
In the complex $[CoC{{l}_{2}}{{(en)}_{2}}]Br$, the coordination number and oxidation state of cobalt are:
(A) 6 and +3
(B) 3 and +3
(C) 4 and +2
(D) 6 and +1
Answer
530.7k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we first need to know what is coordination number and oxidation state.
The coordination of a central atom in a compound is the number of atoms that are attached to it.
In a chemical compound, the oxidation number or the oxidation state is used to determine the degree of oxidation of an atom.
Complete answer:
Now, let us take a look at the structure of $[CoC{{l}_{2}}{{(en)}_{2}}]Br$.
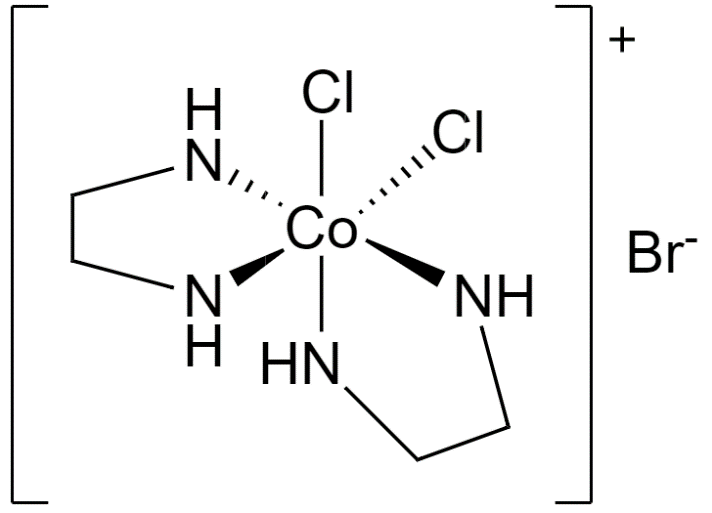
Dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) bromide
Since 6 atoms are attached to the cobalt central atom, its coordination number is 6.
Now, let us look at the rules to determine the oxidation number of an element.
- For a free element, the oxidation number of an element in a is always 0.
For example, in helium and nitrogen, the oxidation number of the He and N molecule will be 0.
Similarly, the sum of all the atom's oxidation numbers of a compound that is neutral is 0.
- The oxidation number of an ion, whether it is monatomic or polyatomic, is equal to the charge on the in.
For example, the oxidation number of $M{{g}^{2+}}$ is +2. The oxidation number of phosphate ions $P{{O}_{4}}^{3-}$ is -3.
- The usual oxidation number of
Hydrogen = +1
Oxygen = -2
Group I(A) = +1
Group II(A) = +2
Group VII(A) = -1
So, from the rules stated above, we can say that in $[CoC{{l}_{2}}{{(en)}_{2}}]Br$,
Co + 2(-1) + 2(0) + (-1) = 0
Co = +3
So, the coordination number and oxidation state of cobalt in $[CoC{{l}_{2}}{{(en)}_{2}}]Br$ are option (A) 6 and +3.
Note:
It should be noted that there are some exceptions while assigning the oxidation states of atoms in a molecule.
- When a hydrogen atom is bonded to a less electronegative atom, its oxidation number is -1.
- When an oxygen atom is bonded to a more electronegative atom, it exists in a peroxide ion, its oxidation number changes.
- When a Group VII(A) atom is bonded to a more electronegative atom, its oxidation number changes.
The coordination of a central atom in a compound is the number of atoms that are attached to it.
In a chemical compound, the oxidation number or the oxidation state is used to determine the degree of oxidation of an atom.
Complete answer:
Now, let us take a look at the structure of $[CoC{{l}_{2}}{{(en)}_{2}}]Br$.

Dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) bromide
Since 6 atoms are attached to the cobalt central atom, its coordination number is 6.
Now, let us look at the rules to determine the oxidation number of an element.
- For a free element, the oxidation number of an element in a is always 0.
For example, in helium and nitrogen, the oxidation number of the He and N molecule will be 0.
Similarly, the sum of all the atom's oxidation numbers of a compound that is neutral is 0.
- The oxidation number of an ion, whether it is monatomic or polyatomic, is equal to the charge on the in.
For example, the oxidation number of $M{{g}^{2+}}$ is +2. The oxidation number of phosphate ions $P{{O}_{4}}^{3-}$ is -3.
- The usual oxidation number of
Hydrogen = +1
Oxygen = -2
Group I(A) = +1
Group II(A) = +2
Group VII(A) = -1
So, from the rules stated above, we can say that in $[CoC{{l}_{2}}{{(en)}_{2}}]Br$,
Co + 2(-1) + 2(0) + (-1) = 0
Co = +3
So, the coordination number and oxidation state of cobalt in $[CoC{{l}_{2}}{{(en)}_{2}}]Br$ are option (A) 6 and +3.
Note:
It should be noted that there are some exceptions while assigning the oxidation states of atoms in a molecule.
- When a hydrogen atom is bonded to a less electronegative atom, its oxidation number is -1.
- When an oxygen atom is bonded to a more electronegative atom, it exists in a peroxide ion, its oxidation number changes.
- When a Group VII(A) atom is bonded to a more electronegative atom, its oxidation number changes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




