resultant velocity at point ‘P’.
In the problem it is given that the wheel executes pure rolling, so the velocity at point ‘G’ is zero.
$\begin{align}
& {{\text{V}}_{\text{G}}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }{{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}-{{\text{V}}_{\text{R}}}=0 \\
\end{align}$
$\therefore {{\text{V}}_{\text{R}}}={{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}$
The angle between ${{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}$ and ${{\text{V}}_{\text{R}}}$ is . So we can calculate the resultant velocity using the formula,
${{\text{V}}_{\text{res}}}=\sqrt{{{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}^{2}+{{\text{V}}_{\text{R}}}^{2}+2{{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}{{\text{V}}_{\text{R}}}\cos \theta }$
Substituting the values of ${{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}$=${{\text{V}}_{\text{R}}}$ and $\theta $, we get
${{\text{V}}_{\text{res}}}=\sqrt{2{{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}^{2}(1+\cos (45))}$
${{\text{V}}_{\text{res}}}=\sqrt{2\times {{\left( 35 \right)}^{2}}\times \cos \left( 45 \right)}$
$\therefore \text{ }{{\text{V}}_{\text{res}}}=64.67\approx 65\text{ cm/s}$
So the answer is option (b) 65 cm/s.
Additional Information: Rolling motion is the combination of pure translational motion pure rotational motion.
At the center of the wheel, only translational velocity will be present, rotational velocity will be zero.
Note: If the rotational velocity is equal to the translational velocity, the velocity at the top part of the wheel will be 2 times the translational or rotational velocity and at the point of contact with the ground the resultant velocity will be zero.
Complete step-by-step solution -

In the figure given above, we have denoted the different velocities at point ‘P’, they are ${{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}$ is the velocity of center of mass, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{R}}}$is the rotational velocity, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{res}}}$ is the resultant velocity at point ‘P’.
In the problem it is given that the wheel executes pure rolling, so the velocity at point ‘G’ is zero.
$\begin{align}
& {{\text{V}}_{\text{G}}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }{{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}-{{\text{V}}_{\text{R}}}=0 \\
\end{align}$
$\therefore {{\text{V}}_{\text{R}}}={{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}$
The angle between ${{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}$ and ${{\text{V}}_{\text{R}}}$ is . So we can calculate the resultant velocity using the formula,
${{\text{V}}_{\text{res}}}=\sqrt{{{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}^{2}+{{\text{V}}_{\text{R}}}^{2}+2{{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}{{\text{V}}_{\text{R}}}\cos \theta }$
Substituting the values of ${{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}$=${{\text{V}}_{\text{R}}}$ and $\theta $, we get
${{\text{V}}_{\text{res}}}=\sqrt{2{{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}^{2}(1+\cos (45))}$
${{\text{V}}_{\text{res}}}=\sqrt{2\times {{\left( 35 \right)}^{2}}\times \cos \left( 45 \right)}$
$\therefore \text{ }{{\text{V}}_{\text{res}}}=64.67\approx 65\text{ cm/s}$
So the answer is option (b) 65 cm/s.
Additional Information: Rolling motion is the combination of pure translational motion pure rotational motion.
At the center of the wheel, only translational velocity will be present, rotational velocity will be zero.
Note: If the rotational velocity is equal to the translational velocity, the velocity at the top part of the wheel will be 2 times the translational or rotational velocity and at the point of contact with the ground the resultant velocity will be zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




