
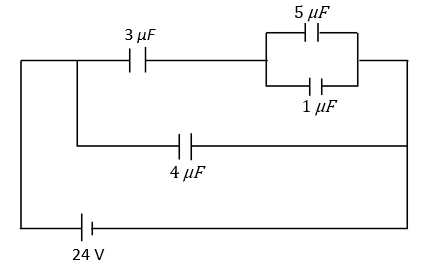
In the circuit shown above, the energy stored in \[1\,\mu F\] capacitor is
A. \[40\,\mu J\]
B. \[64\,\mu J\]
C. \[32\,\mu J\]
D. None

Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: We know that the potential difference across the parallel combination remains constant and the charge across the series capacitors also remains the same. Use this concept to determine the voltage across \[1\,\mu F\] capacitance and use the formula for energy stored in the capacitor.
Formula used:
The energy stored in the capacitor is,
\[W = \dfrac{1}{2}C{V^2}\]
Here, C is the capacitance and V is the potential across the capacitor.
The equivalent capacitance of the series capacitors \[{C_1}\] and \[{C_2}\] is,
\[{C_{12}} = \dfrac{{{C_1}{C_2}}}{{{C_1} + {C_2}}}\]
The equivalent capacitance of the parallel capacitors \[{C_1}\] and \[{C_2}\] is,
\[{C_{12}} = {C_1} + {C_2}\]
Complete step by step answer:
The capacitance \[4\,\mu F\] is in parallel combination with the equivalent capacitance of \[3\,\mu F\], \[5\,\mu F\] and \[1\,\mu F\]. Therefore, the potential difference across \[4\,\mu F\] and equivalent capacitance of \[3\,\mu F\], \[5\,\mu F\] and \[1\,\mu F\] is 24 V.
The equivalent capacitance of \[5\,\mu F\] and \[1\,\mu F\] capacitance is in series with \[3\,\mu F\] capacitance.
Since the capacitance \[5\,\mu F\]and \[1\,\mu F\] are in parallel combination, the equivalent capacitance is the sum of the capacitance \[5\,\mu F\] and \[1\,\mu F\].
\[{C_{51}} = 6\,\mu F\]
Therefore, the equivalent capacitance of \[3\,\mu F\], \[5\,\mu F\] and \[1\,\mu F\] is,
\[{C_{351}} = \dfrac{{\left( {3\,\mu F} \right)\left( {6\,\mu F} \right)}}{{3\,\mu F + 6\,\mu F}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {C_{351}} = 2\,\mu F\]
The charge across \[3\,\mu F\] is the same as the charge across the equivalent capacitance of \[5\,\mu F\] and \[1\,\mu F\].
\[\therefore {Q_3} = {Q_{51}} = {Q_{351}}\]
Therefore, the charge across the capacitance \[{C_{351}}\] is,
\[{Q_{351}} = {C_{351}}V\]
Substitute \[2\,\mu F\] for \[{C_{351}}\] and 24 V for V in the above equation.
\[{Q_{351}} = \left( {2\,\mu F} \right)\left( {24\,V} \right)\]
The potential across the capacitance \[{C_{51}}\] is,
\[{V_{51}} = \dfrac{{{Q_{51}}}}{{{C_{51}}}}\]
Substitute \[48\,\mu C\] for \[{Q_{51}}\] and \[6\,\mu F\] for \[{C_{51}}\] in the above equation.
\[{V_{51}} = \dfrac{{48\,\mu C}}{{6\,\mu F}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {V_{51}} = 8\,V\]
The potential across capacitance \[{C_5}\] and \[{C_1}\] is the same.
Therefore, the energy stored in the \[1\,\mu F\] capacitor is,
\[W = \dfrac{1}{2}{C_1}V_{51}^2\]
Substitute \[1\,\mu F\] for \[{C_1}\] and 8 V for \[{V_{51}}\] in the above equation.
\[W = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {1\,\mu F} \right){\left( {8\,V} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow W = 32\,\mu J\]
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
Remember, there is voltage drop in the series combination of the capacitors. Therefore, the potential across the series capacitors is different. The charge across the parallel circuit divides at the junction, therefore, the charge is different for parallel capacitors.
Formula used:
The energy stored in the capacitor is,
\[W = \dfrac{1}{2}C{V^2}\]
Here, C is the capacitance and V is the potential across the capacitor.
The equivalent capacitance of the series capacitors \[{C_1}\] and \[{C_2}\] is,
\[{C_{12}} = \dfrac{{{C_1}{C_2}}}{{{C_1} + {C_2}}}\]
The equivalent capacitance of the parallel capacitors \[{C_1}\] and \[{C_2}\] is,
\[{C_{12}} = {C_1} + {C_2}\]
Complete step by step answer:
The capacitance \[4\,\mu F\] is in parallel combination with the equivalent capacitance of \[3\,\mu F\], \[5\,\mu F\] and \[1\,\mu F\]. Therefore, the potential difference across \[4\,\mu F\] and equivalent capacitance of \[3\,\mu F\], \[5\,\mu F\] and \[1\,\mu F\] is 24 V.
The equivalent capacitance of \[5\,\mu F\] and \[1\,\mu F\] capacitance is in series with \[3\,\mu F\] capacitance.
Since the capacitance \[5\,\mu F\]and \[1\,\mu F\] are in parallel combination, the equivalent capacitance is the sum of the capacitance \[5\,\mu F\] and \[1\,\mu F\].
\[{C_{51}} = 6\,\mu F\]
Therefore, the equivalent capacitance of \[3\,\mu F\], \[5\,\mu F\] and \[1\,\mu F\] is,
\[{C_{351}} = \dfrac{{\left( {3\,\mu F} \right)\left( {6\,\mu F} \right)}}{{3\,\mu F + 6\,\mu F}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {C_{351}} = 2\,\mu F\]
The charge across \[3\,\mu F\] is the same as the charge across the equivalent capacitance of \[5\,\mu F\] and \[1\,\mu F\].
\[\therefore {Q_3} = {Q_{51}} = {Q_{351}}\]
Therefore, the charge across the capacitance \[{C_{351}}\] is,
\[{Q_{351}} = {C_{351}}V\]
Substitute \[2\,\mu F\] for \[{C_{351}}\] and 24 V for V in the above equation.
\[{Q_{351}} = \left( {2\,\mu F} \right)\left( {24\,V} \right)\]
The potential across the capacitance \[{C_{51}}\] is,
\[{V_{51}} = \dfrac{{{Q_{51}}}}{{{C_{51}}}}\]
Substitute \[48\,\mu C\] for \[{Q_{51}}\] and \[6\,\mu F\] for \[{C_{51}}\] in the above equation.
\[{V_{51}} = \dfrac{{48\,\mu C}}{{6\,\mu F}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {V_{51}} = 8\,V\]
The potential across capacitance \[{C_5}\] and \[{C_1}\] is the same.
Therefore, the energy stored in the \[1\,\mu F\] capacitor is,
\[W = \dfrac{1}{2}{C_1}V_{51}^2\]
Substitute \[1\,\mu F\] for \[{C_1}\] and 8 V for \[{V_{51}}\] in the above equation.
\[W = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {1\,\mu F} \right){\left( {8\,V} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow W = 32\,\mu J\]
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
Remember, there is voltage drop in the series combination of the capacitors. Therefore, the potential across the series capacitors is different. The charge across the parallel circuit divides at the junction, therefore, the charge is different for parallel capacitors.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




