
In $\rm{2sp}$ hybridization, two s-orbital can be mixed with
A: Only $\rm{2p_x}$
B: Only $\rm{2p_y}$
C: Only $\rm{2p_z}$
D: Any one of $\rm{2p_x, 2p_y and \,2p_z}$
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint:An orbit is referred to as the simple planar representation of an electron. On the other hand, an orbital is referred to as the dimensional motion or movement of an electron around the nucleus in the three-dimensional motion. An orbital is actually a space or a region where an electron is most likely to be found.
Complete answer:
The names of the orbital i.e. s, p, d, or f stand for the names given to the groups of lines which are originally noted in the spectra of alkali metals. The line groups are known as sharp, principal, diffuse, or fundamental, respectively.
Orbital hybridisation or simply hybridization is the concept in chemistry which states that mixing of the atomic orbitals into the new hybrid orbitals (which possess different shapes, energies, etc., in comparison to component atomic orbitals) is suitable for the electron pairing in order to form chemical bonds in the valence bond theory.
The $\rm{2sp}$ hybridization is mixing of two s with one p atomic orbitals. S orbital is actually spherically symmetric so it can be mixed with the p orbital from any axis as shown below:
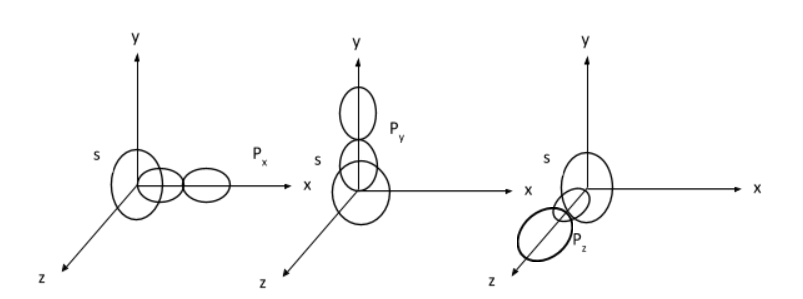
Hence, the correct answer is Option D. Any one of $\rm{2p_x, 2p_y and \,2p_z}$
Note:
The sequence of hybrids according to energy level is $\rm{sp < sp_2 < sp_3}$. If p character is higher, it means that the energy is more, thus indicating that the electrophilicity is higher and moreover, its affinity for reaction is also higher. It should also be noted that hybrids $(\rm{sp, sp_2, sp_3})$ lead to the formation of $\sigma$ bonds and pure-breeds on the other hand, lead to the formation of $\pi$ bonds.
Complete answer:
The names of the orbital i.e. s, p, d, or f stand for the names given to the groups of lines which are originally noted in the spectra of alkali metals. The line groups are known as sharp, principal, diffuse, or fundamental, respectively.
Orbital hybridisation or simply hybridization is the concept in chemistry which states that mixing of the atomic orbitals into the new hybrid orbitals (which possess different shapes, energies, etc., in comparison to component atomic orbitals) is suitable for the electron pairing in order to form chemical bonds in the valence bond theory.
The $\rm{2sp}$ hybridization is mixing of two s with one p atomic orbitals. S orbital is actually spherically symmetric so it can be mixed with the p orbital from any axis as shown below:

Hence, the correct answer is Option D. Any one of $\rm{2p_x, 2p_y and \,2p_z}$
Note:
The sequence of hybrids according to energy level is $\rm{sp < sp_2 < sp_3}$. If p character is higher, it means that the energy is more, thus indicating that the electrophilicity is higher and moreover, its affinity for reaction is also higher. It should also be noted that hybrids $(\rm{sp, sp_2, sp_3})$ lead to the formation of $\sigma$ bonds and pure-breeds on the other hand, lead to the formation of $\pi$ bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




