
In the figure given below, ABCD is a parallelogram. If L and M are mid – points of sides BC and CD respectively. Prove that, 8 (area of \[\Delta ALM\]) = 3 (area of ABCD).
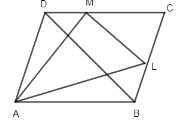

Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint: To solve this question we will use two theorems. One is “Diagonals of a parallelogram divide the parallelogram into two triangles of equal area” and secondly; when in a parallelogram ABCD, L is the mid – point of BC, M is the mid – point of DC then area of \[\Delta LMC\] is equal to \[\dfrac{1}{4}\] area of \[\Delta BCD\]. We will begin by joining the diagonals of the parallelogram and dividing it into two triangles of equal area, ABC and ACD.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given that ABCD is a parallelogram.
First step is to join the diagonals AC and BD of the parallelogram ABCD, as given below –
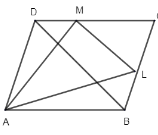
Now let the area of parallelogram ABCD be x then as diagonals of a parallelogram divide the parallelogram into two triangles of equal area.
Therefore diagonal AC divides ABCD in two triangles ABC & ACD of equal area.
\[\Rightarrow \] area (\[\Delta ABC\]) = area (\[\Delta ACD\]) – (1)
Also area (\[\Delta ABC\]) + area (\[\Delta ACD\]) = area (ABCD) = x.
\[\Rightarrow \] area (\[\Delta ABC\]) + area (\[\Delta ABC\]) = x
\[\Rightarrow \] 2area (\[\Delta ABC\]) = x
\[\Rightarrow \] area (\[\Delta ABC\]) = \[\dfrac{x}{2}\].
Hence we got area area (\[\Delta ABC\]) = area (\[\Delta ACD\]) = \[\dfrac{x}{2}\] - (2)
Similar method can be followed while considering diagonal BD of parallelogram ABCD and triangles ABD and BDC.
Therefore \[\Rightarrow \]area (\[\Delta BDC\]) = area (\[\Delta ABD\]) = \[\dfrac{x}{2}\] - (*)
Now given that L and M are the mid – points of side BC and CD respectively.
Then AL and AM are the medians.
Since the median divides the triangle into two equal areas – (3).
\[\Rightarrow \] When median AM is considered then,
Area of \[\Delta AMC=\dfrac{1}{2}\] area of \[\Delta ADC\].
Now using equation (2), we have,
Area of \[\Delta AMC=\dfrac{1}{2}\] area of \[\Delta ADC\] = \[\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \dfrac{x}{2} \right)\].
\[\Rightarrow \] area of \[\Delta AMC=\dfrac{x}{4}\] - (4)
Similarly when we consider median AL of triangle ABC then,
Area of \[\Delta ALC=\dfrac{1}{2}\] area of \[\Delta ABC\].
Again by using equation (2) we get,
Area of \[\Delta ALC=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \dfrac{x}{2} \right)=\dfrac{x}{4}\] - (5)
Now consider quadrilateral ALCM,
Area (ALCM) = area (ALC) + area (AMC)
By using (3) & (4) we get,
Area (ALCM) = \[\dfrac{x}{4}+\dfrac{x}{4}=\dfrac{2x}{4}=\dfrac{x}{2}\].
Now area of \[\Delta ALM\] = area (ALCM) – area (\[\Delta LCM\])
Now area of \[\Delta ALM\] = area (ABCD) – {area (\[\Delta ABL\]) + area (\[\Delta ADM\]) + area (\[\Delta LMC\])}.
Now because area of \[\Delta ABL\] = area of \[\Delta ALC=\dfrac{x}{4}\]
This is obtained by using (3) & (5).
Again similarly the area of \[\Delta ADM\] = area of \[\Delta AMC=\dfrac{x}{4}\].
Using equation (3) and (4),
Then we have,
Area of \[\Delta ALM=x\] - { \[\dfrac{x}{4}+\dfrac{x}{4}\] + area of \[\left( \Delta LMC \right)\] }
Now again the area of \[\Delta LMC=\dfrac{1}{8}\] area of ABCD.
This is to because when L is the mid – point of BC and M is the mid – point of DC then area of \[\Delta LMC\] is equation \[\dfrac{1}{4}\] area of \[\Delta BCD\].
Now from (*) we had an area of \[\Delta BCD=\dfrac{x}{2}\].
Then the area of \[\Delta LMC=\dfrac{1}{4}\left( \dfrac{x}{2} \right)=\dfrac{x}{8}\].
Finally we have,
Area of \[\Delta ALM=x-\left\{ \dfrac{x}{4}+\dfrac{x}{4}+\dfrac{x}{8} \right\}\]
Area of \[\Delta ALM=x-\left\{ \dfrac{x}{2}+\dfrac{x}{8} \right\}\]
Area of \[\Delta ALM=x-\left\{ \dfrac{4x+x}{8} \right\}\]
Area of \[\Delta ALM=x-\dfrac{5x}{8}\]
Area of \[\Delta ALM=\dfrac{\left( 8-5 \right)x}{8}\]
Area of \[\Delta ALM=\dfrac{3}{8}x\]
\[\Rightarrow \] 8 (area of \[\Delta ALM\]) = 3 (area of parallelogram ABCD)
Hence proved.
Note: The solution is a bit longer so you need not confuse and patiently proceed to get the answer. The possibility of error in this question can be at a point where you have taken \[\Delta ALM\]. Be careful that we have to find the area of triangle ALM and area of ABCD therefore it is important to relate the area of \[\Delta BCD\] or \[\Delta BDC\] to the area of ABCD.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given that ABCD is a parallelogram.
First step is to join the diagonals AC and BD of the parallelogram ABCD, as given below –

Now let the area of parallelogram ABCD be x then as diagonals of a parallelogram divide the parallelogram into two triangles of equal area.
Therefore diagonal AC divides ABCD in two triangles ABC & ACD of equal area.
\[\Rightarrow \] area (\[\Delta ABC\]) = area (\[\Delta ACD\]) – (1)
Also area (\[\Delta ABC\]) + area (\[\Delta ACD\]) = area (ABCD) = x.
\[\Rightarrow \] area (\[\Delta ABC\]) + area (\[\Delta ABC\]) = x
\[\Rightarrow \] 2area (\[\Delta ABC\]) = x
\[\Rightarrow \] area (\[\Delta ABC\]) = \[\dfrac{x}{2}\].
Hence we got area area (\[\Delta ABC\]) = area (\[\Delta ACD\]) = \[\dfrac{x}{2}\] - (2)
Similar method can be followed while considering diagonal BD of parallelogram ABCD and triangles ABD and BDC.
Therefore \[\Rightarrow \]area (\[\Delta BDC\]) = area (\[\Delta ABD\]) = \[\dfrac{x}{2}\] - (*)
Now given that L and M are the mid – points of side BC and CD respectively.
Then AL and AM are the medians.
Since the median divides the triangle into two equal areas – (3).
\[\Rightarrow \] When median AM is considered then,
Area of \[\Delta AMC=\dfrac{1}{2}\] area of \[\Delta ADC\].
Now using equation (2), we have,
Area of \[\Delta AMC=\dfrac{1}{2}\] area of \[\Delta ADC\] = \[\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \dfrac{x}{2} \right)\].
\[\Rightarrow \] area of \[\Delta AMC=\dfrac{x}{4}\] - (4)
Similarly when we consider median AL of triangle ABC then,
Area of \[\Delta ALC=\dfrac{1}{2}\] area of \[\Delta ABC\].
Again by using equation (2) we get,
Area of \[\Delta ALC=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \dfrac{x}{2} \right)=\dfrac{x}{4}\] - (5)
Now consider quadrilateral ALCM,
Area (ALCM) = area (ALC) + area (AMC)
By using (3) & (4) we get,
Area (ALCM) = \[\dfrac{x}{4}+\dfrac{x}{4}=\dfrac{2x}{4}=\dfrac{x}{2}\].
Now area of \[\Delta ALM\] = area (ALCM) – area (\[\Delta LCM\])
Now area of \[\Delta ALM\] = area (ABCD) – {area (\[\Delta ABL\]) + area (\[\Delta ADM\]) + area (\[\Delta LMC\])}.
Now because area of \[\Delta ABL\] = area of \[\Delta ALC=\dfrac{x}{4}\]
This is obtained by using (3) & (5).
Again similarly the area of \[\Delta ADM\] = area of \[\Delta AMC=\dfrac{x}{4}\].
Using equation (3) and (4),
Then we have,
Area of \[\Delta ALM=x\] - { \[\dfrac{x}{4}+\dfrac{x}{4}\] + area of \[\left( \Delta LMC \right)\] }
Now again the area of \[\Delta LMC=\dfrac{1}{8}\] area of ABCD.
This is to because when L is the mid – point of BC and M is the mid – point of DC then area of \[\Delta LMC\] is equation \[\dfrac{1}{4}\] area of \[\Delta BCD\].
Now from (*) we had an area of \[\Delta BCD=\dfrac{x}{2}\].
Then the area of \[\Delta LMC=\dfrac{1}{4}\left( \dfrac{x}{2} \right)=\dfrac{x}{8}\].
Finally we have,
Area of \[\Delta ALM=x-\left\{ \dfrac{x}{4}+\dfrac{x}{4}+\dfrac{x}{8} \right\}\]
Area of \[\Delta ALM=x-\left\{ \dfrac{x}{2}+\dfrac{x}{8} \right\}\]
Area of \[\Delta ALM=x-\left\{ \dfrac{4x+x}{8} \right\}\]
Area of \[\Delta ALM=x-\dfrac{5x}{8}\]
Area of \[\Delta ALM=\dfrac{\left( 8-5 \right)x}{8}\]
Area of \[\Delta ALM=\dfrac{3}{8}x\]
\[\Rightarrow \] 8 (area of \[\Delta ALM\]) = 3 (area of parallelogram ABCD)
Hence proved.
Note: The solution is a bit longer so you need not confuse and patiently proceed to get the answer. The possibility of error in this question can be at a point where you have taken \[\Delta ALM\]. Be careful that we have to find the area of triangle ALM and area of ABCD therefore it is important to relate the area of \[\Delta BCD\] or \[\Delta BDC\] to the area of ABCD.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





