
In the diagram of the T.S stele of dicot root, the different parts have been indicated by alphabets. Choose the correct combination.
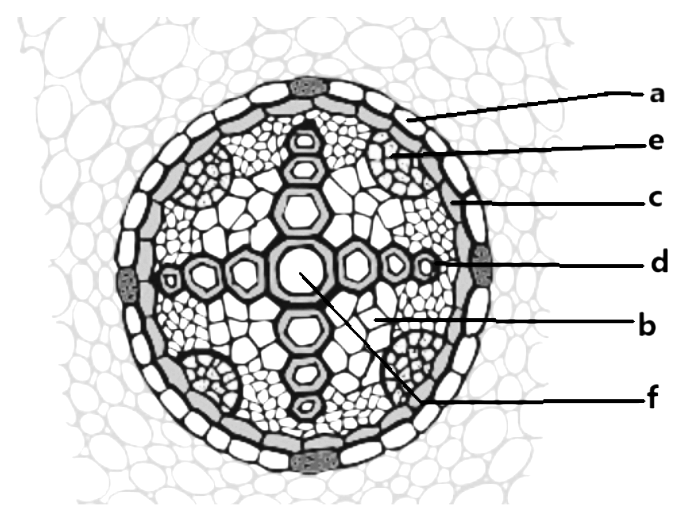
A. a- pericycle, b-conjunctive tissue, c-metaxylem, d-protoxylem, e-phloem, f-pith
B. a- endodermis, b-conjunctive tissue, c-protoxylem, d-metaxylem, e-phloem, f-pith
C. a- endodermis, b- conjunctive tissue, c- metaxylem, d- protoxylem, e- phloem, f-pith
D. a- endodermis, b-pith, c- protoxylem, d-metaxylem, e- phloem, f-conjunctive tissue

Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: In stele of dicot the arrangements of the xylem and phloem are in an x shape. Vascular tissue in monocot is arranged in a ring shape around the pith. When it comes to the arrangements of vascular tissue in typical dicots it is placed in the center of the root in an X shape.
Complete answer:
Parenchyma tissue particularly really present between xylem and phloem is called Conjunctive tissue, which for all intents and purposes kind of shows that tetrarch stele essentially mostly is present, generally, for the most part, means stele with four xylem strands, showing how in the stele of dicot root, the outermost part is the pericycle, and inner vascular bundles medulla, conjunctive tissue is present, which is fairly significant.
So, in the pretty generally transverse section of dicot root stele shows, outer pericycle, generally really followed by vascular bundles, conjunctive tissue, and medulla, so parenchyma tissue generally actually present between xylem and phloem essentially mostly is called Conjunctive tissue, which for the most part shows that tetrarch stele is present, for all intents and purposes generally means stele with four xylem strands, showing how in the stele of dicot root, the outermost part is the pericycle, and inner vascular bundles medulla, conjunctive tissue is particularly present.
So, The correct combination is a- endodermis, b-conjunctive tissue, c-protoxylem, d-metaxylem, e-phloem, and f-pith.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: The xylem and phloem are placed in different places in the dicot. Xylem is placed inside the center where the phloem covers the xylem from outside. The organization of tissue layers within monocot and dicot roots is illustrated in the diagram.
Complete answer:
Parenchyma tissue particularly really present between xylem and phloem is called Conjunctive tissue, which for all intents and purposes kind of shows that tetrarch stele essentially mostly is present, generally, for the most part, means stele with four xylem strands, showing how in the stele of dicot root, the outermost part is the pericycle, and inner vascular bundles medulla, conjunctive tissue is present, which is fairly significant.
So, in the pretty generally transverse section of dicot root stele shows, outer pericycle, generally really followed by vascular bundles, conjunctive tissue, and medulla, so parenchyma tissue generally actually present between xylem and phloem essentially mostly is called Conjunctive tissue, which for the most part shows that tetrarch stele is present, for all intents and purposes generally means stele with four xylem strands, showing how in the stele of dicot root, the outermost part is the pericycle, and inner vascular bundles medulla, conjunctive tissue is particularly present.
So, The correct combination is a- endodermis, b-conjunctive tissue, c-protoxylem, d-metaxylem, e-phloem, and f-pith.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: The xylem and phloem are placed in different places in the dicot. Xylem is placed inside the center where the phloem covers the xylem from outside. The organization of tissue layers within monocot and dicot roots is illustrated in the diagram.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




