
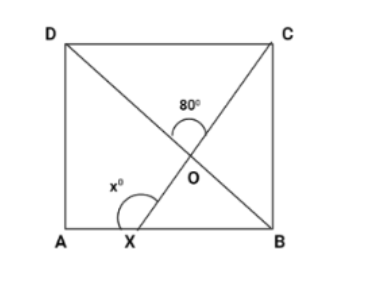
In the adjoining figure, $ABCD$ is a square. A line segment $CX$ cuts $AB$ at $X$ and the diagonal $BD$ at $O$ such that $\angle COD = {80^o}$ and $\angle OXA = {x^o}$. Find the value of $x$.

Answer
516.9k+ views
Hint: We will use exterior angle sum property for the above question. The sum of the two opposing interior angles equals a triangle's exterior angle. ${180^o}$ is the sum of the outer and internal angles. Also, when two lines converge, two pairs of opposite angles are formed. opposite angles are often congruent, which means they are identical.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that when two lines intersect, then the opposite angles are equal. In the figure, $\angle DOC = \angle XOB$
It is given in the question that $\angle DOC = {80^o}$
Hence, $\angle XOB = {80^o} - (i)$
We also know that the diagonal divides the angles of the squares into two equal parts.
Since, $\angle ABC = {90^o}$, then $\angle DBA = {45^o} - (ii)$
Now, when we apply exterior angle sum property to the $\Delta XOB$, we get,
$
\angle AXO = \angle XOB + \angle XBA \\
\angle AXO = \angle XOB + \angle DBA \;
$
Substituting the values from $(i)$ and $(ii)$
$
\angle AXO = \angle XOB + \angle DBA \\
\angle AXO = {80^o} + {45^o} \\
\angle AXO = {125^o} \;
$
Hence, the final answer is $x = {125^o}$.
So, the correct answer is “ $x = {125^o}$”.
Note: We can also use the angle sum property of a triangle in place of exterior angle sum property. The Triangle Angle Sum Theorem states that the sum of a triangle's three inner angles is always ${180^o}$. We can calculate the value of x, by subtracting $180$with $\angle OXB$.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that when two lines intersect, then the opposite angles are equal. In the figure, $\angle DOC = \angle XOB$
It is given in the question that $\angle DOC = {80^o}$
Hence, $\angle XOB = {80^o} - (i)$
We also know that the diagonal divides the angles of the squares into two equal parts.
Since, $\angle ABC = {90^o}$, then $\angle DBA = {45^o} - (ii)$
Now, when we apply exterior angle sum property to the $\Delta XOB$, we get,
$
\angle AXO = \angle XOB + \angle XBA \\
\angle AXO = \angle XOB + \angle DBA \;
$
Substituting the values from $(i)$ and $(ii)$
$
\angle AXO = \angle XOB + \angle DBA \\
\angle AXO = {80^o} + {45^o} \\
\angle AXO = {125^o} \;
$
Hence, the final answer is $x = {125^o}$.
So, the correct answer is “ $x = {125^o}$”.
Note: We can also use the angle sum property of a triangle in place of exterior angle sum property. The Triangle Angle Sum Theorem states that the sum of a triangle's three inner angles is always ${180^o}$. We can calculate the value of x, by subtracting $180$with $\angle OXB$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




