
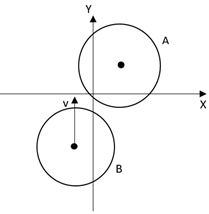
: In the figure shown above, a disc A of mass $m$ and radius $r$ is kept on a smooth horizontal (x-y) plane. The coordinates of the centre of the disk A can be written as $\left( \dfrac{r}{\sqrt{2}},\dfrac{r}{\sqrt{2}} \right)$. Another identical disc B having mass and radius identical as that of A moving along the line $x=\dfrac{-r}{\sqrt{2}}$ with its plane horizontal to x-y plane with speed ${{V}_{0}}$, makes elastic impact with A. The time of impact is $\Delta t$. The kinetic energy of the system is conserved in the elastic impact. The velocity of the disc B after collision will be given as,
$\begin{align}
& A.\dfrac{{{V}_{0}}}{\sqrt{2}}\left( -i+j \right) \\
& B.\dfrac{{{V}_{0}}}{\sqrt{2}}i \\
& C.{{V}_{0}}i \\
& D.\dfrac{{{V}_{0}}}{2}\left( -i+j \right) \\
\end{align}$

Answer
573k+ views
Hint: Calculate the velocity of the disc B after the collision. And after that determine the coordinates of the velocity of disc B. using this find the speed of disc A. The velocity is defined as the time rate of variation of the displacement of the body from one position to another one. This will help you in solving this question.
Complete answer:
A disc A has been mentioned with a mass $m$ and radius $r$.
The coordinates of the centre of the disc is given as,
$\left( \dfrac{r}{\sqrt{2}},\dfrac{r}{\sqrt{2}} \right)$
Then, another identical disc B having a mass and radius same as that of A has been mentioned. The disc B has been lying on the line. That is,
$x=\dfrac{-n}{\sqrt{2}}$
The speed has been mentioned as ${{V}_{0}}$.
The disc A is making an elastic impact with the disc B.
Therefore, the time of impact has been mentioned as,
$\text{time of impact}=\Delta t$
Let us find the velocity of the disc B after the collision. As this is along the X-axis,
$Y=0$
Therefore, the coordinate of the velocity of B after the collision will be given as,
${{V}_{B}}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\left( -i+j \right)$
Where the radius will become,
$r=1$
Now, \[{{V}_{0}}\] will be the speed of A.
Therefore the speed of disc A has been given as,
\[\dfrac{{{V}_{0}}}{\sqrt{2}}\left( -i+j \right)\]
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
An elastic collision is defined as a kind of collision in which there will be no resultant loss in kinetic energy in the system because of the collision. Here the momentum and the kinetic energy will be conserved. The collision in which the kinetic energy is lost is known as inelastic collision.
Complete answer:
A disc A has been mentioned with a mass $m$ and radius $r$.
The coordinates of the centre of the disc is given as,
$\left( \dfrac{r}{\sqrt{2}},\dfrac{r}{\sqrt{2}} \right)$
Then, another identical disc B having a mass and radius same as that of A has been mentioned. The disc B has been lying on the line. That is,
$x=\dfrac{-n}{\sqrt{2}}$
The speed has been mentioned as ${{V}_{0}}$.
The disc A is making an elastic impact with the disc B.
Therefore, the time of impact has been mentioned as,
$\text{time of impact}=\Delta t$
Let us find the velocity of the disc B after the collision. As this is along the X-axis,
$Y=0$
Therefore, the coordinate of the velocity of B after the collision will be given as,
${{V}_{B}}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\left( -i+j \right)$
Where the radius will become,
$r=1$
Now, \[{{V}_{0}}\] will be the speed of A.
Therefore the speed of disc A has been given as,
\[\dfrac{{{V}_{0}}}{\sqrt{2}}\left( -i+j \right)\]
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
An elastic collision is defined as a kind of collision in which there will be no resultant loss in kinetic energy in the system because of the collision. Here the momentum and the kinetic energy will be conserved. The collision in which the kinetic energy is lost is known as inelastic collision.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




