
In the device shown in figure below, the cylinder is in pure rolling motion. At a certain instant the angular speed of the cylinder is $\omega $ . The velocity of the block at that instant is $x\omega R$ then what is the value of $x$? (Inner radius is ‘$R$’ and outer radius is $2R$ )
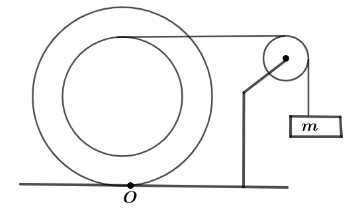

Answer
512.4k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, we must first understand about pure rolling motion, a pure rolling motion is one in which a body rotates with some angular velocity and at the same time it has translational motion, without slipping which means the point of contact between the ground and the body always remains at rest. We will try to find the velocity of the block in terms of the velocity of the cylinder which is in pure rolling through the straight string attached with it.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first draw the diagram in which according to the question, the string of the block is attached with the inner core of cylinder which has a radius of R and as soon as the block starts to moving in downward direction let’s say with a velocity of $v$ , then this velocity acquired by block is due to velocity attained by the straight string which is attached with inner core of cylinder.
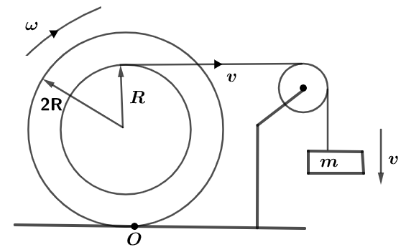
Now, at the point of contact of string and cylinder this point will have the same linear velocity of $v$ which is related with angular frequency of the cylinder and radius as
$v = R\omega $
So, the velocity of block will also be $v = R\omega $ now, in the given relation in the question we have, $x\omega R$
Now, compare both relations we have,
$v = R\omega = x\omega R$
$ \Rightarrow R\omega = xR\omega $
$\therefore x = 1$
Hence, the required value is $x = 1$.
Note:It should be remembered that, the string is straight so, the whole system will move with same linear velocity and $v = R\omega $ is the relation of linear velocity of a body moving in circular path having radius of R and angular velocity of $\omega $ and also if the string was attached to outer core of cylinder having radius of $2R$ then the velocity of the block would be $2R\omega $.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first draw the diagram in which according to the question, the string of the block is attached with the inner core of cylinder which has a radius of R and as soon as the block starts to moving in downward direction let’s say with a velocity of $v$ , then this velocity acquired by block is due to velocity attained by the straight string which is attached with inner core of cylinder.

Now, at the point of contact of string and cylinder this point will have the same linear velocity of $v$ which is related with angular frequency of the cylinder and radius as
$v = R\omega $
So, the velocity of block will also be $v = R\omega $ now, in the given relation in the question we have, $x\omega R$
Now, compare both relations we have,
$v = R\omega = x\omega R$
$ \Rightarrow R\omega = xR\omega $
$\therefore x = 1$
Hence, the required value is $x = 1$.
Note:It should be remembered that, the string is straight so, the whole system will move with same linear velocity and $v = R\omega $ is the relation of linear velocity of a body moving in circular path having radius of R and angular velocity of $\omega $ and also if the string was attached to outer core of cylinder having radius of $2R$ then the velocity of the block would be $2R\omega $.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




