
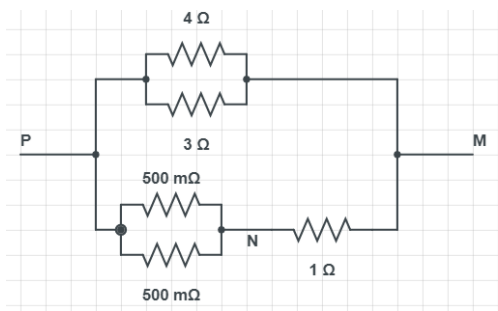
In the circuit shown the current through the 4Ω resistor is 1 amp when the point P and M are connected to a $d.c$ voltage source. The potential difference between the point M and N is:
$\begin{align}
& A.\text{ 0}\text{.5 volt} \\
& B.\text{ 3}\text{.2 volt} \\
& C.\text{ 1}\text{.5 volt} \\
& D.\text{ 1}\text{.0 volt} \\
\end{align}$

Answer
582k+ views
Hint: We have been provided with a circuit that has resistance which is connected to it. First calculate voltage across 4Ω resistance and as we know voltage across parallel branches are same so voltage across lower part of circuit will also be same. Find equivalent resistance in the lower portion. Calculate the voltage through 1Ω resistance this way you will get the answer just by applying series combination or parallel combination.
Complete answer:
We have given value of current (i) which is flowing in resistor 4Ω. Now we need to calculate potential difference between the point M and N as shown in figure:
In the given figure consider the upper position of points P and M. We know that, potential difference in parallel series for resistance is the same. i.e. potential difference across 4Ω and potential difference across 3Ω is same. Therefore potential difference across PM which is denoted by v is given by,
$v=4\times 1=4\text{ volt}$
Hence, potential difference across 4Ω resistance is 4 volts.
Now consider lower portion of point P and point M apply parallel combination we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{{{R}^{1}}}=\dfrac{1}{0.5}+\dfrac{1}{0.5}=\dfrac{0.5+0.5}{0.5+0.5} \\
& \therefore {{R}^{1}}=0.25 \\
\end{align}$
Consider resistance ${{R}^{1}}$ and resistance (1Ω) then equivalent resistance of lower side arm is given by
${{R}_{eq}}=1+0.25=1.25\Omega $
Let I be the current flow in the lower branch i.e. through equivalent resistance. Then,
$\begin{align}
& IR=V \\
& 1.25I=4V.......(1) \\
& I=\dfrac{4}{1.25}=3.2A......(2) \\
\end{align}$
In equation (1) we have taken value of potential difference as 4v because we know the potential difference in parallel branch is same therefore whatever be the potential across 4Ω resistance, same will be across equivalent resistance.
So equation (2) implies that 3.2A current flows through 1Ω resistance, shown in figure. Hence potential difference between M and N is given by
${{v}^{1}}=3.2\times I=3.2volt$
Hence potential difference between two points M and N is 3.2 volt.
Therefore option (b) is the correct option.
Note:
Students should know that when several numbers of resistors are connected in series then the current flowing through each of the components (electrical) will be the same. Equivalent resistance in series is given as
${{\left( {{R}_{eq}} \right)}_{s}}={{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}+{{R}_{3.........}}$
And when several numbers of resistors are connected in parallel the potential difference across each of the electrical components will be the same. Equivalent resistance to parallel combination is given as
${{\left( \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}} \right)}_{p}}=\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{3}}}+..........$
The concept of resistance in series and in parallel is opposite in case of capacitor. So do not get confused.
Complete answer:
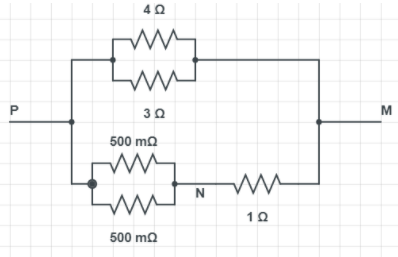
We have given value of current (i) which is flowing in resistor 4Ω. Now we need to calculate potential difference between the point M and N as shown in figure:

In the given figure consider the upper position of points P and M. We know that, potential difference in parallel series for resistance is the same. i.e. potential difference across 4Ω and potential difference across 3Ω is same. Therefore potential difference across PM which is denoted by v is given by,
$v=4\times 1=4\text{ volt}$
Hence, potential difference across 4Ω resistance is 4 volts.
Now consider lower portion of point P and point M apply parallel combination we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{{{R}^{1}}}=\dfrac{1}{0.5}+\dfrac{1}{0.5}=\dfrac{0.5+0.5}{0.5+0.5} \\
& \therefore {{R}^{1}}=0.25 \\
\end{align}$
Consider resistance ${{R}^{1}}$ and resistance (1Ω) then equivalent resistance of lower side arm is given by
${{R}_{eq}}=1+0.25=1.25\Omega $
Let I be the current flow in the lower branch i.e. through equivalent resistance. Then,
$\begin{align}
& IR=V \\
& 1.25I=4V.......(1) \\
& I=\dfrac{4}{1.25}=3.2A......(2) \\
\end{align}$
In equation (1) we have taken value of potential difference as 4v because we know the potential difference in parallel branch is same therefore whatever be the potential across 4Ω resistance, same will be across equivalent resistance.
So equation (2) implies that 3.2A current flows through 1Ω resistance, shown in figure. Hence potential difference between M and N is given by
${{v}^{1}}=3.2\times I=3.2volt$
Hence potential difference between two points M and N is 3.2 volt.
Therefore option (b) is the correct option.
Note:
Students should know that when several numbers of resistors are connected in series then the current flowing through each of the components (electrical) will be the same. Equivalent resistance in series is given as
${{\left( {{R}_{eq}} \right)}_{s}}={{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}+{{R}_{3.........}}$
And when several numbers of resistors are connected in parallel the potential difference across each of the electrical components will be the same. Equivalent resistance to parallel combination is given as
${{\left( \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}} \right)}_{p}}=\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{3}}}+..........$
The concept of resistance in series and in parallel is opposite in case of capacitor. So do not get confused.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




