
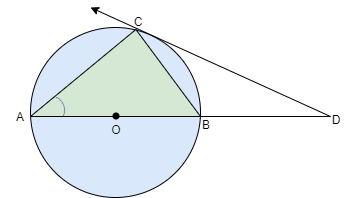
In the figure, AB is a diameter and AC is the chord of a circle such that$\angle BAC = {30^ \circ }$. If DC is a tangent, then $\Delta BCD$ is
A. Isosceles
B. Equilateral
C. Right angled
D. Acute angled

Answer
596.4k+ views
Hint: In this question remember to join point O to C and use $\angle $ACB is equal to ${90^ \circ }$ by property of diameter, using these instructions will help you to approach closer towards the solution to the problem.
Complete step by step solution:
According to the given information we have circle with diameter AB which have a triangle ABC inscribed inside the circle with cord AC and DC is the tangent and also one of the angle of triangle i.e.$\angle BAC = {30^ \circ }$
Now joining point O to C
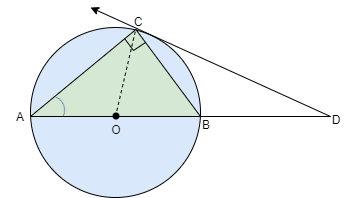
By the property of diameter of circle $\angle $ACB = ${90^ \circ }$
In triangle ABC by angle sum property
$\angle $BAC + $\angle $ACB + $\angle $CBA = ${180^ \circ }$
Substituting the given values in the above equation
${30^ \circ }$ + ${90^ \circ }$+ $\angle $CBA = ${180^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle $CBA = ${180^ \circ }$ – ${120^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle $CBA = ${60^ \circ }$
In the triangle OBC
CO = BO since CO and BO are the radius of circle
Since the side CO = BO therefore $\angle $OCB = $\angle $OBC = ${60^ \circ }$ by the property of isosceles triangle
As we know that the point where tangent touches the circle is perpendicular to the radius of the circle
Therefore $\angle $OCB + $\angle $DCB = ${90^ \circ }$
Substituting the given values in the above equation we get
${60^ \circ }$ + $\angle $DCB = ${90^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle $DCB = ${90^ \circ }$ – ${60^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle $DCB = ${30^ \circ }$
Now In triangle BCD
We know that by the property of external angle $\angle $OBC = $\angle $DCB + $\angle $CDB
No substituting the given values in the above equation we get
${60^ \circ }$= ${30^ \circ }$+ $\angle $CDB
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle $CDB = ${60^ \circ }$ – ${30^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle $CDB = ${30^ \circ }$
In triangle BCD by the angle sum property
$\angle $CDB + $\angle $DCB + $\angle $CBD = ${180^ \circ }$
Substituting the values in the above equation we get
${30^ \circ }$ + ${30^ \circ }$+ $\angle $CBD = ${180^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle $CBD = ${180^ \circ }$ – ${30^ \circ }$ – ${30^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle $CBD = ${180^ \circ }$ – ${60^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle $CBD = ${120^ \circ }$
So in triangle BCD angles $\angle $CDB, $\angle $DCB and$\angle $CBD are${120^ \circ }$, ${30^ \circ }$ and ${30^ \circ }$
Since in triangle BCD $\angle $DCB = $\angle $CBD and $\angle $CDB therefore we can say that triangle BCD is an isosceles triangle
Hence option A is the correct option.
Note: In the above solution isosceles triangle was the correct answer because in isosceles triangle 2 angles are equal to each other this similar properties shown by the triangle BCD which made us to decide that it is a isosceles triangle and the reason that the triangle BCD was not a equilateral triangle, right angled triangle and acute angled triangle because in equilateral triangle all angles are equal to each other and in right angled triangle at least 1 angle of the triangle should be ${90^ \circ }$ and whereas in acute angled triangle all angles are less than ${90^ \circ }$ but these all properties of the triangle were not shown by the triangle BCD due to which these all triangles were not the correct option for this problem.
Complete step by step solution:
According to the given information we have circle with diameter AB which have a triangle ABC inscribed inside the circle with cord AC and DC is the tangent and also one of the angle of triangle i.e.$\angle BAC = {30^ \circ }$
Now joining point O to C

By the property of diameter of circle $\angle $ACB = ${90^ \circ }$
In triangle ABC by angle sum property
$\angle $BAC + $\angle $ACB + $\angle $CBA = ${180^ \circ }$
Substituting the given values in the above equation
${30^ \circ }$ + ${90^ \circ }$+ $\angle $CBA = ${180^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle $CBA = ${180^ \circ }$ – ${120^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle $CBA = ${60^ \circ }$
In the triangle OBC
CO = BO since CO and BO are the radius of circle
Since the side CO = BO therefore $\angle $OCB = $\angle $OBC = ${60^ \circ }$ by the property of isosceles triangle
As we know that the point where tangent touches the circle is perpendicular to the radius of the circle
Therefore $\angle $OCB + $\angle $DCB = ${90^ \circ }$
Substituting the given values in the above equation we get
${60^ \circ }$ + $\angle $DCB = ${90^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle $DCB = ${90^ \circ }$ – ${60^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle $DCB = ${30^ \circ }$
Now In triangle BCD
We know that by the property of external angle $\angle $OBC = $\angle $DCB + $\angle $CDB
No substituting the given values in the above equation we get
${60^ \circ }$= ${30^ \circ }$+ $\angle $CDB
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle $CDB = ${60^ \circ }$ – ${30^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle $CDB = ${30^ \circ }$
In triangle BCD by the angle sum property
$\angle $CDB + $\angle $DCB + $\angle $CBD = ${180^ \circ }$
Substituting the values in the above equation we get
${30^ \circ }$ + ${30^ \circ }$+ $\angle $CBD = ${180^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle $CBD = ${180^ \circ }$ – ${30^ \circ }$ – ${30^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle $CBD = ${180^ \circ }$ – ${60^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle $CBD = ${120^ \circ }$
So in triangle BCD angles $\angle $CDB, $\angle $DCB and$\angle $CBD are${120^ \circ }$, ${30^ \circ }$ and ${30^ \circ }$
Since in triangle BCD $\angle $DCB = $\angle $CBD and $\angle $CDB therefore we can say that triangle BCD is an isosceles triangle
Hence option A is the correct option.
Note: In the above solution isosceles triangle was the correct answer because in isosceles triangle 2 angles are equal to each other this similar properties shown by the triangle BCD which made us to decide that it is a isosceles triangle and the reason that the triangle BCD was not a equilateral triangle, right angled triangle and acute angled triangle because in equilateral triangle all angles are equal to each other and in right angled triangle at least 1 angle of the triangle should be ${90^ \circ }$ and whereas in acute angled triangle all angles are less than ${90^ \circ }$ but these all properties of the triangle were not shown by the triangle BCD due to which these all triangles were not the correct option for this problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




