
In right triangle ABC, right angled at C, M is the mid-point of hypotenuse AB. C is joined to M and produced to a point D such that DM = CM. Point D is joined to point B, then
a)\[\Delta AMC\cong \Delta BMD\]
b)\[\angle DBC\] is a right angle
c)\[\Delta DBC\cong \Delta ACD\]
d)\[CM=\dfrac{1}{2}AB\]
Answer
615.6k+ views
Hint: To solve the question, we have to apply SAS symmetry, parallel lines properties, triangle properties for the given figure to arrive at the conclusions. We have to solve all the given options in the given order since all are inter-connected to ease the procedure of solving.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given
CM = DM
AM = BM
Since M is midpoint of hypotenuse AB
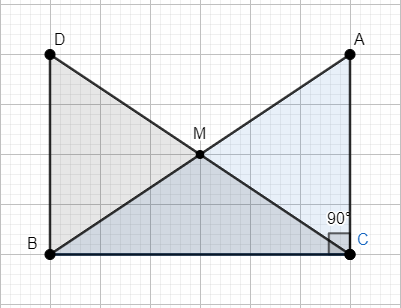
Consider triangles \[\Delta AMC,\Delta BMD\]
AM = BM
CM = DM
\[\angle DMB=\angle AMC\]
Since we know that for a pair of two intersecting lines, the vertically opposite angles are equal.
We know that SAS (Side- Angle- Side) symmetry means that two triangles are congruent when two corresponding sides and one corresponding angle of the triangles are equal.
Thus, we get \[\Delta AMC,\Delta BMD\] are congruent triangles.
\[\Delta AMC\cong \Delta BMD\]
We know that in a congruent triangle, all corresponding sides are equal. Thus, we get
AC = DB
\[\angle DBC+\angle ACB={{180}^{0}}\]
Since AC and BD are parallel to each other and in parallel lines the co-interior angles are supplementary.
\[\angle DBC+{{90}^{0}}={{180}^{0}}\]
Since it is given,\[\angle ACB\] is a right angle.
\[\Rightarrow \angle DBC={{180}^{0}}-{{90}^{0}}={{90}^{0}}\]
Consider triangles \[\Delta DBC,\Delta ACB\]
AC = DB
BC = BC
Since the common side of both the triangles.
\[\angle DBC=\angle ACB={{90}^{0}}\]
Thus, we get \[\Delta DBC,\Delta ACD\] are congruent triangles by SAS symmetry.
\[\Delta DBC\cong \Delta ACD\]
We know that in a congruent triangle, all corresponding sides are equal. Thus, we get
DC = AB
But we know that DC = CM + MD = 2CM. Thus, we get
2CM = AB
\[\Rightarrow CM=\dfrac{1}{2}AB\]
Hence, all the given options satisfy the given question.
Note: The possibility of mistake can be, not applying SAS symmetry, parallel lines properties, triangle properties to arrive at the conclusions. The other possibility of mistake can be solving all the given options independently, since all are inter-connected in the given order, it is better to solve accordingly.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given
CM = DM
AM = BM
Since M is midpoint of hypotenuse AB

Consider triangles \[\Delta AMC,\Delta BMD\]
AM = BM
CM = DM
\[\angle DMB=\angle AMC\]
Since we know that for a pair of two intersecting lines, the vertically opposite angles are equal.
We know that SAS (Side- Angle- Side) symmetry means that two triangles are congruent when two corresponding sides and one corresponding angle of the triangles are equal.
Thus, we get \[\Delta AMC,\Delta BMD\] are congruent triangles.
\[\Delta AMC\cong \Delta BMD\]
We know that in a congruent triangle, all corresponding sides are equal. Thus, we get
AC = DB
\[\angle DBC+\angle ACB={{180}^{0}}\]
Since AC and BD are parallel to each other and in parallel lines the co-interior angles are supplementary.
\[\angle DBC+{{90}^{0}}={{180}^{0}}\]
Since it is given,\[\angle ACB\] is a right angle.
\[\Rightarrow \angle DBC={{180}^{0}}-{{90}^{0}}={{90}^{0}}\]
Consider triangles \[\Delta DBC,\Delta ACB\]
AC = DB
BC = BC
Since the common side of both the triangles.
\[\angle DBC=\angle ACB={{90}^{0}}\]
Thus, we get \[\Delta DBC,\Delta ACD\] are congruent triangles by SAS symmetry.
\[\Delta DBC\cong \Delta ACD\]
We know that in a congruent triangle, all corresponding sides are equal. Thus, we get
DC = AB
But we know that DC = CM + MD = 2CM. Thus, we get
2CM = AB
\[\Rightarrow CM=\dfrac{1}{2}AB\]
Hence, all the given options satisfy the given question.
Note: The possibility of mistake can be, not applying SAS symmetry, parallel lines properties, triangle properties to arrive at the conclusions. The other possibility of mistake can be solving all the given options independently, since all are inter-connected in the given order, it is better to solve accordingly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




