
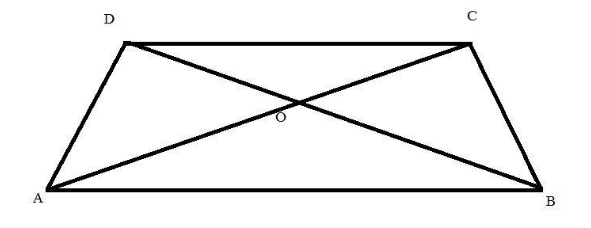
In the adjoining figure ABCD is a trapezium in which \[CD||AB\] and its diagonals intersect O. If \[AO = (5x - 7)\;cm\] , \[OC = (2x + 1)\;cm,\] \[BO = (7x - 5)\;cm\] and \[OD = (7x + 1)\;cm\] , find the value of \[x\]

Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: In this question we have to find the value of \[x\] such that the diagonals values are given. Here we use the properties of triangle, trapezium and Thales theorem to determine the value of \[x\] .
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us consider the trapezium ABCD where \[CD||AB\] . AC and BD are the diagonals of the trapezium and O is the intersect point of the diagonal.
Draw a line EO which is parallel to AB
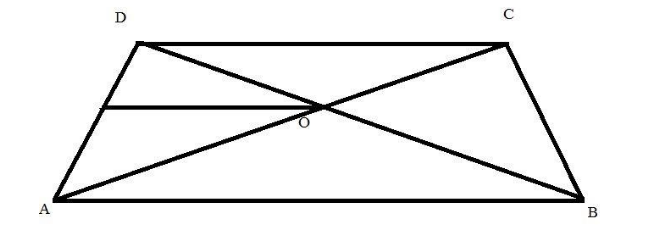
Now, consider the \[\Delta ADC\] here \[EO||AB||CD\]
By the Thales theorem we have \[\dfrac{{AE}}{{DE}} = \dfrac{{AO}}{{OC}}\] ………………. (1)
Consider the \[\Delta ADB\] here \[EO||AB\]
By the Thales theorem we have \[\dfrac{{AE}}{{DE}} = \dfrac{{DO}}{{OB}}\] ………………. (2)
By (1) and (2) we have
\[\dfrac{{AO}}{{OC}} = \dfrac{{DO}}{{OB}}\] ………………… (3)
The values AO, OC, BO and OD are given so we have \[AO = (5x - 7)cm\] , \[OC = (2x + 1)\;cm,\] \[BO = (7x - 5)\;cm\] and \[OD = (7x + 1)\;cm\] . By substituting the values in (3) we have
\[\dfrac{{5x - 7}}{{2x + 1}} = \dfrac{{7x - 5}}{{7x + 1}}\]
By cross multiplying we have
\[(5x - 7)(7x + 1) = (7x - 5)(2x + 1)\]
On multiplication,
\[
5x(7x + 1) - 7(7x + 1) = 7x(2x + 1) - 5(2x + 1) \\
\Rightarrow 35{x^2} + 5x - 49x - 7 = 14{x^2} + 7x - 10x - 5 \\
\Rightarrow 35{x^2} - 44x - 7 = 14{x^2} - 3x - 5 \;
\]
Further simplification
\[
35{x^2} - 14{x^2} - 44x + 3x - 7 + 5 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 21{x^2} - 41x - 2 = 0 \;
\]
On factorization:
\[21{x^2} - 42x + x - 2 = 0\]
By taking common we have
\[
21x(x - 2) + 1(x - 2) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow (21x + 1)(x - 2) = 0 \;
\]
Therefore, \[x = - \dfrac{1}{{21}}\] or \[x = 2\]
Since \[x = - \dfrac{1}{{21}}\] is least value so we neglect this value and hence we have \[x = 2\]
Therefore, the value of \[x = 2\]
So, the correct answer is “x = 2”.
Note: Here we are considering the Thales theorem where it is stated as “If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio”. And by substituting we can find the value of an unknown term.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us consider the trapezium ABCD where \[CD||AB\] . AC and BD are the diagonals of the trapezium and O is the intersect point of the diagonal.
Draw a line EO which is parallel to AB

Now, consider the \[\Delta ADC\] here \[EO||AB||CD\]
By the Thales theorem we have \[\dfrac{{AE}}{{DE}} = \dfrac{{AO}}{{OC}}\] ………………. (1)
Consider the \[\Delta ADB\] here \[EO||AB\]
By the Thales theorem we have \[\dfrac{{AE}}{{DE}} = \dfrac{{DO}}{{OB}}\] ………………. (2)
By (1) and (2) we have
\[\dfrac{{AO}}{{OC}} = \dfrac{{DO}}{{OB}}\] ………………… (3)
The values AO, OC, BO and OD are given so we have \[AO = (5x - 7)cm\] , \[OC = (2x + 1)\;cm,\] \[BO = (7x - 5)\;cm\] and \[OD = (7x + 1)\;cm\] . By substituting the values in (3) we have
\[\dfrac{{5x - 7}}{{2x + 1}} = \dfrac{{7x - 5}}{{7x + 1}}\]
By cross multiplying we have
\[(5x - 7)(7x + 1) = (7x - 5)(2x + 1)\]
On multiplication,
\[
5x(7x + 1) - 7(7x + 1) = 7x(2x + 1) - 5(2x + 1) \\
\Rightarrow 35{x^2} + 5x - 49x - 7 = 14{x^2} + 7x - 10x - 5 \\
\Rightarrow 35{x^2} - 44x - 7 = 14{x^2} - 3x - 5 \;
\]
Further simplification
\[
35{x^2} - 14{x^2} - 44x + 3x - 7 + 5 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 21{x^2} - 41x - 2 = 0 \;
\]
On factorization:
\[21{x^2} - 42x + x - 2 = 0\]
By taking common we have
\[
21x(x - 2) + 1(x - 2) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow (21x + 1)(x - 2) = 0 \;
\]
Therefore, \[x = - \dfrac{1}{{21}}\] or \[x = 2\]
Since \[x = - \dfrac{1}{{21}}\] is least value so we neglect this value and hence we have \[x = 2\]
Therefore, the value of \[x = 2\]
So, the correct answer is “x = 2”.
Note: Here we are considering the Thales theorem where it is stated as “If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio”. And by substituting we can find the value of an unknown term.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




