
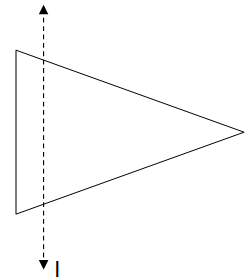
In the figure, I is the line of symmetry. Draw the image of the triangle and complete the diagram so that it becomes symmetric.

Answer
597k+ views
Hint: In order to solve the problem first we will understand the meaning of the line of symmetry with the help of some example and concept and then we will draw the diagram of the given figure such that the figure becomes symmetric about the given line "I".
Complete step by step answer:
We have the figure given which is unsymmetrical about the given line "I". And we have to make the figure symmetrical about the line.
Line of symmetry can be defined as some type of imaginary axis or line which passes through the centre of the figure and divides the figure into two identical halves which can be overlapped over each other if the figure is folded about the line of symmetry.
For example any diameter of the circle is the line of symmetry for the circle.
As the line of symmetry is "I" so the part of the figure on the left side of the line will be drawn on the right side of the line and the part of the figure initially on the right side of the figure will be drawn on the left side of the line as shown below in the figure.
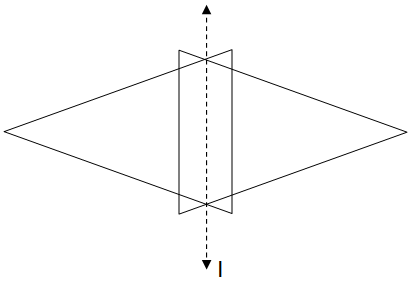
Hence, we can see that the above figure is symmetrical about the line "I".
Note: In order to solve such types of problems, students must visualize the problem and the figure. There may be different types of lines of symmetry on the basis of types of figure and there may also be one or more lines of symmetry for a particular figure. There is something symmetrical because all sides are the same. If a central dividing line (a mirror line) can be drawn on it, a shape has symmetry, to indicate that all sides of the form are precisely the same.
Complete step by step answer:
We have the figure given which is unsymmetrical about the given line "I". And we have to make the figure symmetrical about the line.
Line of symmetry can be defined as some type of imaginary axis or line which passes through the centre of the figure and divides the figure into two identical halves which can be overlapped over each other if the figure is folded about the line of symmetry.
For example any diameter of the circle is the line of symmetry for the circle.
As the line of symmetry is "I" so the part of the figure on the left side of the line will be drawn on the right side of the line and the part of the figure initially on the right side of the figure will be drawn on the left side of the line as shown below in the figure.

Hence, we can see that the above figure is symmetrical about the line "I".
Note: In order to solve such types of problems, students must visualize the problem and the figure. There may be different types of lines of symmetry on the basis of types of figure and there may also be one or more lines of symmetry for a particular figure. There is something symmetrical because all sides are the same. If a central dividing line (a mirror line) can be drawn on it, a shape has symmetry, to indicate that all sides of the form are precisely the same.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




