
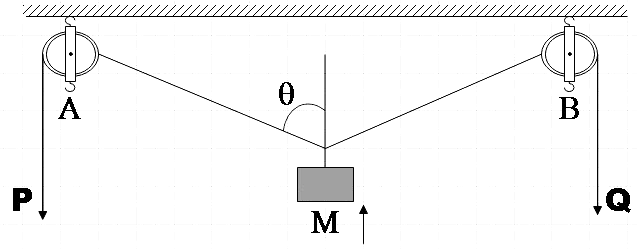
In the arrangement shown in figure, the ends P and Q of an inextensible string move downwards with uniform speed u. Pulleys A and B are fixed. The mass M moves upwards with a speed of
A. $2u\cos \theta $
B.$\dfrac{u}{\cos \theta }$
C.$\dfrac{2u}{\cos \theta }$
D.$u\cos \theta $

Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint: As a first step, make necessary constructions in the given diagram and thus consider a triangle. Apply Pythagorean theorem to get an expression. Differentiate with respect to time and then do necessary substitutions. You may then use basic trigonometry to get the required velocity in terms of u and $\cos \theta $.
Complete Step by step solution:
Let the velocity with which mass M moves upwards be v and we are already given that ends on the string P and Q move downwards with velocity u. So, every point on the string moves with the same velocity u.
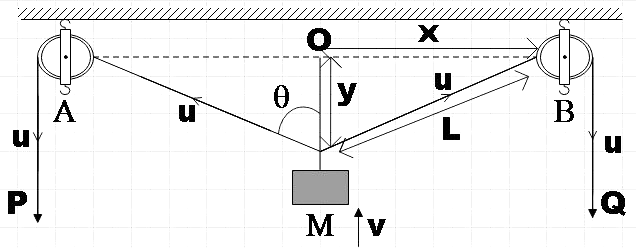
Consider the triangle MOB. By Pythagorus theorem we have,
${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{L}^{2}}$
Differentiating both sides with respect to time, we get,
$2y\dfrac{dy}{dt}=2L\dfrac{dL}{dt}$
Since x remains constant at all points of time.
We know that $\dfrac{dy}{dt}=v$and$\dfrac{dL}{dt}=u$,
$\Rightarrow y\times v=L\times u$
$\Rightarrow v=\dfrac{L}{y}\times u$
But from the figure we see that,
$\cos \theta =\dfrac{y}{L}$
$\therefore v=\dfrac{u}{\cos \theta }$
Therefore, we found that the mass M moves upwards with a speed of$\dfrac{u}{\cos \theta }$.
Hence, option B is found to be the correct answer.
Note:
We also have a very simple alternative method to solve this problem which doesn’t involve calculus. For that we could resolve the velocity v of the mass M into its components. We would find the cosine component along the string. But as the ends have velocity u downward, every point on the string should have the same velocity. Thus we could equate both to get,
$v\cos \theta =u$
$\therefore v=\dfrac{u}{\cos \theta }$
Complete Step by step solution:
Let the velocity with which mass M moves upwards be v and we are already given that ends on the string P and Q move downwards with velocity u. So, every point on the string moves with the same velocity u.

Consider the triangle MOB. By Pythagorus theorem we have,
${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{L}^{2}}$
Differentiating both sides with respect to time, we get,
$2y\dfrac{dy}{dt}=2L\dfrac{dL}{dt}$
Since x remains constant at all points of time.
We know that $\dfrac{dy}{dt}=v$and$\dfrac{dL}{dt}=u$,
$\Rightarrow y\times v=L\times u$
$\Rightarrow v=\dfrac{L}{y}\times u$
But from the figure we see that,
$\cos \theta =\dfrac{y}{L}$
$\therefore v=\dfrac{u}{\cos \theta }$
Therefore, we found that the mass M moves upwards with a speed of$\dfrac{u}{\cos \theta }$.
Hence, option B is found to be the correct answer.
Note:
We also have a very simple alternative method to solve this problem which doesn’t involve calculus. For that we could resolve the velocity v of the mass M into its components. We would find the cosine component along the string. But as the ends have velocity u downward, every point on the string should have the same velocity. Thus we could equate both to get,
$v\cos \theta =u$
$\therefore v=\dfrac{u}{\cos \theta }$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




