
In silica, $Si{O_2}$ , each silicon atom is bonded to how many oxygen atoms?
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint:$SiO$ and $Si{O_2}$ are two common oxides of silicon. Silicon monoxide is formed by high temperature reduction of $Si{O_2}$ with Si but at room temperature its existence is in doubt. Silicon dioxide is commonly called silica, and it is widely found in sand and quartz.
Complete answer:
We must know which group the silicon belongs to, so that we can understand the structure it will form with oxygen atoms by sharing its electrons and forming respective bonds. Therefore silicon belongs to group 14 and group 14 elements typically form four bonds. Similarly like carbon it forms four bonds due to four valence electrons in its p orbital since we know that the electronic configuration of silicon is:
$[Ne]3{s^2}3{p^2}$
Unlike carbon that forms double bond with oxygen, silicon in silica forms single covalent bonds as it is much larger in size as it lies lower than carbon in the group which is why its p orbitals are far enough to not allow sideways overlap with the orbitals of oxygen atom and form double bonds. Silica has a structure like:
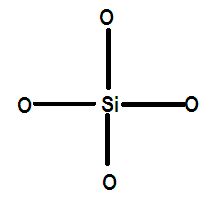
Silica is an infinite three dimensional structure of these tetrahedral units of silicon attached to four oxygen atoms each. Silica exists in 12 different forms some of which are quartz, tridymite, cristobalite etc.
Therefore each silicon atom is attached to four oxygen atoms.
Note:
Heating any solid form of to its softening temperature, or slow cooling of molten gives a glass like solid. This is amorphous and contains a disordered mixture of rings, chains and three dimensional units. Siliain in any form is unreactive and does not react with acids as it is an acidic.
Complete answer:
We must know which group the silicon belongs to, so that we can understand the structure it will form with oxygen atoms by sharing its electrons and forming respective bonds. Therefore silicon belongs to group 14 and group 14 elements typically form four bonds. Similarly like carbon it forms four bonds due to four valence electrons in its p orbital since we know that the electronic configuration of silicon is:
$[Ne]3{s^2}3{p^2}$
Unlike carbon that forms double bond with oxygen, silicon in silica forms single covalent bonds as it is much larger in size as it lies lower than carbon in the group which is why its p orbitals are far enough to not allow sideways overlap with the orbitals of oxygen atom and form double bonds. Silica has a structure like:

Silica is an infinite three dimensional structure of these tetrahedral units of silicon attached to four oxygen atoms each. Silica exists in 12 different forms some of which are quartz, tridymite, cristobalite etc.
Therefore each silicon atom is attached to four oxygen atoms.
Note:
Heating any solid form of to its softening temperature, or slow cooling of molten gives a glass like solid. This is amorphous and contains a disordered mixture of rings, chains and three dimensional units. Siliain in any form is unreactive and does not react with acids as it is an acidic.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




