
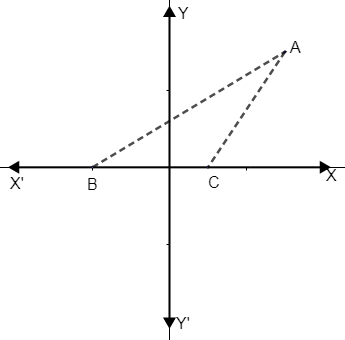
In the diagram given, the equation of AB is \[x=\sqrt{3}y+1=0\] and the equation of AC is \[x-y-2=0\].
(i) Write down the angles that the line AC and AB make with the positive direction of x – axis.
(ii) Find \[\angle BAC\].

Answer
601.8k+ views
Hint: Find the slope of line AB and AC by comparing with \[y=mx+b\], which is the formula to find the slope of line. Thus \[m=\tan \theta \] and find \[{{\theta }_{1}}\] and \[{{\theta }_{2}}\] which makes angle with AB and AC. Thus in \[\Delta ABC\] apply angle sum property and find \[\angle BAC\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been given the line AB, \[x=\sqrt{3}y+1\].
Now let us find the slope of line AB.
We know that the slope of the line is given by the formula, \[y=mx+b\].
Now given to us the equation, \[x=\sqrt{3}y+1\].
Now let us rearrange this equation,
\[x=\sqrt{3}y+1\]
\[\begin{align}
& \therefore \sqrt{3}y=x-1 \\
& y=\dfrac{x-1}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{x}{\sqrt{3}}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore y=\dfrac{x}{\sqrt{3}}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\], now this is of the form \[y=mx+b\].
Let us compare them.
In the equation, slope of a line is given by m.
Thus by comparing both equations, we get, \[m=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\].
Let us consider \[\theta \] as the angle which the line AB makes with the positive x – axis.
\[\therefore \tan {{\theta }_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\Rightarrow {{\theta }_{1}}={{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\]
From the trigonometric table we know that, \[\tan {{30}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\].
Thus the value of \[{{\theta }_{1}}={{30}^{\circ }}\].
Similarly, we have been given the equation of line of AC as \[x-y-2=0\].
We need to find the slope of AC.
\[x-y-2=0\]
\[y=x-2\], now this is of the form \[y=mx+b\]. By comparing we get m = 1.
Thus slope of AC = 1.
Hence, \[\tan {{\theta }_{2}}=1\].
\[{{\theta }_{2}}={{\tan }^{-1}}1={{45}^{\circ }}\]
From the trigonometric table we know that, \[\tan {{45}^{\circ }}=1\]. Thus, \[{{\theta }_{2}}={{45}^{\circ }}\].
Hence, we got the angles that the lines AB and AC make with the positive direction of x – axis.
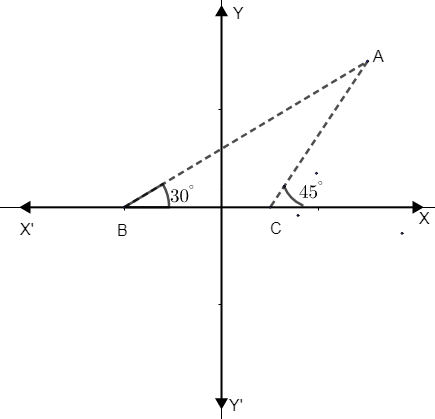
(i) \[{{\theta }_{1}}={{30}^{\circ }}\], angle that line AB makes with the positive direction of x – axis. Similarly, \[{{\theta }_{1}}={{45}^{\circ }}\], angle that line AC makes with the positive direction of x –axis.
(ii) Let us now consider the figure, \[{{\theta }_{1}}=\angle ABC={{30}^{\circ }}\]. Similarly, \[{{\theta }_{2}}={{45}^{\circ }}\]. Now to get, \[\angle ACB=180-45={{135}^{\circ }}\].
We know that straight line angle is \[{{180}^{\circ }}\]. Thus to get \[\angle ACB\], subtract \[{{45}^{\circ }}\] from \[{{180}^{\circ }}\].
Let us consider the \[\Delta ABC\], by angle sum property we know that the sum of all angles in a triangle is \[{{180}^{\circ }}\].
Hence, we can say that,
\[\angle ABC+\angle ACB+\angle BAC={{180}^{\circ }}\]
We need to find the \[\angle BAC\].
\[\angle ABC={{30}^{\circ }}\], \[\angle ACB={{135}^{\circ }}\].
Thus, \[{{30}^{\circ }}+{{135}^{\circ }}+\angle BAC={{180}^{\circ }}\].
i.e. \[\angle BAC={{180}^{\circ }}-{{30}^{\circ }}-{{135}^{\circ }}\]
\[\begin{align}
& ={{180}^{\circ }}-{{165}^{\circ }} \\
& ={{15}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence we got, \[\angle BAC\] as \[{{15}^{\circ }}\].
Note: The angle inclination of a line is the angle formed by the intersection of the line and the x – axis. Using horizontal run of 1 and m for slope, the angle of inclination, \[\theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}m\]. That’s why we took \[\tan \theta =m\] here.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been given the line AB, \[x=\sqrt{3}y+1\].
Now let us find the slope of line AB.
We know that the slope of the line is given by the formula, \[y=mx+b\].
Now given to us the equation, \[x=\sqrt{3}y+1\].
Now let us rearrange this equation,

\[x=\sqrt{3}y+1\]
\[\begin{align}
& \therefore \sqrt{3}y=x-1 \\
& y=\dfrac{x-1}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{x}{\sqrt{3}}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore y=\dfrac{x}{\sqrt{3}}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\], now this is of the form \[y=mx+b\].
Let us compare them.
In the equation, slope of a line is given by m.
Thus by comparing both equations, we get, \[m=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\].
Let us consider \[\theta \] as the angle which the line AB makes with the positive x – axis.
\[\therefore \tan {{\theta }_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\Rightarrow {{\theta }_{1}}={{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\]
From the trigonometric table we know that, \[\tan {{30}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\].
Thus the value of \[{{\theta }_{1}}={{30}^{\circ }}\].
Similarly, we have been given the equation of line of AC as \[x-y-2=0\].
We need to find the slope of AC.
\[x-y-2=0\]
\[y=x-2\], now this is of the form \[y=mx+b\]. By comparing we get m = 1.
Thus slope of AC = 1.
Hence, \[\tan {{\theta }_{2}}=1\].
\[{{\theta }_{2}}={{\tan }^{-1}}1={{45}^{\circ }}\]
From the trigonometric table we know that, \[\tan {{45}^{\circ }}=1\]. Thus, \[{{\theta }_{2}}={{45}^{\circ }}\].
Hence, we got the angles that the lines AB and AC make with the positive direction of x – axis.
(i) \[{{\theta }_{1}}={{30}^{\circ }}\], angle that line AB makes with the positive direction of x – axis. Similarly, \[{{\theta }_{1}}={{45}^{\circ }}\], angle that line AC makes with the positive direction of x –axis.
(ii) Let us now consider the figure, \[{{\theta }_{1}}=\angle ABC={{30}^{\circ }}\]. Similarly, \[{{\theta }_{2}}={{45}^{\circ }}\]. Now to get, \[\angle ACB=180-45={{135}^{\circ }}\].
We know that straight line angle is \[{{180}^{\circ }}\]. Thus to get \[\angle ACB\], subtract \[{{45}^{\circ }}\] from \[{{180}^{\circ }}\].
Let us consider the \[\Delta ABC\], by angle sum property we know that the sum of all angles in a triangle is \[{{180}^{\circ }}\].
Hence, we can say that,
\[\angle ABC+\angle ACB+\angle BAC={{180}^{\circ }}\]
We need to find the \[\angle BAC\].
\[\angle ABC={{30}^{\circ }}\], \[\angle ACB={{135}^{\circ }}\].
Thus, \[{{30}^{\circ }}+{{135}^{\circ }}+\angle BAC={{180}^{\circ }}\].
i.e. \[\angle BAC={{180}^{\circ }}-{{30}^{\circ }}-{{135}^{\circ }}\]
\[\begin{align}
& ={{180}^{\circ }}-{{165}^{\circ }} \\
& ={{15}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence we got, \[\angle BAC\] as \[{{15}^{\circ }}\].
Note: The angle inclination of a line is the angle formed by the intersection of the line and the x – axis. Using horizontal run of 1 and m for slope, the angle of inclination, \[\theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}m\]. That’s why we took \[\tan \theta =m\] here.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




