
In Pythagoras theorem in right angled triangle the longest side is called the
A) Hypotenuse
B) Height
C) Perpendicular
D) Bisector
Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint:
Here, we will first draw the right-angled triangle and state its different sides. Then we will state Pythagoras theorem and find out what is the longest side of the right-angled triangle called.
Complete step by step solution:
First, we will draw the right-angled triangle here. A right-angled triangle is a triangle in which one angle is \[90^\circ \] and also the sum of the other two angles of a right-angled triangle is \[90^\circ \].
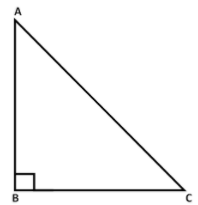
The right-angle triangle consists of three sides named as perpendicular, base and hypotenuse. We also have a relation between base, perpendicular, and hypotenuse of a right-angle triangle from Pythagoras theorem. Pythagoras theorem states that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of base and perpendicular sides of a right angles triangle.
Thus, the longest side of a right-angled triangle is called a hypotenuse.
Here, in \[\Delta ABC\], \[AC\] is the hypotenuse and it is just opposite to the right angle i.e. \[\angle ABC\] of \[\Delta ABC\].
Using Pythagoras theorem in \[\Delta ABC\], we get
\[A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}\]
AC is the longest side of the right-angled triangle and it is called the hypotenuse.
Thus, the correct option is option A.
Note:
Pythagoras theorem can only be used in the right-angled triangle and not in any other triangle. We need to keep in mind that the sum of any two sides of a triangle is always greater than the third side. In a right-angle triangle also, the sum of the length of the base and perpendicular is greater than the hypotenuse.
Here, we will first draw the right-angled triangle and state its different sides. Then we will state Pythagoras theorem and find out what is the longest side of the right-angled triangle called.
Complete step by step solution:
First, we will draw the right-angled triangle here. A right-angled triangle is a triangle in which one angle is \[90^\circ \] and also the sum of the other two angles of a right-angled triangle is \[90^\circ \].

The right-angle triangle consists of three sides named as perpendicular, base and hypotenuse. We also have a relation between base, perpendicular, and hypotenuse of a right-angle triangle from Pythagoras theorem. Pythagoras theorem states that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of base and perpendicular sides of a right angles triangle.
Thus, the longest side of a right-angled triangle is called a hypotenuse.
Here, in \[\Delta ABC\], \[AC\] is the hypotenuse and it is just opposite to the right angle i.e. \[\angle ABC\] of \[\Delta ABC\].
Using Pythagoras theorem in \[\Delta ABC\], we get
\[A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}\]
AC is the longest side of the right-angled triangle and it is called the hypotenuse.
Thus, the correct option is option A.
Note:
Pythagoras theorem can only be used in the right-angled triangle and not in any other triangle. We need to keep in mind that the sum of any two sides of a triangle is always greater than the third side. In a right-angle triangle also, the sum of the length of the base and perpendicular is greater than the hypotenuse.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





