
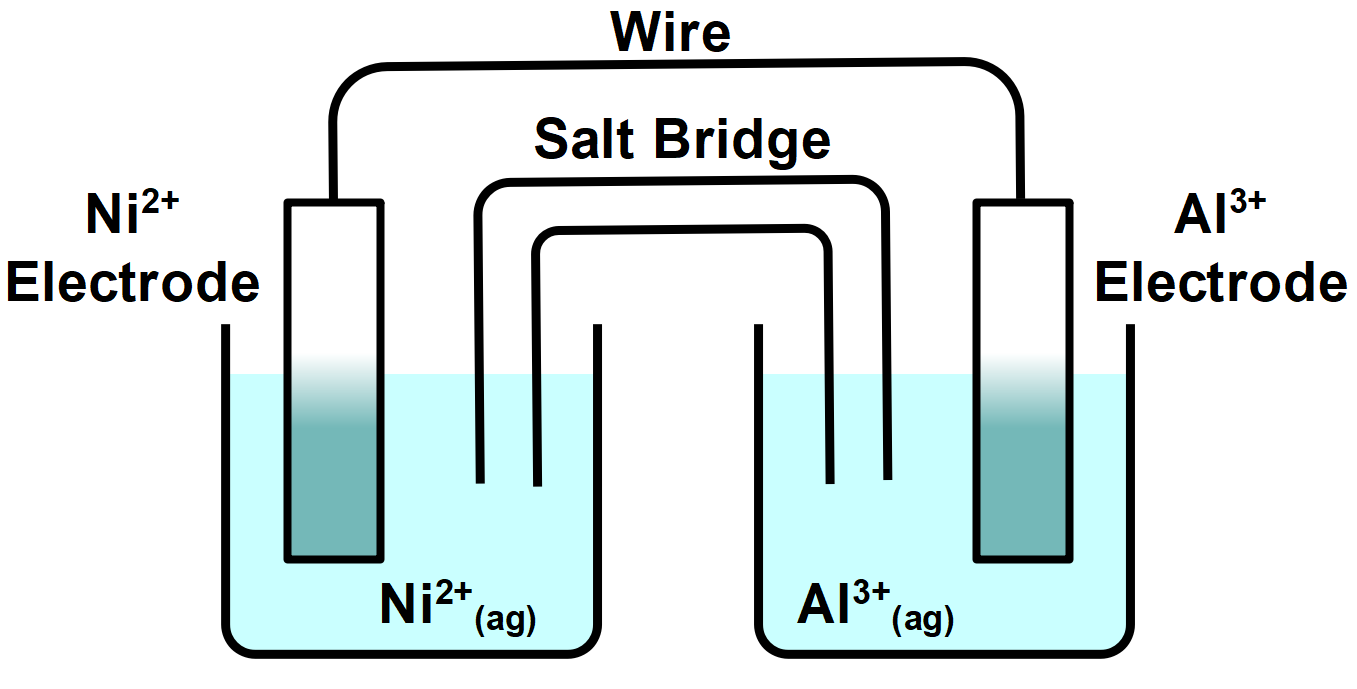
In the diagram below, what is the half reaction that occurs at the cathode?
A.$Al\to A{{l}^{3+}}+3{{e}^{-}}.$
B.$N{{i}^{2+}}+2{{e}^{-}}\to Ni.$
C.$Ni\to N{{i}^{2+}}+2{{e}^{-}}.$
D.$2A{{l}^{3+}}+6{{e}^{-}}\to 2Al.$
E.None of these.

Answer
493.2k+ views
Hint: We know that the electrochemical which is also called voltaic or galvanic cell is made up of two half cells. In one half-cell, the oxidation reaction takes place and in one half-cell reduction reaction takes place. Both the half-cells are connected by a salt bridge (usually made of a strong electrolyte.
Complete answer:
As we know that the electrochemistry is an important branch in physical chemistry, it deals with the study of electricity and related chemical reactions. In which electricity is generated in a reaction by the movements of electrons from one element to another, the reaction is known as redox or oxidation -reduction reaction. An electrochemical cell is a device which produces electric current from energy released by a spontaneous redox reaction.
Examples of such cells are galvanic cells, voltaic cells etc. ere we have given an electrochemical reaction, for an electrochemical reaction certain rules have to be followed to write the cell notation for a reaction. The rules are given below Here the half-cell which is described first is anode followed by the cathode half-cell. Within the half-cell, reactants are written first then the products. A single vertical line which is drawn between two chemical species used to describe that chemical species are in two different phases but are in physical contact with each other.
The double vertical line is used to represent a salt bridge or a porous membrane which is used to separate the individual half-cell. The phase of each chemical is given in the cell notation. If the electrolytes in the cells are not in standard conditions, then concentrations and pressure will be included with the phase notation. The half-reaction that occurs at the cathode is the reduction of \[Ni\left( II \right)\] ions to Ni atoms. \[N{{i}^{2+}}+2{{e}^{-}}\to Ni\] Thus, the gain of electrons is called reduction. Cathode is the electrode where reduction occurs. In the electrochemical series, \[Al\left( III \right)\] has more negative standard reduction potential than \[Ni\left( II \right).\]
Therefore, correct answer is option B i.e. Al is oxidized and \[Ni\left( II \right)\] is reduced.
Note:
Remember that the half-cell reaction can be an oxidation reaction or it can be a reduction reaction. In the oxidation reaction, electrons are lost and in the reduction reaction, electrons are gained. The half-cell reaction occurs in an electrochemical cell at the electrodes. At anode, oxidation reaction occurs which is known as oxidation half reaction.
Complete answer:
As we know that the electrochemistry is an important branch in physical chemistry, it deals with the study of electricity and related chemical reactions. In which electricity is generated in a reaction by the movements of electrons from one element to another, the reaction is known as redox or oxidation -reduction reaction. An electrochemical cell is a device which produces electric current from energy released by a spontaneous redox reaction.
Examples of such cells are galvanic cells, voltaic cells etc. ere we have given an electrochemical reaction, for an electrochemical reaction certain rules have to be followed to write the cell notation for a reaction. The rules are given below Here the half-cell which is described first is anode followed by the cathode half-cell. Within the half-cell, reactants are written first then the products. A single vertical line which is drawn between two chemical species used to describe that chemical species are in two different phases but are in physical contact with each other.
The double vertical line is used to represent a salt bridge or a porous membrane which is used to separate the individual half-cell. The phase of each chemical is given in the cell notation. If the electrolytes in the cells are not in standard conditions, then concentrations and pressure will be included with the phase notation. The half-reaction that occurs at the cathode is the reduction of \[Ni\left( II \right)\] ions to Ni atoms. \[N{{i}^{2+}}+2{{e}^{-}}\to Ni\] Thus, the gain of electrons is called reduction. Cathode is the electrode where reduction occurs. In the electrochemical series, \[Al\left( III \right)\] has more negative standard reduction potential than \[Ni\left( II \right).\]
Therefore, correct answer is option B i.e. Al is oxidized and \[Ni\left( II \right)\] is reduced.
Note:
Remember that the half-cell reaction can be an oxidation reaction or it can be a reduction reaction. In the oxidation reaction, electrons are lost and in the reduction reaction, electrons are gained. The half-cell reaction occurs in an electrochemical cell at the electrodes. At anode, oxidation reaction occurs which is known as oxidation half reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




