
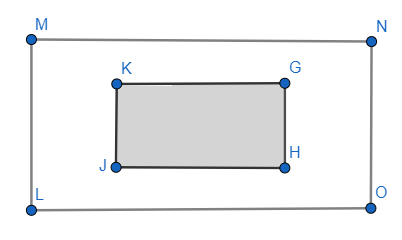
In the figure, LMNO and GHJK are rectangles where $GH=\dfrac{1}{2}LM$ and $HJ=\dfrac{1}{2}MN$. What fraction of LMNO is not shaded?

Answer
612.9k+ views
Hint: Fraction in the question refers to the fraction of the area shaded from the area of the whole region bounded by the rectangle LMNO. For finding the area of the unshaded region, we subtract the area of the shaded region from the whole bounded area.
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
$GH=\dfrac{1}{2}LM$
$HJ=\dfrac{1}{2}MN$
Let’s start with the formula for the area of the rectangle.
The area of the rectangle is the product of its length and breadth.
Area of a rectangle with length ‘l’ and breadth ‘b’ $=l\times b$ .
Using the above formula:
Area of rectangle LMNO $=l\times b=MN\times LM.......................(i)$
Now, finding the area of the shaded region GHJK.
Using the formula for the area of the rectangle, we have;
Area of rectangle GHJK $=l\times b=GH\times HJ$ .
Substituting the value of GH and HJ with the data given in the question:
$\text{Area of rectangle GHJK}=GH\times HJ=\dfrac{1}{2}LM\times \dfrac{1}{2}MN=\dfrac{1}{4}LM\times MN............(ii)$
Now, from the figure:
Area of unshaded region = (Area of bounded region LMNO) – (Area of shaded region GHJK)
Substituting from equation (i) and equation (ii), we get:
\[\text{Area of unshaded region=}\left( \text{MN}\times \text{LM} \right)\text{-}\dfrac{\left( \text{MN}\times \text{LM} \right)}{4}\].
\[\therefore \text{Area of unshaded region=}\dfrac{\text{3}\left( \text{MN}\times \text{LM} \right)}{4}\].
The fraction of unshaded region = $\dfrac{\text{Area of unshaded region}}{\text{Area of bounded region LMNO}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{\text{3}\left( \text{MN }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ LM} \right)}{\text{4}}}{\text{MN }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ LM}}=\dfrac{3}{4}$.
Therefore, the fraction of LMNO that is not shaded is $\dfrac{3}{4}$ .
Note: Always try to break the 2-D geometrical figures in known forms like a combination of circles, squares, and other simple figures which you know well as this helps you to solve the problems faster and reach a correct conclusion. If you cannot break to simple geometrical figures, then you need to take the route of coordinate geometry along with integration for finding the area.
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
$GH=\dfrac{1}{2}LM$
$HJ=\dfrac{1}{2}MN$
Let’s start with the formula for the area of the rectangle.
The area of the rectangle is the product of its length and breadth.
Area of a rectangle with length ‘l’ and breadth ‘b’ $=l\times b$ .
Using the above formula:
Area of rectangle LMNO $=l\times b=MN\times LM.......................(i)$
Now, finding the area of the shaded region GHJK.
Using the formula for the area of the rectangle, we have;
Area of rectangle GHJK $=l\times b=GH\times HJ$ .
Substituting the value of GH and HJ with the data given in the question:
$\text{Area of rectangle GHJK}=GH\times HJ=\dfrac{1}{2}LM\times \dfrac{1}{2}MN=\dfrac{1}{4}LM\times MN............(ii)$
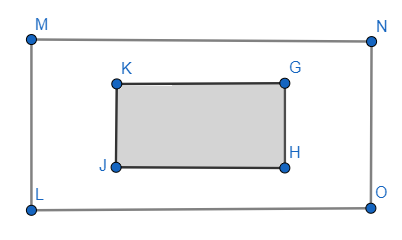
Now, from the figure:

Area of unshaded region = (Area of bounded region LMNO) – (Area of shaded region GHJK)
Substituting from equation (i) and equation (ii), we get:
\[\text{Area of unshaded region=}\left( \text{MN}\times \text{LM} \right)\text{-}\dfrac{\left( \text{MN}\times \text{LM} \right)}{4}\].
\[\therefore \text{Area of unshaded region=}\dfrac{\text{3}\left( \text{MN}\times \text{LM} \right)}{4}\].
The fraction of unshaded region = $\dfrac{\text{Area of unshaded region}}{\text{Area of bounded region LMNO}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{\text{3}\left( \text{MN }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ LM} \right)}{\text{4}}}{\text{MN }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ LM}}=\dfrac{3}{4}$.
Therefore, the fraction of LMNO that is not shaded is $\dfrac{3}{4}$ .
Note: Always try to break the 2-D geometrical figures in known forms like a combination of circles, squares, and other simple figures which you know well as this helps you to solve the problems faster and reach a correct conclusion. If you cannot break to simple geometrical figures, then you need to take the route of coordinate geometry along with integration for finding the area.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




