
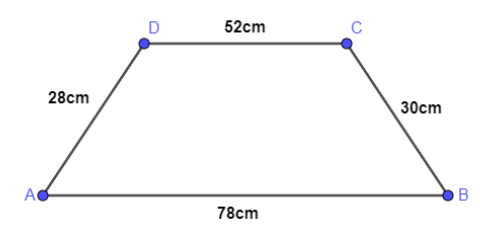
In the adjoining figure, ABCD is a trapezium in which parallel sides are $AB=78cm$ , $DC=52cm$ and the non-parallel sides are $BC=30cm$ and $AD=28cm$ . Find the area of the trapezium.

Answer
599.7k+ views
Hint: First, we will draw line CF perpendicular to AB and CE parallel to DA. Then we will find the area of triangle CEB using the heron’s formula given as \[Area\left( A \right)=\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)}\] . Here, s is a semi-perimeter obtained by using \[s=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( a+b+c \right)\] . And then form this we will find length of CF using normal area of triangle formula i.e. \[A=\dfrac{1}{2}\times base\times altitude\] . Then we will use formula \[=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left( \text{addition of non parallel sides} \right)\times \text{altitude}\] for calculating area of given trapezium.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Here, we are given length of all the four sides of trapezium ABCD i.e. $AB=78cm$ , $DC=52cm$ , $BC=30cm$ , $AD=28cm$ .
So, first we will draw a parallel line to AD i.e. CE and CF line perpendicular to AB. We will get as,
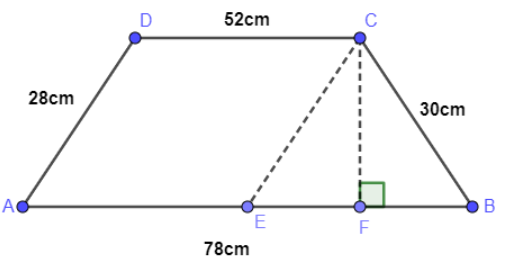
Now, we can see that $AE+EB=AB$ so, making EB as subject on LHS we get equation as
$EB=AB-AE$ ……………………….(1)
Now, we can see that $AE \parallel DC=52cm$. So, putting value of AB and AE in the above equation, we get
\[EB=78-52=26cm\] ……………………………..(2)
Now, we have \[CE=DA=28cm\] , \[BC=30cm\]
Now, we will use heron’s formula for \[\Delta CEB\] using the formula
\[Area\left( A \right)=\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)}\]
So, now in triangle CEB, semi perimeter of \[\Delta CEB\] will be
\[s=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( CE+CB+EB \right)\]
Here, we will consider CE as a, CB as b and EB as c.
So, substituting all the values we will get
\[s=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( a+b+c \right)\]
\[s=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 28+30+26 \right)\]
\[s=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 84 \right)=42cm\] ……………………………(3)
Now finding \[\left( s-a \right),\left( s-b \right),\left( s-c \right)\] , we will get
\[\left( s-a \right)=42-28=14cm\]
\[\left( s-b \right)=42-30=12cm\]
\[\left( s-c \right)=42-26=16cm\]
Now, we will substitute all the values in the formula \[Area\left( A \right)=\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)}\] So, we will get
\[Area\left( A \right)=\sqrt{42\left( 14 \right)\left( 12 \right)\left( 16 \right)}\]
On simplifying the brackets, we will get
\[A=\sqrt{6\times 7\times 7\times 2\times 4\times 3\times 4\times 4}\]
On solving we will get
\[A=7\times 4\times 4\times 3=336c{{m}^{2}}\]……………………………….(4)
No, to find CF we will use normal formula of triangle CEB for area i.e. \[A=\dfrac{1}{2}\times base\times altitude\]
\[\therefore A=\dfrac{1}{2}\times EB\times CF\]
Putting the values, we get
\[\therefore 336=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 26\times CF\]
\[\therefore 336=13\times CF\Rightarrow CF=\dfrac{336}{13}c{{m}^{2}}\] …………………………….(5)
Now, area of trapezium ABCD will be find by using the formula
\[=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left( \text{addition of non parallel sides} \right)\times \text{altitude}\]
\[=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left( AB+CD \right)\times CF\]
On substituting the values, we get
\[=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left( 78+52 \right)\times \dfrac{336}{13}\]
\[=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left( 130 \right)\times \dfrac{336}{13}\]
\[=5\times 336=1680c{{m}^{2}}\]
Thus, the area of trapezium ABCD is \[1680c{{m}^{2}}\] .
Note: Another approach to solve this problem is by making CF and DE perpendicular to AB.
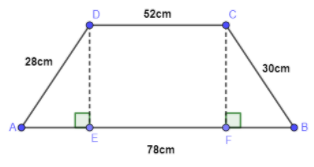
Here, we have to find separate areas of triangle AED, CFB and rectangle CDEF. So, \[CD=FE=52cm\] , \[AE+EF+FB=78\Rightarrow 52+2AE=78\] , so we get a value of AE as 13 cm. \[AE=FB=13cm\] . Now, using Pythagoras theorem, we can find the value of CF and DE which will be different. So, the area of both triangles will be different. Also, the area of the rectangle CDEF will also be tricky to calculate. As all the four sides of trapezium ABCD are different. So, this approach is a little bit difficult to solve. Thus, using Heron’s formula will be easier to solve in this case.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Here, we are given length of all the four sides of trapezium ABCD i.e. $AB=78cm$ , $DC=52cm$ , $BC=30cm$ , $AD=28cm$ .
So, first we will draw a parallel line to AD i.e. CE and CF line perpendicular to AB. We will get as,

Now, we can see that $AE+EB=AB$ so, making EB as subject on LHS we get equation as
$EB=AB-AE$ ……………………….(1)
Now, we can see that $AE \parallel DC=52cm$. So, putting value of AB and AE in the above equation, we get
\[EB=78-52=26cm\] ……………………………..(2)
Now, we have \[CE=DA=28cm\] , \[BC=30cm\]
Now, we will use heron’s formula for \[\Delta CEB\] using the formula
\[Area\left( A \right)=\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)}\]
So, now in triangle CEB, semi perimeter of \[\Delta CEB\] will be
\[s=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( CE+CB+EB \right)\]
Here, we will consider CE as a, CB as b and EB as c.
So, substituting all the values we will get
\[s=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( a+b+c \right)\]
\[s=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 28+30+26 \right)\]
\[s=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 84 \right)=42cm\] ……………………………(3)
Now finding \[\left( s-a \right),\left( s-b \right),\left( s-c \right)\] , we will get
\[\left( s-a \right)=42-28=14cm\]
\[\left( s-b \right)=42-30=12cm\]
\[\left( s-c \right)=42-26=16cm\]
Now, we will substitute all the values in the formula \[Area\left( A \right)=\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)}\] So, we will get
\[Area\left( A \right)=\sqrt{42\left( 14 \right)\left( 12 \right)\left( 16 \right)}\]
On simplifying the brackets, we will get
\[A=\sqrt{6\times 7\times 7\times 2\times 4\times 3\times 4\times 4}\]
On solving we will get
\[A=7\times 4\times 4\times 3=336c{{m}^{2}}\]……………………………….(4)
No, to find CF we will use normal formula of triangle CEB for area i.e. \[A=\dfrac{1}{2}\times base\times altitude\]
\[\therefore A=\dfrac{1}{2}\times EB\times CF\]
Putting the values, we get
\[\therefore 336=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 26\times CF\]
\[\therefore 336=13\times CF\Rightarrow CF=\dfrac{336}{13}c{{m}^{2}}\] …………………………….(5)
Now, area of trapezium ABCD will be find by using the formula
\[=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left( \text{addition of non parallel sides} \right)\times \text{altitude}\]
\[=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left( AB+CD \right)\times CF\]
On substituting the values, we get
\[=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left( 78+52 \right)\times \dfrac{336}{13}\]
\[=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left( 130 \right)\times \dfrac{336}{13}\]
\[=5\times 336=1680c{{m}^{2}}\]
Thus, the area of trapezium ABCD is \[1680c{{m}^{2}}\] .
Note: Another approach to solve this problem is by making CF and DE perpendicular to AB.

Here, we have to find separate areas of triangle AED, CFB and rectangle CDEF. So, \[CD=FE=52cm\] , \[AE+EF+FB=78\Rightarrow 52+2AE=78\] , so we get a value of AE as 13 cm. \[AE=FB=13cm\] . Now, using Pythagoras theorem, we can find the value of CF and DE which will be different. So, the area of both triangles will be different. Also, the area of the rectangle CDEF will also be tricky to calculate. As all the four sides of trapezium ABCD are different. So, this approach is a little bit difficult to solve. Thus, using Heron’s formula will be easier to solve in this case.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




