
In series combination of resistance:
A. Potential difference is same across each resistance
B. Total resistance is reduced
C. Current is same in each resistance
D. All of the above
Answer
611.4k+ views
Hint – In order to solve this problem we need to draw a rough figure of series combination of resistances and analyze which option is true and which are false. Current has to flow through all the resistance in series. Knowing this will solve your problem.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
The rough figure of the resistances can be drawn as:
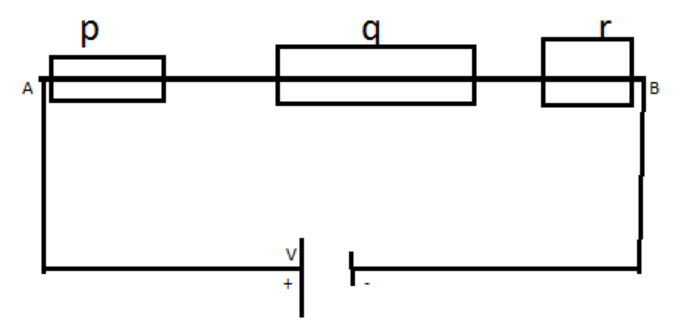
In the above figure p, q, r are the resistances on the single wire AB.
Let the current through the wire be i and let the potential difference through AB be V. A is at the positive terminal of the battery and B at negative.
So, if the current crosses the resistance p the voltage is reduced by ip, so the resistance q will get less voltage than p and it will again reduce the voltage by iq and similarly with the resistance r. so, the potential difference is not the same across each of the resistance if the resistances are different.
The equivalent resistance in series is the sum of all the resistances and it will always be larger than the largest resistance.
But we can say that the current flowing from A to B is i and it goes through all the resistances in series. So, the right option is C.
Note – To solve this problem you just need to know that resistors in Series carry the same current, but the voltage drop across them is not the same as their individual resistance values will create different voltage drops across each resistor as determined by Ohm's Law ( V = I*R ). Then series circuits are voltage dividers.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
The rough figure of the resistances can be drawn as:

In the above figure p, q, r are the resistances on the single wire AB.
Let the current through the wire be i and let the potential difference through AB be V. A is at the positive terminal of the battery and B at negative.
So, if the current crosses the resistance p the voltage is reduced by ip, so the resistance q will get less voltage than p and it will again reduce the voltage by iq and similarly with the resistance r. so, the potential difference is not the same across each of the resistance if the resistances are different.
The equivalent resistance in series is the sum of all the resistances and it will always be larger than the largest resistance.
But we can say that the current flowing from A to B is i and it goes through all the resistances in series. So, the right option is C.
Note – To solve this problem you just need to know that resistors in Series carry the same current, but the voltage drop across them is not the same as their individual resistance values will create different voltage drops across each resistor as determined by Ohm's Law ( V = I*R ). Then series circuits are voltage dividers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




