
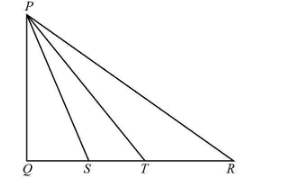
In the figure, S and T trisect the side QR of a right triangle PQR
Prove that ${\rm{8 P}}{{\rm{T}}^2} = 3{\rm{P}}{{\rm{R}}^2} + 5{\rm{P}}{{\rm{S}}^2}$

Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: This question is based on Trigonometry. In this question, a right-angled triangle is given and also two points in the base of the triangle trisect the base of the triangle into three equal parts. By doing so, there are now three right-angled triangles and in order to find the relation between them, we use the Pythagoras Theorem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the given right-angled triangle $\Delta PQR$ two points S and T trisect the side QR into three equal parts. Which means that,
\[
QS{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}ST{\rm{ }}\\
= {\rm{ TR}}
\]
Let us assume the value of \[QS{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}ST{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ TR}}\] is $x$ then,
\[
\;QS{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}ST{\rm{ }}\\
= {\rm{ }}TR\\
{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}x
\]
From the $\Delta PQR$ we have,
\[
QR{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}QS + ST + TR\\
= x + x + x\\
= 3x
\]
And,
\[
QT{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}QS + ST\\
= x + x\\
= 2x
\]
Now applying the Pythagoras Theorem in the right-angled triangle $\Delta PQR$ we get,
\[P{R^{2\;}} = {\rm{ }}P{Q^2}\; + {\rm{ }}Q{R^2}\]
Substituting the value of $QR$ in the expression we get,
\[
{P{R^{2\;}} = {\rm{ }}P{Q^2}\; + {{\left( {3x} \right)}^2}}\\
{P{R^{2\;}} = {\rm{ }}P{Q^2}\; + {\rm{ }}9{x^2}}
\]
Similarly, applying Pythagoras Theorem in the right-angled triangle $\Delta PQT$ we get,
\[P{T^2}\; = {\rm{ }}P{Q^{2\;}} + {\rm{ Q}}{T^2}\]
Substituting the value of $QT$ in the expression we get,
\[
{P{T^2}\; = {\rm{ }}P{Q^{2\;}} + {\rm{ }}{{\left( {2x} \right)}^2}}\\
{P{T^2}\; = {\rm{ }}P{Q^{2\;}} + {\rm{ }}4{x^2}}
\]
And, applying Pythagoras Theorem in the right-angled triangle$\Delta PQS$ we get,
\[P{S^2}\; = {\rm{ }}P{Q^2}\; + Q{S^2}\]
Substituting the value of $QS$ in the expression we get,
\[P{S^2}\; = {\rm{ }}P{Q^2}\; + {x^2}\]
We have to prove that,
${\rm{8 P}}{{\rm{T}}^2} = 3{\rm{P}}{{\rm{R}}^2} + 5{\rm{P}}{{\rm{S}}^2}$
Substituting the values of $PT,PR{\rm{ and }}PS$ that we have calculated in this expression, we get,
\[
8\left( {P{Q^{2\;}} + {\rm{ }}4{x^2}} \right){\rm{ }} = 3\left( {P{Q^2}\; + {\rm{ }}9{x^2}} \right){\rm{ + }}5{\rm{ }}\left( {P{Q^2}\; + {\rm{ }}{x^2}} \right)\\
8P{Q^{2\;}} + {\rm{ }}32{x^2} = 3P{Q^2}\; + {\rm{ }}27{x^2}\; + {\rm{ }}5P{Q^2}\; + {\rm{ }}5{x^2}\\
8P{Q^{2\;}} + {\rm{ }}32{x^2} = \;8P{Q^{2\;}} + {\rm{ }}32{x^2}
\]
Therefore, LHS = RHS.
Hence, it is proven that ${\rm{8 P}}{{\rm{T}}^2} = 3{\rm{P}}{{\rm{R}}^2} + 5{\rm{P}}{{\rm{S}}^2}$
Note: The alternate method of solving this question was to take either LHS or RHS of the expression that we have to prove and get the other side of the expression from it.
For example, taking the RHS of the expression we have,
$
3{\rm{P}}{{\rm{R}}^2} + 5{\rm{P}}{{\rm{S}}^2} = 3\left( {P{Q^2}\; + {\rm{ }}9{x^2}} \right){\rm{ + }}5{\rm{ }}\left( {P{Q^2}\; + {\rm{ }}{x^2}} \right)\\
= 3P{Q^2}\; + {\rm{ }}27{x^2}\; + {\rm{ }}5P{Q^2}\; + {\rm{ }}5{x^2}\\
= 8P{Q^{2\;}} + {\rm{ }}32{x^2}
$
We know that \[P{T^2}\; = {\rm{ }}P{Q^{2\;}} + {\rm{ }}4{x^2}\] or \[\;{\rm{ }}P{Q^{2\;}} = P{T^2}{\rm{ - }}4{x^2}\]
Substituting this value in the expression we get,
$
3{\rm{P}}{{\rm{R}}^2} + 5{\rm{P}}{{\rm{S}}^2} = 8\left( {P{T^2}{\rm{ - }}4{x^2}} \right) + {\rm{ }}32{x^2}\\
= 8P{T^2} - 32{x^2} + 32{x^2}\\
= 8P{T^2}
$
Therefore, RHS = LHS.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the given right-angled triangle $\Delta PQR$ two points S and T trisect the side QR into three equal parts. Which means that,
\[
QS{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}ST{\rm{ }}\\
= {\rm{ TR}}
\]
Let us assume the value of \[QS{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}ST{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ TR}}\] is $x$ then,
\[
\;QS{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}ST{\rm{ }}\\
= {\rm{ }}TR\\
{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}x
\]
From the $\Delta PQR$ we have,
\[
QR{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}QS + ST + TR\\
= x + x + x\\
= 3x
\]
And,
\[
QT{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}QS + ST\\
= x + x\\
= 2x
\]
Now applying the Pythagoras Theorem in the right-angled triangle $\Delta PQR$ we get,
\[P{R^{2\;}} = {\rm{ }}P{Q^2}\; + {\rm{ }}Q{R^2}\]
Substituting the value of $QR$ in the expression we get,
\[
{P{R^{2\;}} = {\rm{ }}P{Q^2}\; + {{\left( {3x} \right)}^2}}\\
{P{R^{2\;}} = {\rm{ }}P{Q^2}\; + {\rm{ }}9{x^2}}
\]
Similarly, applying Pythagoras Theorem in the right-angled triangle $\Delta PQT$ we get,
\[P{T^2}\; = {\rm{ }}P{Q^{2\;}} + {\rm{ Q}}{T^2}\]
Substituting the value of $QT$ in the expression we get,
\[
{P{T^2}\; = {\rm{ }}P{Q^{2\;}} + {\rm{ }}{{\left( {2x} \right)}^2}}\\
{P{T^2}\; = {\rm{ }}P{Q^{2\;}} + {\rm{ }}4{x^2}}
\]
And, applying Pythagoras Theorem in the right-angled triangle$\Delta PQS$ we get,
\[P{S^2}\; = {\rm{ }}P{Q^2}\; + Q{S^2}\]
Substituting the value of $QS$ in the expression we get,
\[P{S^2}\; = {\rm{ }}P{Q^2}\; + {x^2}\]
We have to prove that,
${\rm{8 P}}{{\rm{T}}^2} = 3{\rm{P}}{{\rm{R}}^2} + 5{\rm{P}}{{\rm{S}}^2}$
Substituting the values of $PT,PR{\rm{ and }}PS$ that we have calculated in this expression, we get,
\[
8\left( {P{Q^{2\;}} + {\rm{ }}4{x^2}} \right){\rm{ }} = 3\left( {P{Q^2}\; + {\rm{ }}9{x^2}} \right){\rm{ + }}5{\rm{ }}\left( {P{Q^2}\; + {\rm{ }}{x^2}} \right)\\
8P{Q^{2\;}} + {\rm{ }}32{x^2} = 3P{Q^2}\; + {\rm{ }}27{x^2}\; + {\rm{ }}5P{Q^2}\; + {\rm{ }}5{x^2}\\
8P{Q^{2\;}} + {\rm{ }}32{x^2} = \;8P{Q^{2\;}} + {\rm{ }}32{x^2}
\]
Therefore, LHS = RHS.
Hence, it is proven that ${\rm{8 P}}{{\rm{T}}^2} = 3{\rm{P}}{{\rm{R}}^2} + 5{\rm{P}}{{\rm{S}}^2}$
Note: The alternate method of solving this question was to take either LHS or RHS of the expression that we have to prove and get the other side of the expression from it.
For example, taking the RHS of the expression we have,
$
3{\rm{P}}{{\rm{R}}^2} + 5{\rm{P}}{{\rm{S}}^2} = 3\left( {P{Q^2}\; + {\rm{ }}9{x^2}} \right){\rm{ + }}5{\rm{ }}\left( {P{Q^2}\; + {\rm{ }}{x^2}} \right)\\
= 3P{Q^2}\; + {\rm{ }}27{x^2}\; + {\rm{ }}5P{Q^2}\; + {\rm{ }}5{x^2}\\
= 8P{Q^{2\;}} + {\rm{ }}32{x^2}
$
We know that \[P{T^2}\; = {\rm{ }}P{Q^{2\;}} + {\rm{ }}4{x^2}\] or \[\;{\rm{ }}P{Q^{2\;}} = P{T^2}{\rm{ - }}4{x^2}\]
Substituting this value in the expression we get,
$
3{\rm{P}}{{\rm{R}}^2} + 5{\rm{P}}{{\rm{S}}^2} = 8\left( {P{T^2}{\rm{ - }}4{x^2}} \right) + {\rm{ }}32{x^2}\\
= 8P{T^2} - 32{x^2} + 32{x^2}\\
= 8P{T^2}
$
Therefore, RHS = LHS.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




