
In the figure if F=4N, m=2kg and M=4kg then,
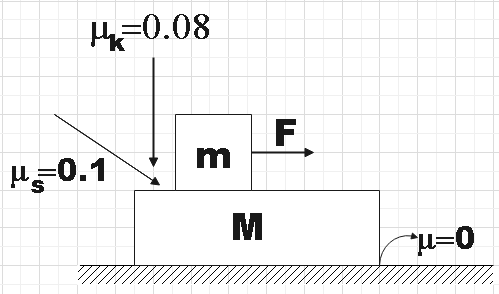
A. the acceleration of m with respect to ground is $\dfrac{2}{3}m{{s}^{-2}}$
B. The acceleration of m with respect to ground is $1.2m{{s}^{-2}}$
C. Acceleration of M is $0.4m{{s}^{-2}}$
D. Acceleration of m with respect to ground is zero.

Answer
533.1k+ views
Hint: As a first step, you could make a free body diagram of the first block of mass marking all the forces acting on it. Thus you could find the net force on this block and hence the net acceleration. After that find the magnitude of the force on the second block and follow the same steps to find the acceleration.
Formula used:
Newton’s second law of motion,
$F=ma$
Frictional force,
$f={{\mu }_{k}}N$
Complete answer:
In the question we are given two blocks of masses m=2kg and M=4kg. We are given a figure followed by four options regarding the accelerations of the two blocks. In order to solve the question, we have to make free body diagrams.
The forces on the first block of mass m could be given by the following free body diagram,
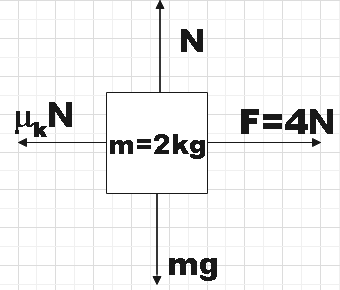
From the figure, we see that the normal reaction on the block is balanced by the weight of the body.
$N=mg=2\times 10=20$
The coefficient of kinetic friction between the two blocks is given as,
${{\mu }_{k}}=0.08$
Now we have the frictional force,
$f={{\mu }_{k}}N=0.08\times 20=1.6N$
The net force on this block can be given by,
${{F}_{net}}=F-f=4-1.6$
From Newton’s second law of motion, we have,
$\Rightarrow ma=3.4$
$\therefore a=\dfrac{3.4}{2}=1.2m{{s}^{-2}}$
Therefore, we found the acceleration of the block of mass m=2kg to be,
$a=1.2m{{s}^{-2}}$
Now, for the second block we are given that the coefficient of friction between the block and the floor is 0, so there would be a force on the second block which would be equal in magnitude to the frictional force on the first block.
${{F}_{net}}'=1.6N$
$\Rightarrow Ma'=1.6N$
$\therefore a'=\dfrac{1.6}{4}=0.4m{{s}^{-2}}$
Therefore, we found the acceleration of the second block to be$0.4m{{s}^{-2}}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option B and C”.
Note: Quite obviously when we are given that the coefficient of friction is zero it would mean that the block would slip. Also, both the accelerations are asked to be found with respect to the ground and we have found them accordingly. Always remember to mark all the forces acting on the block while making the free body diagram.
Formula used:
Newton’s second law of motion,
$F=ma$
Frictional force,
$f={{\mu }_{k}}N$
Complete answer:
In the question we are given two blocks of masses m=2kg and M=4kg. We are given a figure followed by four options regarding the accelerations of the two blocks. In order to solve the question, we have to make free body diagrams.
The forces on the first block of mass m could be given by the following free body diagram,

From the figure, we see that the normal reaction on the block is balanced by the weight of the body.
$N=mg=2\times 10=20$
The coefficient of kinetic friction between the two blocks is given as,
${{\mu }_{k}}=0.08$
Now we have the frictional force,
$f={{\mu }_{k}}N=0.08\times 20=1.6N$
The net force on this block can be given by,
${{F}_{net}}=F-f=4-1.6$
From Newton’s second law of motion, we have,
$\Rightarrow ma=3.4$
$\therefore a=\dfrac{3.4}{2}=1.2m{{s}^{-2}}$
Therefore, we found the acceleration of the block of mass m=2kg to be,
$a=1.2m{{s}^{-2}}$
Now, for the second block we are given that the coefficient of friction between the block and the floor is 0, so there would be a force on the second block which would be equal in magnitude to the frictional force on the first block.
${{F}_{net}}'=1.6N$
$\Rightarrow Ma'=1.6N$
$\therefore a'=\dfrac{1.6}{4}=0.4m{{s}^{-2}}$
Therefore, we found the acceleration of the second block to be$0.4m{{s}^{-2}}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option B and C”.
Note: Quite obviously when we are given that the coefficient of friction is zero it would mean that the block would slip. Also, both the accelerations are asked to be found with respect to the ground and we have found them accordingly. Always remember to mark all the forces acting on the block while making the free body diagram.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




