
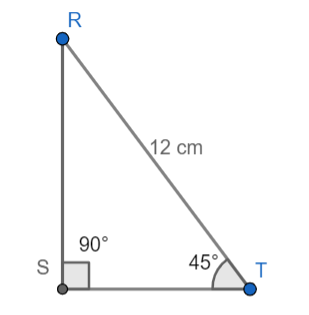
In the figure below, a triangle RST with $\angle S=90{}^\circ ,\angle T=45{}^\circ $, RT = 12 cm is given. Find RS and ST.

Answer
610.8k+ views
Hint: We will use that the sum of all three angles in a triangle is $180{}^\circ $ and we use Pythagoras theorem to find the length of sides as the above triangle is a right-angled triangle.
Complete step-by-step solution -
The sum of three angles in a triangle is $180{}^\circ $. So, we will use this condition to find the $\angle R$ in this triangle.
The above triangle is a right-angled triangle and right-angled at S.
So, $\angle S=90{}^\circ $ and $\angle T=45{}^\circ $. We will find $\angle R$ by subtracting $\angle S$ and $\angle T$ from $180{}^\circ $.
So, $\angle R=180{}^\circ -(\angle S+\angle T)$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 180{}^\circ -(90{}^\circ +45{}^\circ ) \\
& \Rightarrow 180{}^\circ -(135{}^\circ ) \\
& \Rightarrow 45{}^\circ \\
\end{align}$
Both $\angle R$ and $\angle S$ are equal. So, the above triangle is a right-angled isosceles triangle.
In the above right-angled isosceles triangle, the hypotenuse is the side opposite to the right-angled triangle. So, the length of hypotenuse ST is 12 cm and let the length of side ST be x and length of the side RS also becomes x, as the triangle is an isosceles triangle.
We use Pythagoras theorem as the above triangle is a right-angled triangle, Pythagoras theorem states that in a right angle triangle square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of other two sides in it.
So, by Pythagoras theorem $R{{S}^{2}}+S{{T}^{2}}=R{{T}^{2}}\cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \left( 1 \right)$
Now we will substitute RT = 12 cm, RS = x cm, ST = x cm in equation (1).
Equation (1) becomes, $\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}={{12}^{2}}$
Now we will solve for x, $\Rightarrow 2{{x}^{2}}=144$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}=72 \\
& \Rightarrow x=\sqrt{72} \\
\end{align}$
$\sqrt{72}$ can be expressed as $\sqrt{36\times 2}$ then further simplifying it, we obtain $\pm 6\sqrt{2}$.
Therefore, $x=\pm 6\sqrt{2}$.
We do not consider $x=-6\sqrt{2}$ because the length of the side of a triangle cannot be negative.
Hence, $x=6\sqrt{2}$.
So, RS = ST = $6\sqrt{2}$.
Note: The length of the side of a triangle cannot be negative and in an isosceles triangle two sides will be equal. The Pythagora's theorem is only applicable to right-angled triangles. We can also solve this question using the relation between angles and sides of a right-angles triangle. We can compute side RS by using sine of angle $45{}^\circ $, as RS $=12\sin 45{}^\circ =6\sqrt{2}$ and ST using the cosine of angle $45{}^\circ $, as ST $=12\cos 45{}^\circ =6\sqrt{2}$.
Complete step-by-step solution -
The sum of three angles in a triangle is $180{}^\circ $. So, we will use this condition to find the $\angle R$ in this triangle.
The above triangle is a right-angled triangle and right-angled at S.
So, $\angle S=90{}^\circ $ and $\angle T=45{}^\circ $. We will find $\angle R$ by subtracting $\angle S$ and $\angle T$ from $180{}^\circ $.
So, $\angle R=180{}^\circ -(\angle S+\angle T)$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 180{}^\circ -(90{}^\circ +45{}^\circ ) \\
& \Rightarrow 180{}^\circ -(135{}^\circ ) \\
& \Rightarrow 45{}^\circ \\
\end{align}$
Both $\angle R$ and $\angle S$ are equal. So, the above triangle is a right-angled isosceles triangle.
In the above right-angled isosceles triangle, the hypotenuse is the side opposite to the right-angled triangle. So, the length of hypotenuse ST is 12 cm and let the length of side ST be x and length of the side RS also becomes x, as the triangle is an isosceles triangle.
We use Pythagoras theorem as the above triangle is a right-angled triangle, Pythagoras theorem states that in a right angle triangle square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of other two sides in it.
So, by Pythagoras theorem $R{{S}^{2}}+S{{T}^{2}}=R{{T}^{2}}\cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \left( 1 \right)$
Now we will substitute RT = 12 cm, RS = x cm, ST = x cm in equation (1).
Equation (1) becomes, $\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}={{12}^{2}}$
Now we will solve for x, $\Rightarrow 2{{x}^{2}}=144$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}=72 \\
& \Rightarrow x=\sqrt{72} \\
\end{align}$
$\sqrt{72}$ can be expressed as $\sqrt{36\times 2}$ then further simplifying it, we obtain $\pm 6\sqrt{2}$.
Therefore, $x=\pm 6\sqrt{2}$.
We do not consider $x=-6\sqrt{2}$ because the length of the side of a triangle cannot be negative.
Hence, $x=6\sqrt{2}$.
So, RS = ST = $6\sqrt{2}$.
Note: The length of the side of a triangle cannot be negative and in an isosceles triangle two sides will be equal. The Pythagora's theorem is only applicable to right-angled triangles. We can also solve this question using the relation between angles and sides of a right-angles triangle. We can compute side RS by using sine of angle $45{}^\circ $, as RS $=12\sin 45{}^\circ =6\sqrt{2}$ and ST using the cosine of angle $45{}^\circ $, as ST $=12\cos 45{}^\circ =6\sqrt{2}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




