
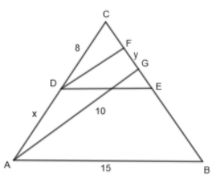
In the figure, DF||AG, DE||AB, AB = 15, CD = 8, AD = x, DE = 10, FG = y and CG = 6. The ratio x:y equals to:
(a) 1:2
(b) 1:3
(c) 2:1
(d) 3:2

Answer
599.1k+ views
Hint: In order to find the solution of this question, we should have the knowledge of similar triangles like if any 2 of the 3 angles of a triangle are congruent with the 2 angles of the other triangle, then the triangles are similar triangles by AA criteria. Also, we should have knowledge about the properties of parallel lines like corresponding angles of the parallel lines are equal. By using this concept, we can find the required answer to the question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we have been asked to find the value of x and y in the given figure with few given conditions.
To solve this question, we should know about the properties of the similar triangles, that is, if any 2 pairs of angles of the triangles are congruent then the triangles are similar and then the ratio of the corresponding sides are equal.
So, let us consider triangle ABC and triangle DEC, then we have been given that DE is parallel to AB. So, we can say by the properties of the corresponding angles,
\[\angle CDE=\angle CAB\]
\[\angle CED=\angle CBA\]
Therefore, we can say by AA criteria that,
\[\Delta ABC\sim \Delta DEC\]
Hence, we can say,
\[\dfrac{AC}{DC}=\dfrac{AB}{DE}=\dfrac{BC}{CE}\]
So, we can say, \[\dfrac{AC}{DC}=\dfrac{AB}{DE}.\] Now, we know that it can be further written as,
\[\dfrac{8+x}{8}=\dfrac{15}{10}\]
Now, we will simplify it to get the value of x. So, we get,
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{8+x}{8}=\dfrac{3}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow 16+2x=24\]
\[\Rightarrow 2x=24-16\]
\[\Rightarrow 2x=8\]
\[\Rightarrow x=4.....\left( i \right)\]
Now, we will consider triangle ACG and triangle DCF. We have been given that DF is parallel to AG. So, we can say, by the properties of corresponding angles,
\[\angle CDF=\angle CAG\]
\[\angle CFD=\angle CGA\]
Therefore, we can say by AA criteria that,
\[\Delta ACG\sim \Delta DCF\]
Hence, we can say,
\[\dfrac{AC}{DC}=\dfrac{AG}{DF}=\dfrac{CG}{CF}\]
So, we can say, \[\dfrac{AC}{DC}=\dfrac{CG}{CF}.\] Now, we know that it can be further written as,
\[\dfrac{8+x}{8}=\dfrac{6}{6-y}\]
Now, we will put the value of x from equation (i) and get the value of y. So, we get,
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{8+4}{8}=\dfrac{6}{6-y}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{12}{8}=\dfrac{6}{6-y}\]
\[\Rightarrow 6-y=\dfrac{6\times 8}{12}\]
\[\Rightarrow 6-y=4\]
\[\Rightarrow y=6-4\]
\[\Rightarrow y=2.....\left( ii \right)\]
From equation (i) and (ii), we can say,
\[\dfrac{x}{y}=\dfrac{4}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{y}=\dfrac{2}{1}\]
Hence, we can say, x:y = 2:1.
Therefore, option (c) is the right answer.
Note: While solving the question, the possible mistake one can make is by taking the wrong pair of the side after proving the triangles similar which will give us the wrong answer, and hence we will lose our marks. So, we have to be very careful while choosing the sides at the time of taking the ratio.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we have been asked to find the value of x and y in the given figure with few given conditions.

To solve this question, we should know about the properties of the similar triangles, that is, if any 2 pairs of angles of the triangles are congruent then the triangles are similar and then the ratio of the corresponding sides are equal.
So, let us consider triangle ABC and triangle DEC, then we have been given that DE is parallel to AB. So, we can say by the properties of the corresponding angles,
\[\angle CDE=\angle CAB\]
\[\angle CED=\angle CBA\]
Therefore, we can say by AA criteria that,
\[\Delta ABC\sim \Delta DEC\]
Hence, we can say,
\[\dfrac{AC}{DC}=\dfrac{AB}{DE}=\dfrac{BC}{CE}\]
So, we can say, \[\dfrac{AC}{DC}=\dfrac{AB}{DE}.\] Now, we know that it can be further written as,
\[\dfrac{8+x}{8}=\dfrac{15}{10}\]
Now, we will simplify it to get the value of x. So, we get,
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{8+x}{8}=\dfrac{3}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow 16+2x=24\]
\[\Rightarrow 2x=24-16\]
\[\Rightarrow 2x=8\]
\[\Rightarrow x=4.....\left( i \right)\]
Now, we will consider triangle ACG and triangle DCF. We have been given that DF is parallel to AG. So, we can say, by the properties of corresponding angles,
\[\angle CDF=\angle CAG\]
\[\angle CFD=\angle CGA\]
Therefore, we can say by AA criteria that,
\[\Delta ACG\sim \Delta DCF\]
Hence, we can say,
\[\dfrac{AC}{DC}=\dfrac{AG}{DF}=\dfrac{CG}{CF}\]
So, we can say, \[\dfrac{AC}{DC}=\dfrac{CG}{CF}.\] Now, we know that it can be further written as,
\[\dfrac{8+x}{8}=\dfrac{6}{6-y}\]
Now, we will put the value of x from equation (i) and get the value of y. So, we get,
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{8+4}{8}=\dfrac{6}{6-y}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{12}{8}=\dfrac{6}{6-y}\]
\[\Rightarrow 6-y=\dfrac{6\times 8}{12}\]
\[\Rightarrow 6-y=4\]
\[\Rightarrow y=6-4\]
\[\Rightarrow y=2.....\left( ii \right)\]
From equation (i) and (ii), we can say,
\[\dfrac{x}{y}=\dfrac{4}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{y}=\dfrac{2}{1}\]
Hence, we can say, x:y = 2:1.
Therefore, option (c) is the right answer.
Note: While solving the question, the possible mistake one can make is by taking the wrong pair of the side after proving the triangles similar which will give us the wrong answer, and hence we will lose our marks. So, we have to be very careful while choosing the sides at the time of taking the ratio.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




