
In the adjoining figure, a protuberance found in Yeast is:
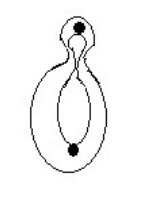
a. Fusion of two yeast cells for sexual reproduction
b. A bud
c. An internal bud fusing into parent cell
d. Discarded out growth

Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint: The protuberance found in yeast occurs for the process of asexual reproduction. In this, a new organism is developed from this protuberance which is formed due to the cell division in one place. The new organism developed is a clone and identical to the parent.
Complete answer:
• Yeast is the single-celled, eukaryotic organisms belonging to the kingdom of fungi. Most of the yeast asexually reproduce by mitosis and many yeasts reproduce by budding which is an asymmetrical division.
• Budding is a type of asexual division, which is commonly found in unicellular and multicellular organisms. In yeast, it usually occurs when there is a great availability of nutrition. In this type of reproduction, an outgrowth has arisen from the parent body which is called a bud or daughter cell. In the daughter cell, the daughter nuclei move which is formed by the splitting of the parent nuclei.
• The newly developed bud is then divided and grows into a cell. This new bud is generally smaller as compared to the parent cell and also genetically similar to the parent.
Yeast reproduces sexually through sexual spores called ascospores which are formed by the fusion of two cell's nuclei followed by meiosis.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: Bud is a small bulb-like projection that grows from the yeast cell and it is a type of asexual reproduction. Internal budding is also a process of asexual reproduction in which two daughters are developed inside the mother cell. Internal budding is so known as endodyogeny.
Complete answer:
• Yeast is the single-celled, eukaryotic organisms belonging to the kingdom of fungi. Most of the yeast asexually reproduce by mitosis and many yeasts reproduce by budding which is an asymmetrical division.
• Budding is a type of asexual division, which is commonly found in unicellular and multicellular organisms. In yeast, it usually occurs when there is a great availability of nutrition. In this type of reproduction, an outgrowth has arisen from the parent body which is called a bud or daughter cell. In the daughter cell, the daughter nuclei move which is formed by the splitting of the parent nuclei.
• The newly developed bud is then divided and grows into a cell. This new bud is generally smaller as compared to the parent cell and also genetically similar to the parent.
Yeast reproduces sexually through sexual spores called ascospores which are formed by the fusion of two cell's nuclei followed by meiosis.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: Bud is a small bulb-like projection that grows from the yeast cell and it is a type of asexual reproduction. Internal budding is also a process of asexual reproduction in which two daughters are developed inside the mother cell. Internal budding is so known as endodyogeny.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




